Traditional content delivery networks (CDNs) help deliver static assets faster by caching content closer to users, but images require more specialized handling.
Overview
Image CDNs extend traditional CDNs with real-time image optimization, transformation, and device-aware delivery, ensuring that images load quickly without sacrificing quality.
How Image CDNs Enhance Website Performance:
- Image Compression and Optimization: Reduces file sizes without losing quality, speeding up load times.
- Lazy Loading: Delays image loading until visible on the screen, improving initial page load speed.
- Responsive Image Delivery: Automatically serves images in optimal sizes based on device and screen resolution.
- Edge Servers: Delivers images from geographically distributed servers, reducing latency and improving load times.
- Format Optimization: Automatically converts images to modern formats (e.g., WebP) for better compression and faster delivery.
- Automatic Resizing and Cropping: Adjusts images on-the-fly based on user device or layout requirements.
This article explores how image CDNs work, their key benefits, and best practices for leveraging them to boost website performance and user engagement.
Understanding CDN
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is a geographically distributed network of servers designed to deliver web content faster and more reliably to users across the globe.
Instead of serving all content from a single origin server, a CDN caches copies of static assets, such as images, videos, and scripts, on multiple edge servers strategically located near users.
When a user requests content, the CDN routes the request to the closest edge server, significantly reducing latency, bandwidth usage, and server load.
This optimized delivery not only speeds up page load times but also enhances the overall user experience, accommodating traffic spikes and minimizing downtime. CDNs have become essential infrastructure for modern websites and applications, powering fast, scalable, and resilient online experiences worldwide.
What is an Image CDN?
An Image CDN (Content Delivery Network) is a specialized type of CDN designed not only to deliver images quickly but also to optimize, transform, and tailor them dynamically based on the user’s device and network conditions.
Unlike traditional CDNs that simply cache and deliver the original files, Image CDNs process images on the fly by resizing, compressing, converting formats (such as WebP or AVIF), and applying visual effects as needed.
The core functionality of an Image CDN includes:
- Rapid Content Delivery: Utilizing a global network of edge servers to cache and deliver images from the location closest to the user, minimizing latency and speeding up load times.
- Dynamic Image Optimization: Automatically adjusting image size, resolution, and format in real-time to match the user’s device capabilities and screen size, improving performance and reducing bandwidth.
- Image Manipulation: Supporting operations like cropping, resizing, watermarking, and filtering via simple URL parameters without needing to store multiple versions of the same image.
- Cost Efficiency: Reducing bandwidth consumption and storage costs by serving optimized images rather than bulky originals.
Key Benefits of Using Image CDNs
Using an Image CDN provides multiple benefits that significantly enhance website speed, user experience, and operational efficiency:
- Faster Image Loading: Image CDNs cache images on edge servers closer to users, drastically reducing latency and boosting load times. They also dynamically optimize images for the user’s device and network conditions.
- Improved User Experience: Quick, smooth image loading keeps visitors engaged, reduces bounce rates, and increases overall satisfaction. Adaptive delivery ensures images look great on any device, from desktop to mobile.
- Better SEO Rankings: Faster loading pages with optimized images improve Core Web Vitals, helping websites rank higher in search engine results.
- Reduced Server Load and Bandwidth Costs: Offloading image delivery to a CDN reduces strain on origin servers and cuts bandwidth consumption through intelligent compression and format conversion.
- Scalability and Reliability: Image CDNs handle spikes in traffic efficiently, ensuring consistent performance even during high-demand periods.
- Enhanced Mobile Performance: By delivering device-specific, often smaller-sized images, Image CDNs optimize mobile user experience and loading speeds on varying network qualities.
Overall, Image CDNs not only speed up your website but also reduce operational costs and help create a competitive edge through superior user engagement and search visibility.
How Image CDNs Enhance Website Performance
Image CDNs play a pivotal role in boosting website performance through several key mechanisms:
- Image Compression and Optimization: Image CDNs automatically compress and optimize images without compromising quality. This reduces file sizes, which leads to faster load times, especially for users on slower networks.
- Lazy Loading: By deferring the loading of images until they are in the viewport (visible on the screen), image CDNs enhance initial page load speed. This technique minimizes the main thread’s workload during the first render.
- Responsive Image Delivery: Image CDNs automatically serve images in the appropriate size based on the user’s device, screen resolution, or network conditions. This ensures that users don’t download unnecessarily large images, improving load times on mobile and desktop devices.
