Many testers assume TestNG annotations are simple setup and teardown markers that rarely need attention.
I thought the same—until a test suite started running out of order, skipping setup steps, and failing inconsistently.
I wasted hours rerunning tests and tweaking waits before realizing the issue wasn’t Selenium, but how TestNG annotations controlled execution flow. Once that clicked, test behavior finally made sense.
Overview
TestNG annotations are predefined keywords that control the execution flow of test methods in a TestNG framework, defining when setup, test, and teardown logic should run.
Key TestNG annotations and their execution order:
- @BeforeSuite – Runs once before the entire test suite starts
- @BeforeTest – Executes before any test defined in a <test> tag in testng.xml
- @BeforeClass – Runs once before the first method of the current test class
- @BeforeMethod – Executes before each @Test method
- @Test – Contains the actual test logic
- @AfterMethod – Runs after each @Test method
- @AfterClass – Executes once after all test methods in the class
- @AfterTest – Runs after all tests in a <test> tag
- @AfterSuite – Executes once after the entire test suite finishes
Example TestNG annotation workflow:
public class TestNGExample {
@BeforeMethod
public void setUp() {
System.out.println("Setup before test");
}
@Test
public void testMethod() {
System.out.println("Running test");
}
@AfterMethod
public void tearDown() {
System.out.println("Cleanup after test");
}
}Here the example demonstrates how TestNG runs setup logic before each test and cleanup logic after execution, helping maintain consistent and reliable test behavior.
This article explains TestNG annotations in Selenium, how they work, and why they’re critical for building reliable automation.
What are TestNG Annotations?
TestNG annotations are predefined keywords used in the TestNG framework to control the execution flow of test methods in a Selenium automation suite.
They help define when a particular piece of code should run—such as before a test, after a test, or once for an entire test class or suite.
According to Crissy Joshua, a software testing expert, clearly scoping TestNG annotations to the appropriate level—method, class, or suite—helps prevent unexpected execution order issues and keeps test behavior predictable and easier to maintain.
By using annotations like @BeforeMethod, @Test, and @AfterMethod, testers can organize setup, execution, and cleanup logic in a structured and predictable way.
This makes test suites easier to maintain, reduces duplication, and ensures consistent behavior across test runs, especially as automation frameworks scale.
When these annotation-driven tests are executed across multiple browsers and environments, visibility and consistency become critical.
Platforms like BrowserStack Automate enable teams to run TestNG-based Selenium tests on real browsers and devices, automatically capturing logs and artifacts to simplify debugging and improve test reliability.
Types of TestNG Annotations
TestNG provides a rich set of annotations that help control the execution order of Selenium test cases. These annotations define when setup, test, and cleanup logic should run during a test cycle.
Below are the commonly used TestNG annotations in Selenium:
- @BeforeSuite – Runs once before all tests in the test suite are executed
- @BeforeTest – Executes before any test methods defined inside the <test> tag in testng.xml
- @BeforeClass – Runs once before the first @Test method in the current class
- @BeforeMethod – Executes before every @Test method
- @Test – Contains the actual test case logic
- @AfterMethod – Runs after every @Test method
- @AfterClass – Executes once after all test methods in the current class have run
- @AfterTest – Runs after all test methods inside the <test> tag complete execution
- @AfterSuite – Executes once after all tests in the suite have finished
Group-Level Annotations
TestNG also supports annotations for handling grouped test execution:
- @BeforeGroups – Runs before the first test method of a specified group
- @AfterGroups – Executes after all test methods in a specified group have completed
Read More: All About TestNG Listeners
Let’s explore how these annotations work together to control test execution flow.
Working of TestNG Annotations
The example below verifies the title of the Browserstack Home Page. The entire test case has been split into 3 parts.
- Launching the browser will be the first step and hence it is included under the @BeforeTest Annotation.
- Next is the actual test case which verifies the title, and is therefore included in the @Test annotation.
- Finally, the quit browser test case is considered under the @AfterTest annotation.
