GraphQL introspection is a powerful feature that enables dynamic querying of an API’s schema, offering flexibility for developers. While it provides great benefits for tooling, debugging, and API exploration, it also requires careful consideration around best practices and security.
Overview
GraphQL introspection allows clients to query the GraphQL schema itself, enabling them to discover available types, fields, and operations programmatically.
Use Cases of GraphQL Introspection
- Generate API Documentation: Automatically generate and update API documentation.
- Enhance Tooling: Improve autocompletion, validation, and error-checking in GraphQL IDEs.
- Dynamic Query Building: Build queries on the fly based on the schema.
- API Exploration: Easily explore and understand unfamiliar GraphQL APIs.
- Testing and Debugging: Validate schema and query structures during development.
This article explores the key components, benefits, and use cases of introspection, and discusses how to debug introspection queries effectively using Requestly HTTP Interceptor.
What is GraphQL Introspection?
GraphQL Introspection is a feature that allows clients to query a GraphQL schema to get details about the types, fields, and operations available. It enables developers to dynamically explore the schema, making it easier to build tools, generate documentation, and create queries without needing to manually reference the schema.
Key Components of Introspection
GraphQL introspection relies on several key components to provide detailed schema information. These components allow you to query the schema and understand the structure of types, fields, and operations:
- __schema: Provides information about the entire schema, including types, query operations, and mutation operations.
- __type: Retrieves details about a specific type (e.g., object types, scalar types, etc.), including its fields and possible values.
- __typename: Returns the name of the type of a field, useful for identifying the type when querying union or interface types.
- __field: Provides information about specific fields within a type, including field names, arguments, and return types.
How GraphQL Introspection Works
GraphQL introspection works by allowing clients to query special introspection fields in the schema. These fields are prefixed with __, and querying them provides detailed information about the types, fields, and operations defined in the GraphQL schema.
Clients can dynamically retrieve this metadata, which can be used for generating documentation, building dynamic queries, or debugging.
- Querying __schema: This returns the overall structure of the GraphQL API, including all types, queries, and mutations available.
- Querying __type: Allows you to fetch details about specific types, such as the fields and arguments they contain.
- Querying __typename: Helps identify the type of any given field or value, particularly useful in union and interface types.
By leveraging these introspection queries, clients can explore and interact with the GraphQL schema without needing prior knowledge of its structure.
Benefits of GraphQL Introspection
GraphQL introspection offers several key advantages that improve developer workflows and enhance the flexibility of the API:
- Self-Documentation: Introspection automatically generates up-to-date documentation of the GraphQL schema. This removes the need for manual documentation maintenance, ensuring that developers always have access to the most current details about the schema, types, fields, and operations. It helps keep the API documentation consistent and reliable.
- Improved Tooling and IDE Support: Introspection enriches developer tools such as GraphiQL, Apollo Client, and other IDEs by providing features like autocompletion, syntax validation, and real-time error checking. This allows developers to write and test queries more efficiently, reducing the chances of errors and speeding up development cycles.
- Dynamic Query Generation: With introspection, clients can dynamically query the schema to discover the available fields, types, and operations. This flexibility allows developers to build dynamic queries based on the schema, making it easier to interact with APIs without manually crafting complex queries. This is especially useful in dynamic applications and tools like admin panels or automated testing scripts.
- Faster Debugging: By querying the schema directly, introspection helps identify schema-related issues quickly. Developers can inspect field definitions, arguments, and types in real time to troubleshoot queries. It streamlines the debugging process, allowing developers to work more efficiently when resolving issues in the schema or queries.
- Adaptability to Schema Changes: Introspection allows clients to adapt to changes in the schema without needing manual updates. This is particularly useful in projects with rapidly evolving schemas or in environments where schema changes are frequent. Clients can query the schema dynamically and update their queries automatically as the schema evolves, making it easier to maintain compatibility as APIs change.
Use Cases of GraphQL Introspection
GraphQL introspection is a versatile feature with a wide range of applications. Here are some common and valuable use cases:
- API Documentation Generation: Automatically generate up-to-date API documentation, making it easy to understand the schema structure.
- Dynamic Query Building: Enable dynamic creation of queries based on the schema, useful for flexible applications like admin panels.
- Client and IDE Enhancements: Improve tooling with features like autocompletion, syntax validation, and error checking in GraphQL clients and IDEs.
- Building API Integrations: Dynamically query and integrate with third-party GraphQL APIs by discovering available operations and fields.
- Schema Testing and Validation: Validate GraphQL schema integrity by querying its metadata to ensure fields and types are correct.