- Edge Servers: With distributed edge servers around the world, image CDNs deliver images from the closest server to the user, reducing latency and improving content delivery speed.
- Format Optimization: Modern image formats like WebP or AVIF offer superior compression rates compared to traditional formats like JPG and PNG. Image CDNs automatically convert and serve these formats, providing faster loading times and smaller file sizes without sacrificing visual quality.
- Automatic Resizing and Cropping: Image CDNs can resize or crop images in real time based on user context (e.g., screen size, resolution, layout). This ensures images are appropriately sized, improving loading speed and maintaining a clean layout.
How Image CDN Works
An Image CDN combines three key components to deliver and optimize images efficiently: delivery, processing, and storage.
Delivery
The core of an Image CDN’s delivery mechanism is a traditional Content Delivery Network (CDN) like AWS CloudFront, Akamai, or Fastly. These CDNs have globally distributed servers (edge servers) that cache images closer to end users, reducing latency and speeding up load times.
Processing
Image processing servers are separate from the CDN’s delivery servers. They perform critical image optimizations and transformations such as resizing, cropping, watermarking, and format conversion in real-time. When an image request misses the CDN cache, it is routed to these processing servers to deliver an optimized image tailored to the user’s device and context.
Storage
Some Image CDNs include integrated storage or media libraries that allow users to upload and manage images directly. When processing servers need to optimize an image, they fetch it from this storage or an external origin server if the image is not cached or already processed.
Workflow Details
- When a user requests an image, the CDN first checks if the image is available in its cache. If found, the image is served immediately from the nearest edge server.
- If the image is not cached, the request goes to the processing servers.
- Processing servers then check if an optimized version of the image already exists. If yes, it returns that optimized copy.
- If no optimized version is available, the processing server retrieves the original image from storage or the origin server, applies requested real-time transformations and optimizations, caches the optimized image, and delivers it.
- Subsequent user requests for the same optimized image are served from the CDN’s cache, ensuring faster delivery.
This architecture ensures images are delivered quickly, optimized for various devices and network conditions, and managed seamlessly without manual intervention.
Important Infrastructure-Level Features of an image CDN
Infrastructure-level features form the foundation of a reliable and effective Image CDN. These features ensure the CDN can deliver optimized images quickly, securely, and integrate smoothly with your existing systems:
- Integration with Existing Storage and Servers: An ideal Image CDN should seamlessly integrate with your current image storage solutions, such as AWS S3 or your origin servers. This allows you to deliver optimized images without needing to migrate your entire image library or overhaul your content management processes.
- Choice of Underlying CDN with Third-Party Integrations: Since building a global delivery network from scratch is complex, most Image CDNs use established general-purpose CDNs. Leading Image CDNs offer options to integrate with multiple CDNs to ensure optimal delivery performance, regional coverage, and flexibility based on your preferences or contractual obligations.
- Geographically Distributed Image Processing Regions: The processing servers responsible for generating optimized images are fewer and located in select regions. Choosing an Image CDN with processing regions close to your users or origin storage minimizes the time needed for on-the-fly optimizations, reducing latency and speeding up image delivery.
- Support for Secure Protocols (HTTPS and HTTP/2): Security and performance go hand-in-hand. An Image CDN must support HTTPS to secure data transmission and HTTP/2 for faster, multiplexed requests. Additionally, supporting custom domain names for secure, branded image URLs helps maintain consistency and trust.
- Availability of Integrated Media Library: Some Image CDNs include a media library that allows centralized image storage, search, and management. This feature helps teams collaborate efficiently on image assets, simplifies uploads, and streamlines the delivery pipeline, especially for large organizations with complex workflows.
These infrastructure-level capabilities ensure that an Image CDN not only accelerates image delivery but also fits cohesively within your existing technology stack, providing scalability, security, and operational ease.
Read More: Top 15 Ways to Improve Website Performance
Image-related features of an Image CDN
Image CDNs offer advanced features that go beyond simple caching to optimize image delivery for performance and quality:
- Automatic Format Conversion: Converts images to modern formats like WebP or AVIF based on browser support to reduce file size without losing quality.
- Dynamic Resizing and Cropping: Adjusts image dimensions and crops images in real-time to fit different devices and screen sizes perfectly.
- Adjustable Compression: Balances image quality and file size with customizable compression settings optimized for different use cases.