Code Example for the above scenario
package testngtest;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
import org.testng.Assert;
import org.testng.annotations.AfterTest;
import org.testng.annotations.BeforeTest;
public class Test1 {
public String baseUrl = "https://www.browserstack.com/";
String driverPath = "D:\\Selenium\\chromedriver.exe";
public WebDriver driver ;
@BeforeTest
public void launchBrowser() {
System.out.println("launching Chrome browser");
System.setProperty("webdriver.chrome.driver", driverPath);
driver = new ChromeDriver();
driver.get(baseUrl);
}
@Test
public void verifyHomepageTitle() {
String expectedTitle = "Most Reliable App & Cross Browser Testing Platform | BrowserStack";
String actualTitle = driver.getTitle();
Assert.assertEquals(actualTitle, expectedTitle);
}
@AfterTest
public void terminateBrowser(){
driver.close();
}
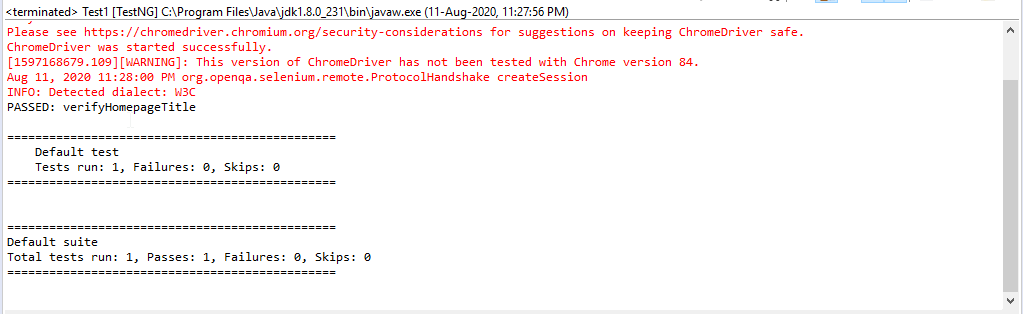
}On executing the code above, the output looks as follows:
This is how it works. Now let’s understand how to include @BeforeSuite and @BeforeMethod Annotations.
import org.testng.annotations.AfterClass;
import org.testng.annotations.AfterMethod;
import org.testng.annotations.AfterSuite;
import org.testng.annotations.AfterTest;
import org.testng.annotations.BeforeClass;
import org.testng.annotations.BeforeMethod;
import org.testng.annotations.BeforeSuite;
import org.testng.annotations.BeforeTest;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class testngAnnotations {
// Test Case 1
@Test
public void test1() {
System.out.println("Test Case 1");
}// Test Case 2
@Test
public void test2() {
System.out.println("Test Case 2");
}
@BeforeMethod
public void beforeMethod() {
System.out.println("Before Method");
}
@AfterMethod
public void afterMethod() {
System.out.println("After Method");
}
@BeforeClass
public void beforeClass() {
System.out.println("Before Class");
}
@AfterClass
public void afterClass() {
System.out.println("After Class");
}
@BeforeTest
public void beforeTest() {
System.out.println("Before Test");
}
@AfterTest
public void afterTest() {
System.out.println("After Test");
}
@BeforeSuite
public void beforeSuite() {
System.out.println("Before Suite");
}
@AfterSuite
public void afterSuite() {
System.out.println("After Suite");
}
}In the above example, the sequence is changed and then the program is executed. When this program is run, the output will appear in the sequence as shown below.
[RemoteTestNG] detected TestNG version 7.2.0 Before Suite Before Test Before Class Before Method Test Case 1 After Method Before Method Test Case 2 After Method After Class After Test PASSED: test1 PASSED: test2 =============================================== Default test Tests run: 2, Failures: 0, Skips: 0 =============================================== After Suite =============================================== Default suite Total tests run: 2, Passes: 2, Failures: 0, Skips: 0 ===============================================
So it always starts from executing Suite and then ends by executing method. This is how one uses TestNG Annotations.
Follow-up Read: Types of Listeners in Selenium (with Code Examples)
Enhance TestNG-Based Selenium Testing with BrowserStack Automate
TestNG annotations help structure and control Selenium test execution, but validating those tests across multiple browsers and environments requires scalable execution and strong debugging support.
BrowserStack Automate enhances TestNG-based Selenium testing by:
- Running TestNG Selenium tests on 3500+ real browsers and devices with no changes to existing code
- Supporting parallel execution, allowing annotation-driven tests to run faster across multiple browser–OS combinations
- Ensuring annotations like @BeforeMethod, @AfterMethod, and @Test behave consistently across real environments
- Automatically capturing screenshots, video recordings, console logs, and network logs for every test session
- Centralizing all test artifacts in the BrowserStack dashboard for easier analysis and collaboration
By combining TestNG’s structured execution model with real-browser testing and built-in debugging, BrowserStack Automate helps teams improve test reliability, speed up feedback, and streamline Selenium automation at scale.
Conclusion
TestNG annotations play a crucial role in structuring Selenium test execution, helping teams manage setup, execution order, and cleanup in a predictable and maintainable way.
When used correctly, they reduce flakiness, improve readability, and make automation frameworks easier to scale.
However, structured execution alone isn’t enough. Running TestNG-based Selenium tests across real browsers and environments is essential to catch browser-specific issues early.
By combining a strong understanding of TestNG annotations with scalable real-browser execution using BrowserStack Automate, teams can build faster, more reliable, and production-ready automation pipelines.