One of the main reasons tests either stay reliable or turn flaky is because the wait strategy is wrong. I’ve seen tests fail not because the application was broken, but because they gave up too early or waited far longer than needed.
Playwright timeouts define how long a test is allowed to wait before it gives up, and understanding how they work makes it easier to decide when a test should be patient and when it should fail fast.
Overview
What is Playwright Timeout?
Playwright timeout refers to the maximum time Playwright will wait for an action, such as page loading or element interaction, before throwing an error.
When to Use Playwright Timeout?
Use Playwright timeout to handle cases where actions may take longer due to network conditions, slow-loading elements, or dynamic content, ensuring tests don’t hang indefinitely.
In this article, you will learn about the various timeouts that Playwright offers and when to use which.
What is Playwright Timeout?
Playwright timeouts define how long the framework waits for something to happen before failing a test. That “something” could be a page load, an element appearing, a navigation finishing, or an assertion becoming true.
Unlike older automation tools where timeouts act as hard sleeps, Playwright uses timeouts as upper limits for intelligent waiting. It continuously checks conditions and moves forward as soon as they are met, instead of waiting for the full duration.
At a practical level, Playwright timeouts answer questions like:
- How long should a test wait for an element to appear?
- How long is acceptable for a page or navigation to complete?
- When should a test fail instead of waiting indefinitely?
Playwright provides multiple timeout layers to control this behavior:
- Test timeout: Maximum time a single test is allowed to run.
- Action timeout: Time limit for actions like click, fill, or hover.
- Navigation timeout: Time limit for page loads or URL changes.
- Assertion timeout: Time Playwright waits for an assertion to pass.
Because Playwright automatically waits for elements to become ready, timeouts are not about slowing tests down. They act as guardrails, ensuring tests fail fast when the expected condition never occurs, while still allowing flexibility for real-world delays like network latency or rendering time.
Read More: Playwright vs Puppeteer: Which to Choose
Types of Playwright Timeouts
Playwright timeouts can be broadly classified into two levels, depending on how and where they are applied. This separation helps control execution flow at both the test level and the underlying action level.
Playwright timeout can be classified into two levels:
Timeouts
- Test timeout
- Expect timeout
Advanced: Low Level Timeouts
- Action timeout
- Navigation timeout
- Global timeout
- beforeAll/afterAll timeout
- Fixture timeout
Timeouts
These timeouts operate at the test and assertion level, focusing on overall execution limits and validation behavior.
- Test timeout: Defines the maximum time a single test is allowed to run. If this limit is exceeded, Playwright stops the test and marks it as failed, preventing stalled tests from blocking the suite.
- Expect timeout:Controls how long Playwright retries assertions before failing. It allows assertions to wait for UI conditions to stabilize without introducing manual delays.
Advanced: Low-Level Timeouts
Low-level timeouts apply to individual operations and framework internals, offering finer control over how Playwright waits during execution.
- Action timeout: Limits how long Playwright waits for an element to become actionable during interactions like click, fill, or hover.
- Navigation timeout: Determines how long Playwright waits for page loads, redirects, or route changes to complete.
- Global timeout: Sets default timeout values across the entire test suite, acting as a baseline for all timeout-related behavior.
- beforeAll / afterAll timeout: Applies specifically to setup and teardown hooks, ensuring environment initialization or cleanup does not hang indefinitely.
- Fixture timeout: Controls the maximum duration allowed for fixture setup and teardown, which is especially useful when fixtures perform network calls or environment configuration.
When to use which Playwright timeout?
In order to write a stable test, you must first understand which timeout to use and when.
When to use which Playwright timeout?
- Test timeout – When a specific test needs a strict or extended time limit
- Expect timeout – When assertions rely on delayed UI or data updates
- Action timeout – When user actions may take time to become actionable
- Navigation timeout – When page loads or route changes are slow
- Fixture timeout – When fixture setup or teardown is slow
- Global timeout – When total test execution time must be capped
- Hooks timeout – When setup or cleanup logic needs extra time
The below section describes in detail about each timeout:
1. Test timeout
Test timeout is the timeout for a particular test to complete. For example if the test timeout is set to 10 seconds, then the test has to complete its execution within 10 seconds and if it takes more than 10 seconds, the execution will be aborted with timeout exception.
