GraphQL has become a powerful alternative to REST APIs, offering flexibility and efficiency in handling data requests. As applications grow more complex, testing GraphQL requests effectively becomes crucial.
Overview
What is a GraphQL Request?
A GraphQL request is a query, mutation, or subscription sent to a GraphQL server to fetch, modify, or subscribe to data. It allows clients to request specific data fields, reducing over-fetching and optimizing performance.
Key Concepts in GraphQL Requests:
- Queries: Requesting specific data from the server.
- Mutations: Modifying data on the server (e.g., create, update, delete).
- Subscriptions: Real-time updates from the server.
- Variables: Dynamic data input for flexible queries.
- Fragments: Reusable parts of queries for efficiency.
GraphQL Request Testing Strategies:
- Validate Responses: Check for correct status codes, data structure, and error handling.
- Test Authorization: Ensure proper user authentication and permission checks.
- Simulate Different Scenarios: Test edge cases with modified or mock requests.
- Inspect Network Traffic: Monitor requests and responses for performance and accuracy.
- Automate Tests: Integrate testing into CI/CD pipelines for continuous validation.
This article explores best practices, strategies, and tools to help you master GraphQL request testing, ensuring that your APIs are both functional and reliable.
Understanding GraphQL Request
A GraphQL request is an interaction between a client and a server, where the client sends a query, mutation, or subscription to request, modify, or subscribe to data. Unlike traditional REST APIs, which require multiple endpoints to retrieve different data, GraphQL uses a single endpoint to handle all data requests. This makes it highly flexible and efficient by allowing clients to specify exactly what data they need, reducing over-fetching and under-fetching issues.
- Query: A request for data, where the client specifies the fields needed. For example, if an application needs user data, it would send a query asking only for specific fields (name, email, etc.) rather than all user details.
- Mutation: A request to modify data on the server. Mutations allow clients to create, update, or delete data. Each mutation is structured like a query but impacts the state of the server.
- Subscription: A request for real-time data. Unlike queries, which are one-time requests, subscriptions maintain a continuous connection between the client and server, allowing the client to receive updates whenever the data changes.
This flexibility in requesting, modifying, and subscribing to data allows developers to design APIs that are more efficient and easier to scale.
Anatomy of a GraphQL Request
A GraphQL request consists of several components that work together to communicate with the server. Understanding these components is essential for crafting efficient and effective queries, mutations, and subscriptions.
1. Query
A query is used to request data from the server. It allows clients to specify exactly what data they need, avoiding over-fetching. For example:
{
user(id: 1) {
name
email
}
}In this case, the query requests only the name and email fields of the user with id = 1.
2. Mutation
Mutations are used to modify data on the server, such as creating, updating, or deleting records. Unlike queries, which only retrieve data, mutations affect the state of the data.
mutation {
createUser(name: “John”, email: “john@example.com”) {
id
name
}
}- This mutation creates a new user and requests the id and name of the newly created user.
3. Subscription
Subscriptions are used for real-time updates. They allow clients to subscribe to data changes and receive updates whenever the data changes, without needing to send a new request.
subscription {
messageAdded {
content
author
}
}This subscription listens for new messages and returns the content and author of any new message added.
4. Variables
Variables allow for dynamic data input within a query, mutation, or subscription, making it more flexible. Instead of hardcoding values in the query, you pass variables to the request.
query getUser($id: ID!) {
user(id: $id) {
name
email
}
}Variables are sent separately in the request body, ensuring that the query remains reusable with different inputs.
5. Fragments
Fragments are reusable pieces of a GraphQL query, enabling you to define fields that can be shared across multiple queries or mutations. This reduces redundancy in your request.
fragment userFields on User {
name
email
}
query {
user(id: 1) {
…userFields
}
}
Fragments help keep queries concise and maintainable by allowing common fields to be reused.
6. Directives
Directives are used to conditionally include or skip fields in a query or mutation, based on runtime conditions. The most common directives are @include and @skip.
query getUser($includeEmail: Boolean!) {
user(id: 1) {
name
email @include(if: $includeEmail)
}
}In this example, the email field will only be included if the includeEmail variable is set to true.