- API Exploration: Explore unfamiliar or evolving APIs by querying the schema to understand available types and fields.
Best Practices for Using Introspection
To make the most of GraphQL introspection while maintaining security and performance, consider the following best practices:
- Limit Introspection in Production: Disable or restrict introspection in production to prevent exposing sensitive schema details to unauthorized users.
- Use Introspection for Documentation: Leverage introspection to automatically generate accurate and up-to-date API documentation.
- Monitor Introspection Queries: Regularly audit introspection queries to ensure they aren’t being misused or exposing unnecessary data.
- Implement Role-Based Access: Enforce access control to restrict introspection based on user roles or authentication status.
- Educate Developers: Ensure your team understands the implications of introspection, particularly in relation to security and performance.
- Optimize for Performance: Use introspection selectively in development and testing environments to avoid unnecessary overhead in production.
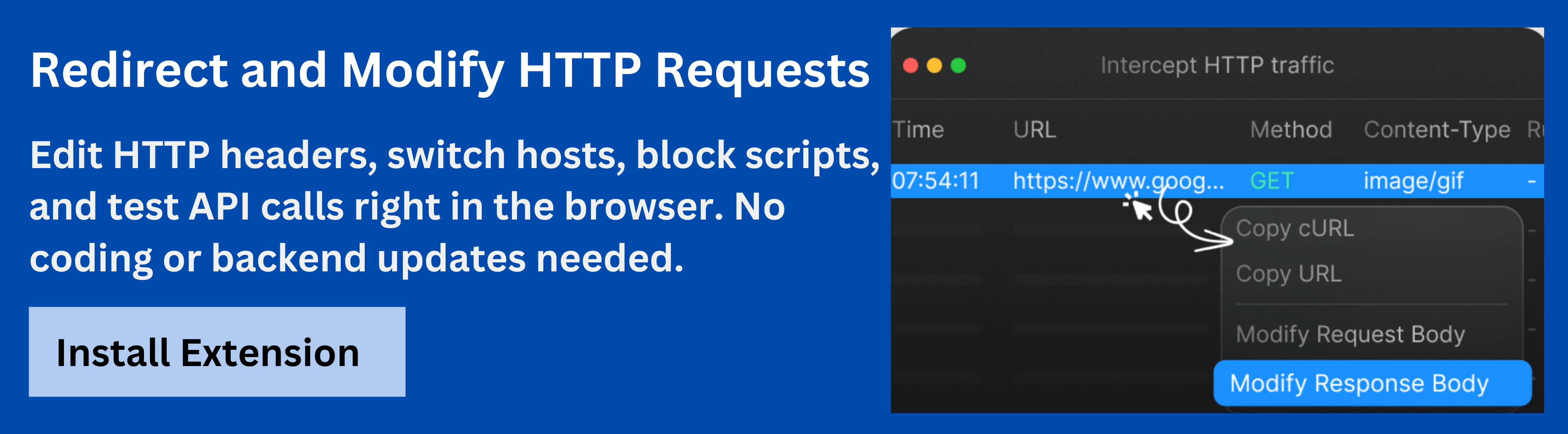
Debugging GraphQL Introspection with Requestly HTTP Interceptor
Requestly HTTP Interceptor offers an efficient way to debug and manage GraphQL introspection queries in real-time. By intercepting and modifying GraphQL requests, it helps developers troubleshoot, optimize, and test GraphQL queries with ease.
- Inspect Introspection Queries: Intercept GraphQL introspection queries to view the schema details being requested, ensuring the right types and fields are being queried.
- Modify Requests on the Fly: Dynamically adjust introspection queries to test different schema scenarios or modify the fields and types requested, all without changing the backend.
- Simulate Schema Changes: Test how introspection behaves when the schema evolves by simulating field additions, removals, or changes, helping you spot potential issues early.
- Monitor Access to Sensitive Data: Track introspection queries to ensure that sensitive schema information is not being exposed to unauthorized users, enhancing security during development.
Try Requestly HTTP Interceptor Now
By integrating Requestly HTTP Interceptor into your GraphQL workflow, you can streamline the debugging and management of introspection queries, ensuring that your API is performing as expected while maintaining security best practices.
Conclusion
GraphQL introspection is a powerful tool for exploring and interacting with your API’s schema, enabling dynamic query generation, better tooling, and faster debugging. However, to ensure security and maintain performance, it’s essential to follow best practices and carefully manage introspection access.
Tools like Requestly HTTP Interceptor can greatly simplify the debugging process, providing real-time insights and the ability to modify queries on the fly. By using introspection effectively, developers can enhance both the development experience and the overall performance of GraphQL APIs.