Note that by default, the test timeout in Playwright is set to 30 seconds.
We are using BrowserStack’s demo application for writing the example tests
In the below example, you must set the test timeout for a specific test. This is helpful when you want to override the global timeout and want to set a timeout for a specific test.
import { test, expect } from '../../fixtures/fixtures';
test("example for timeout", async ({page}) => {
test.setTimeout(2000)
await page.goto("https://bstackdemo.com/")
const phone = await page.locator(".shelf-item__title", {hasText:"iPhone 12 Mini", })
const phoneParent = await phone.locator("..")
const phonePrice = phoneParent.locator(".shelf-item__price .val b")
await expect(phonePrice).toHavePrice("699")
})2. Expect timeout
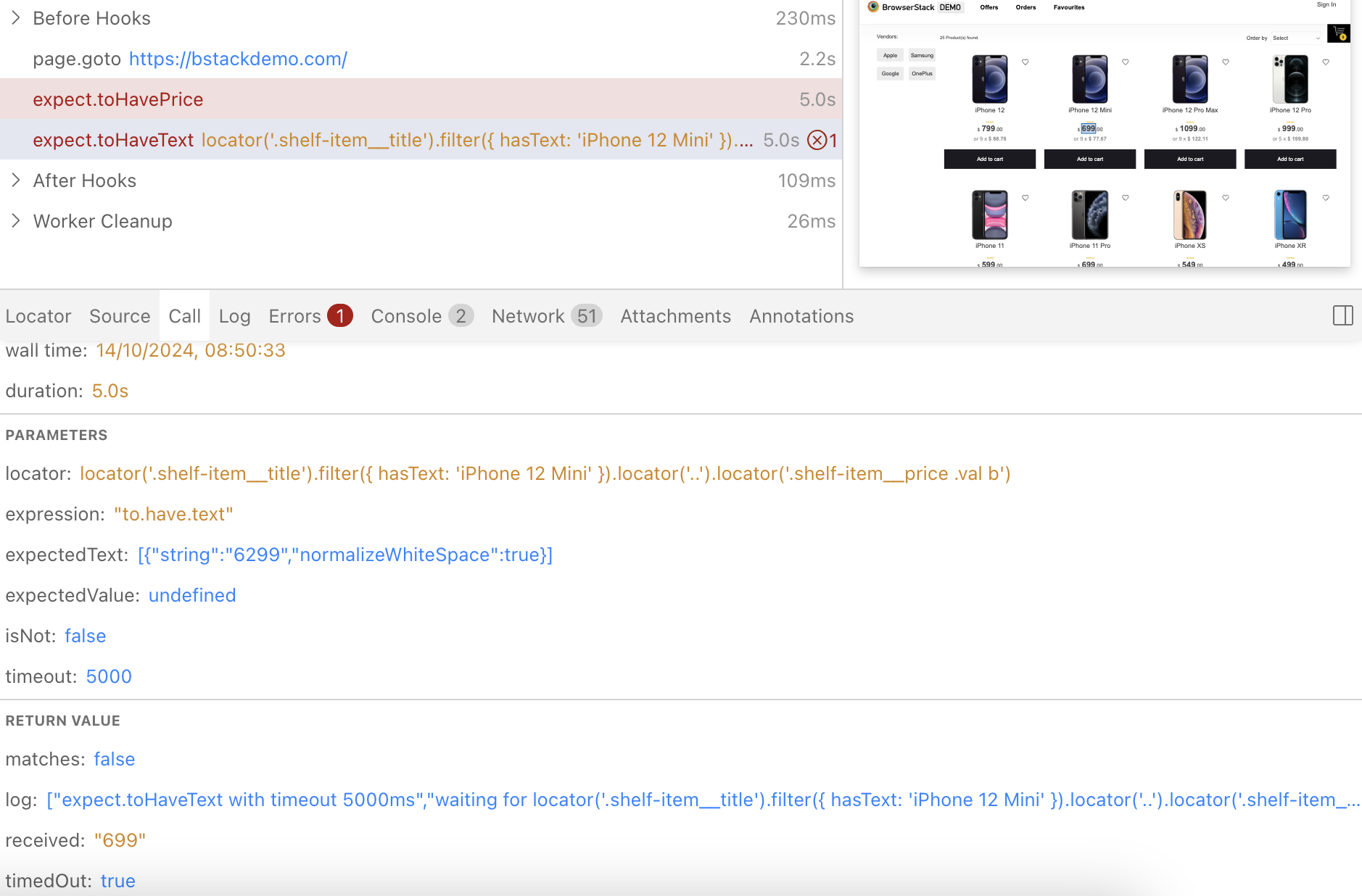
Assertion, by default, has 5 seconds of timeout in the playwright.