Together, these components enable GraphQL requests to be both flexible and efficient, allowing clients to retrieve and modify exactly the data they need in a highly customizable way.
GraphQL Request Testing Strategies
Effective testing of GraphQL requests ensures your API functions as expected, handles errors gracefully, and performs optimally. Here are key strategies for testing GraphQL requests:
- Validate Responses: Ensure that the server’s response matches the expected data structure and status codes, checking for correct field types and error handling.
- Authorization & Authentication: Test queries and mutations with valid and invalid authentication tokens to verify that only authorized users can access or modify data.
- Performance Testing: Simulate complex queries and test pagination to ensure the API handles large data sets efficiently without performance degradation.
- Edge Case Handling: Test for invalid inputs, missing fields, or incomplete data to ensure the API can handle unusual or error-prone scenarios.
- Automated Testing: Integrate GraphQL request tests into CI/CD pipelines to automate validation and ensure consistent, reliable API behavior across updates.
These strategies help ensure that your GraphQL API remains functional, secure, and performant.
Common Issues in GraphQL Requests and How to Troubleshoot
When working with GraphQL, there are several common issues that can arise. Understanding how to troubleshoot these issues is key to maintaining a robust API. Here are some common problems and how to address them:
1. Invalid Queries or Syntax Errors:
- Issue: Incorrectly formatted queries or misspelled fields can result in errors.
- Solution: Double-check query syntax, field names, and ensure that the query structure matches the GraphQL schema.
2. Authentication and Authorization Failures:
- Issue: Unauthorized users might try to access protected data.
- Solution: Ensure that authentication tokens are correctly passed in the headers, and check that the API implements proper authorization logic to restrict access to sensitive data.
3. Over-fetching or Under-fetching Data:
- Issue: A query may either request too much data (over-fetching) or not enough data (under-fetching).
- Solution: Optimize queries by requesting only the necessary fields, and ensure that the schema allows clients to request specific data to avoid over-fetching.
4. Nested Query Limitations and Depth Issues:
- Issue: Deeply nested queries can cause performance problems or result in timeouts.
- Solution: Implement query depth or complexity limiting to prevent overly expensive or nested queries from overwhelming the server.
5. Missing or Incorrect Data in Responses:
- Issue: Data might be incomplete or missing, especially after schema changes.
- Solution: Confirm that the fields being requested exist in the schema and that data is properly populated in the database.
6. Mutation Failures:
- Issue: Mutations may not execute as expected, or they may return incorrect results.
- Solution: Test mutations in isolation to ensure they are working correctly, and check server logs to debug issues like data validation errors or constraint violations.
7. Timeouts or Slow Responses:
- Issue: Complex queries can result in slow responses or timeouts.
- Solution: Profile query performance and optimize it by reducing query complexity or using pagination to limit data returned in each request.
By addressing these common issues and using proper troubleshooting techniques, you can ensure a smoother experience when developing and testing GraphQL APIs.
Advanced GraphQL Request Techniques
To maximize the efficiency and functionality of your GraphQL API, it’s important to employ advanced techniques. Here are some strategies for handling more complex scenarios:
1. Batching Requests:
- What it is: Batching allows you to send multiple GraphQL queries or mutations in a single request, reducing the number of network calls.
- When to use: This technique is useful for minimizing overhead in applications where multiple data points need to be fetched at once.
2.Query Optimization:
- What it is: Query optimization helps prevent over-fetching or under-fetching by selecting only the necessary fields and limiting data returned.
- When to use: Use this technique when you want to minimize the payload size and improve performance.
3.Pagination:
- What it is: Pagination breaks down large datasets into smaller, manageable chunks, improving performance and user experience.
- When to use: Use pagination when dealing with large lists or collections of data, like fetching blog posts or user comments.
4. Fragments for Reusability:
- What it is: Fragments allow you to reuse parts of queries, ensuring that you don’t repeat the same fields in multiple places.
- When to use: Use fragments to keep your queries clean and reusable, especially for large or frequently used queries.
5. Rate Limiting and Throttling:
- What it is: Rate limiting controls the number of requests that can be made in a certain time frame to protect the server from being overwhelmed.
- When to use: Implement this technique when you want to prevent abuse and ensure the API remains stable under high load.