- Real-Time Visual Effects: Allows adding watermarks, overlays, or filters on images dynamically through URL parameters without manual edits.
- URL-Based Security: Protects images with tokenized URLs and access controls to prevent unauthorized usage.
- Developer Tools: Provides SDKs and APIs to streamline integration and automate image optimization within websites and apps.
Best Practices with Image CDNs
To maximize the benefits of an Image CDN, follow these best practices:
- Use Responsive Images: Serve properly sized images based on the user’s device and screen resolution using responsive techniques like srcset and CSS media queries.
- Adopt Modern Image Formats: Utilize next-generation formats such as WebP and AVIF for superior compression and quality compared to traditional JPEG or PNG.
- Set Explicit Image Dimensions: Define width and height attributes to prevent layout shifts and improve Core Web Vitals metrics like Largest Contentful Paint (LCP).
- Implement Efficient Caching: Use cache-control headers and leverage stale-while-revalidate strategies to serve fresh yet fast-loading images.
- Enable Lazy Loading: Load images only when they are about to enter the viewport to reduce initial page load times and conserve bandwidth.
- Protect Images with Security Measures: Use signed URLs, Content Security Policy (CSP) headers, and rate limiting to prevent unauthorized access and abuse.
- Monitor and Audit Performance Regularly: Track image performance regularly and identify optimization opportunities.
Conclusion
Image CDNs play a vital role in accelerating website performance by delivering optimized, device-specific images quickly and efficiently. They reduce load times, lower bandwidth usage, and improve the overall user experience, making them indispensable for websites with rich visual content.
Implementing Image CDNs with best practices ensures improved SEO rankings, scalability during traffic surges, and seamless image delivery across various devices and network conditions.
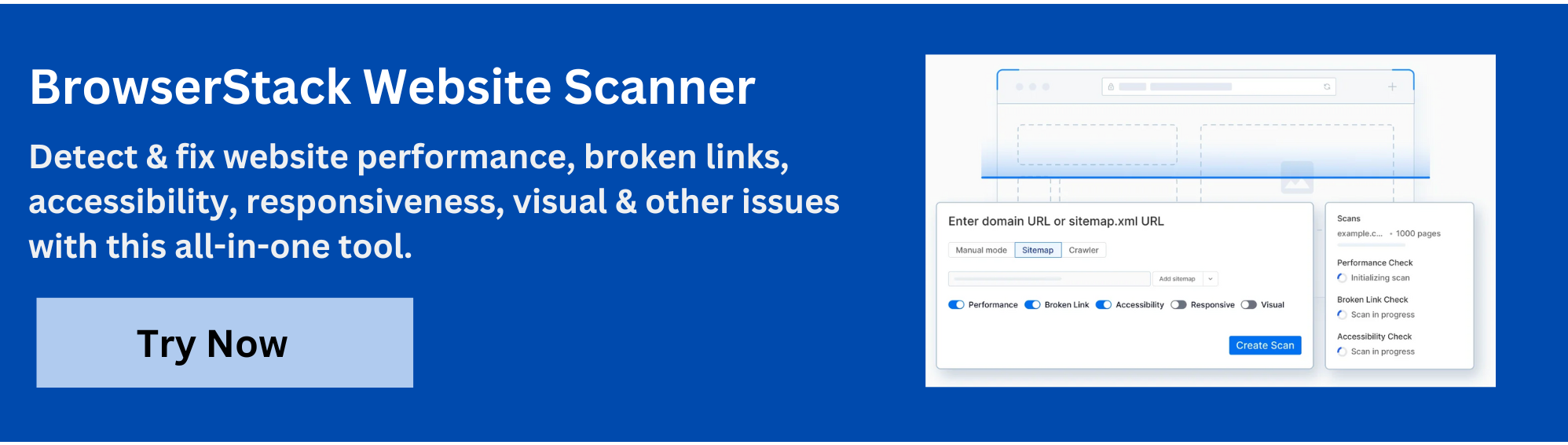
To further enhance website quality and streamline your optimization efforts, BrowserStack Website Scanner offers a powerful no-code solution that automates comprehensive website health checks within minutes.
It detects critical issues related to performance, accessibility, broken links, missing images, visual defects, and responsiveness, consolidating them into actionable reports for faster debugging.
With scheduling options and support for testing in development, staging, or production environments, BrowserStack Website Scanner empowers teams to maintain high-quality websites, ship releases faster, and deliver exceptional user experiences confidently.