In the example below, the assertion failed with a timeout of 5 seconds. You can find this information in the Playwright test runner > Call tab.
To overwrite this open playwright.config.js{ts} file and add the below object inside defineConfig
expect: {
timeout: 10000
},Our playwright.config.js{ts} file will look like below
// @ts-check
const { defineConfig, devices } = require('@playwright/test');
/**
* @see https://playwright.dev/docs/test-configuration
*/
module.exports = defineConfig({
expect: {
timeout: 10000
},
testDir: './tests/timeout-examples/',
/* Run tests in files in parallel */
fullyParallel: true,
/* Fail the build on CI if you accidentally left test.only in the source code. */
forbidOnly: !!process.env.CI,
/* Retry on CI only */
retries: process.env.CI ? 2 : 0,
/* Opt out of parallel tests on CI. */
workers: process.env.CI ? 1 : undefined,
/* Reporter to use. See https://playwright.dev/docs/test-reporters */
reporter: 'html',
/* Shared settings for all the projects below. See https://playwright.dev/docs/api/class-testoptions. */
use: {
/* Base URL to use in actions like `await page.goto('/')`. */
// baseURL: 'http://127.0.0.1:3000',
/* Collect trace when retrying the failed test. See https://playwright.dev/docs/trace-viewer */
trace: 'on-first-retry',
},
/* Configure projects for major browsers */
projects: [
{
name: 'chromium',
use: { ...devices['Desktop Chrome'] },
},
{
name: 'firefox',
use: { ...devices['Desktop Firefox'] },
},
{
name: 'webkit',
use: { ...devices['Desktop Safari'] },
},
],
});By setting the timeout property value inside the expected object, you overwrite the default assertion timeout value globally.
3. Action timeout
Action timeout refers to the maximum time playwright actions like click() can take to complete.
You can set the action timeout at the individual action level as well as the global level.
Below is an example of actionTimeout at the function level.
await page.getByText("Apple").click({timeout: 3000})Below is the example of actionTimeout at the global level in the playwright.config.js{ts} file
module.exports = defineConfig({
use: {
actionTimeout: 1 * 10000
}
})Note that global timeout will be overridden when specified at individual command/function level
4. Navigation timeout
Navigation timeout specifies the maximum amount that the page navigation can take.
Navigation timeout can be specified at the global level as well as at the individual command level.
Below is an example at the command level.
await page.goto("https://bstackdemo.com/", {timeout: 30000})Below is an example of navigationTimeout at the global level, in the playwright.config.js{ts} file
module.exports = defineConfig({
use: {
actionTimeout: 1 * 10,
navigationTimeout: 1 * 10000,
}
})5. Fixture timeout
Playwright uses the concept of test fixtures to establish the environment for each test, providing the test with everything it needs.
Playwright allows the users to create new fixtures. With the Fixture timeout, you can control the maximum time the fixture can take to complete.
By default, the fixture will consider the test timeout.
const test = base.extend<{ slowFixture: string }>({
slowFixture: [async ({}, use) => {
// ... perform a slow operation ...
await use('hello');
}, { timeout: 60000 }]
});The Fixture timeout is to ensure the setup and tasks that are relatively slow in the fixtures are isolated from the tests so that the overall test timeout can be kept small, and the slow fixtures will get their own time to complete the tasks.
6. Global timeout
With Global timeout, you can set the maximum timeout for complete test execution.
Setting the Global timeout will ensure there is no over usage of resources. Upon reaching the timeout specified in the global timeout, the execution will be aborted.