6. Error Handling with Custom Error Messages:
- What it is: Custom error handling allows you to provide more meaningful error messages when something goes wrong with a query or mutation.
- When to use: Implement detailed error handling for a better debugging experience and clearer communication with clients.
These advanced techniques help optimize and scale GraphQL APIs, improve query efficiency, and offer better control over data retrieval, error handling, and performance. By using these strategies, you can enhance the reliability and responsiveness of your API.
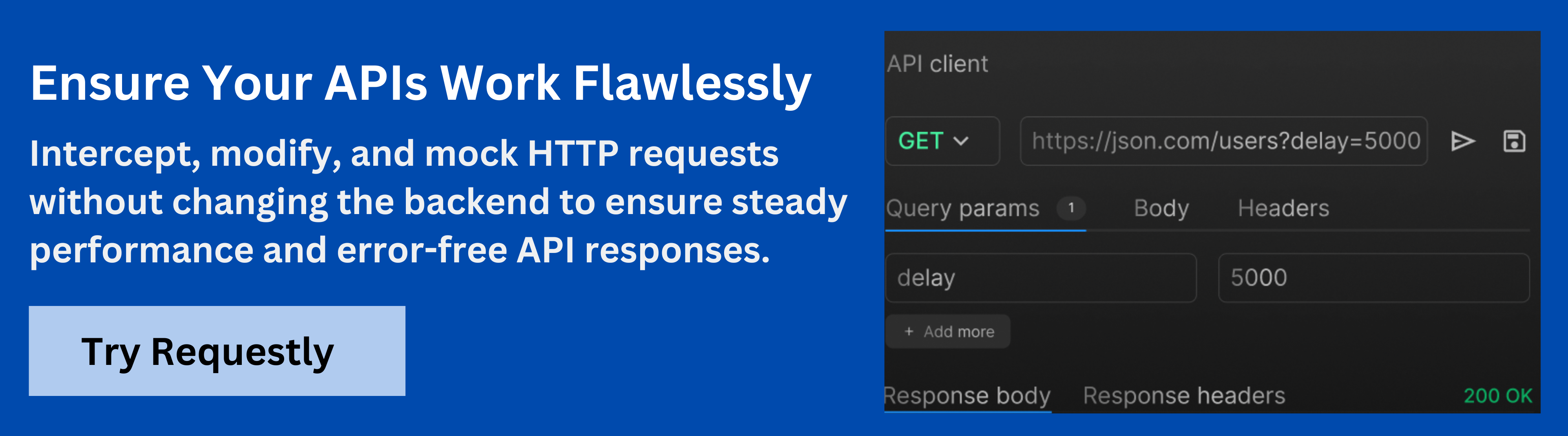
Enhance GraphQL API Testing with Requestly
Requestly is a powerful tool that allows developers to intercept, modify, and mock GraphQL requests in real-time, streamlining the testing and debugging process. Here’s how Requestly enhances GraphQL API testing:
- Real-Time HTTP Interception: Modify GraphQL requests and responses on the fly without changing backend code.
- Advanced Request Filtering: Intercept specific queries or mutations by filtering based on operation names or query content, allowing for precise testing.
- Mocking Responses: Simulate error states, incomplete data, or slow network conditions to test how the frontend handles edge cases.
- Dynamic Testing: Modify request payloads and input variables in real time without changing the client-side code.
- Performance Testing: Simulate API delays, introspection, and monitor access to sensitive schema fields to ensure security and performance.
- Seamless Integration: Easily share test rules, collaborate with team members, and manage testing tasks across multiple workspaces.
By using Requestly, developers can simplify the testing process, ensuring that their GraphQL APIs are functional, efficient, and secure.
Conclusion
Mastering GraphQL requests and their testing strategies is crucial for building efficient and reliable APIs. By understanding the core components of GraphQL, such as queries, mutations, and subscriptions, along with advanced techniques like batching and pagination, you can optimize performance and ensure scalability.
Incorporating tools like Requestly further streamlines the testing process by allowing real-time request modifications, mocking, and precise control over test scenarios. By implementing these best practices and testing strategies, you can ensure your GraphQL APIs are robust, secure, and perform seamlessly across all environments.