Below is the example to set Global timeout in the playwright.config.js{ts} file
export default defineConfig({
globalTimeout: 60 * 60 * 1000,
});Read More: Understanding Playwright waitForResponse
7. Hooks timeout
Playwright allows the specification of timeout at hook level, beforeEach/afterEach and beforeAll/afterAll.
By default, the hook timeout will be the same as the test timeout, and below example shows how to set timeout at beforeEach and beforeAll level
test.beforeEach(async() => {
//Below code sets the timeout for this hook
test.setTimeout(60);
//Setup code
})test.beforeAll(async() => {
//Below code sets the timeout for this hook
test.setTimeout(6000);
//Setup code
})How to test Playwright timeout using BrowserStack?
If you are looking to execute Playwright Automation Testing on Cloud using a testing platform like BrowserStack, follow the below steps:
Step 1. Create a folder in your machine, Example, playwright-timeout-example
Step 2. Open the terminal and access the newly created folder
Step 3. Execute npm init and complete the installation
Step 4. Install Playwright by executing the below command in the terminal
npm init playwright@latest
Step 5. Once the installation is complete, you can see the folder tests created in the root folder
Step 6. Create a new file timeoutExample.spec.js
Step 7. Paste the below code and save
import { test, expect } from '../fixtures/fixtures';
test("example for timeout", async ({page}) => {
await page.goto("https://bstackdemo.com")
const phone = await page.locator(".shelf-item__title", {hasText:"iPhone 12 Mini",})
const phoneParent = await phone.locator("..")
const phonePrice = phoneParent.locator(".shelf-item__price .val b")
await expect(phonePrice).toHavePrice("699")
await page.getByText("Apple").click({timeout: 3000})
})Step 8. You can update playwright.config.js file with the timeouts given in the above sections
Step 9. To run the playwright test in UI mode, execute the below command.
npx playwright test –-ui
Step 10. Get the username and access key from your BrowserStack account and execute the below command in your terminal
export BROWSERSTACK_USERNAME="YOUR_USERNAME" export BROWSERSTACK_ACCESS_KEY="YOUR_ACCESS_KEY"
Step 11. Install BrowserStack nodejs sdk and setup username/key with the below command:
npm i2 -D browserstack-node-sdk@latest npx setup --username "YOUR_USERNAME" --key "YOUR_ACCESS_KEY"
Step 13. Once the installation is complete, there will be a BrowserStack config file, “browserstack.yml” file created at the root of the project. This file contains all the capabilities required to execute tests in BrowserStackCloud
Step 14. Detailed setup instruction can be found here
Step 15. Below command can be executed to run the Playwright tests in BrowserStack cloud
npx browserstack-node-sdk <Your existing command for running your test suite>
Why choose BrowserStack to test Playwright Timeouts?
Playwright timeouts often behave differently across environments. A test that passes locally may fail in CI because of network latency, device performance, or browser-specific rendering delays.
BrowserStack Automate is a cloud based testing tool that helps validate timeout behavior under conditions that closely resemble real user environments.
- Real browsers and devices: Timeouts can be accurately tested on real desktop and mobile browsers instead of relying on simulated environments that mask timing issues.
- Consistent CI behavior: BrowserStack provides stable infrastructure, making it easier to identify whether a timeout failure is caused by the application or by environmental inconsistencies.
- Network and performance variability: Tests can be run under realistic network conditions, helping fine-tune action, navigation, and assertion timeouts without over-inflating them.
- Scalable parallel execution: Running Playwright tests in parallel highlights hidden timeout dependencies that often surface only at scale.
By validating Playwright timeouts on BrowserStack, teams can set tighter, more reliable timeout thresholds and reduce flaky failures caused by environment-specific delays rather than real defects.
Conclusion
You have seen how beneficial it is to specify timeout at various levels and how to set the timeout at individual/Global level. Timeout is very crucial in order to ensure the test will never get into forever looping mode and the application always performs the operation under an expected timeframe.
BrowserStack Automate is an excellent choice for running Playwright tests because it offers a scalable, cloud-based infrastructure that eliminates the need for complex local setups.
With support for real-time cross-browser testing, parallel execution, and integrations with CI/CD pipelines, BrowserStack ensures faster test runs and streamlined workflows. Choose BrowserStack Automate to enhance the reliability and performance of your Playwright test suite with ease.