Scaling modern APIs demands a balance between flexibility, autonomy, and performance. GraphQL Federation addresses this by reshaping how teams design, test, and deliver APIs at scale.
Overview
GraphQL Federation is an architectural approach that unifies multiple GraphQL services (subgraphs) into a single gateway, giving clients one seamless API while allowing teams to own and scale their schemas independently.
Benefits of Using GraphQL Federation
- Enables team autonomy with independent schema ownership.
- Supports modular and scalable API design across domains.
- Provides a unified API for clients without tight coupling.
- Simplifies schema evolution and reduces breaking changes.
- Improves development velocity with parallel subgraph updates.
This article explores how GraphQL Federation works, its architecture, benefits, challenges, and best practices.
Understanding GraphQL Federation
GraphQL Federation is a way to extend GraphQL beyond a single monolithic schema by combining multiple subgraphs into a unified API. Each subgraph is owned and maintained by independent teams, while a central gateway stitches them together seamlessly for clients. This approach balances scalability with flexibility, allowing organizations to evolve their APIs without sacrificing consistency or developer experience.
Core Architecture & Components
At the heart of GraphQL Federation is a layered architecture that connects multiple services while presenting a unified API to clients. Its key components include:
- Subgraphs: Independent GraphQL services, each responsible for a specific domain or bounded context (e.g., users, products, orders). Subgraphs define their own schemas and resolvers, giving teams autonomy to build and scale independently.
- Gateway / Supergraph: A central service that composes all subgraph schemas into one federated schema. It receives client queries, breaks them down into sub-queries for the relevant subgraphs, and stitches together the responses into a single result.
- Schema Directives: Special annotations such as @key, @external, @requires, and @extends enable entities to be referenced and resolved across subgraphs. These directives are the glue that lets types and fields connect seamlessly across services.
- Query Planning & Execution: The gateway generates a query plan that determines which subgraphs to contact, in what order, and how to merge the results. This ensures clients see consistent, predictable responses, even when data spans multiple services.
Together, these components provide a modular yet unified foundation for scaling GraphQL across distributed teams and systems.
Benefits of using GraphQL Federation
GraphQL Federation unlocks a range of advantages for organizations scaling their APIs across teams and domains:
- Team Autonomy: Each team manages its own subgraph, enabling faster development without being blocked by centralized schema governance.
- Scalable API Design: Large, complex domains can be broken into modular subgraphs, making the system easier to maintain and evolve.
- Unified Client Experience: Clients interact with a single GraphQL endpoint, avoiding the complexity of knowing which service owns which data.
- Flexible Schema Evolution: Changes can be rolled out incrementally across subgraphs, reducing the risk of breaking existing queries.
- Faster Development Velocity: Independent deployments and schema ownership allow parallel progress across multiple teams.
By combining distributed ownership with a seamless API for clients, federation strikes a balance between scalability and usability that’s hard to achieve with monolithic GraphQL or REST.
Challenges & Risks
While GraphQL Federation offers clear benefits, it also introduces new complexities that teams must carefully manage:
- Operational Overhead: Adding a gateway and multiple subgraphs increases moving parts, requiring stronger DevOps practices for deployment and monitoring.
- Latency & Performance: Queries that span multiple subgraphs can result in extra network hops and slower response times if not optimized.
- Schema Conflicts: Overlapping type definitions or poorly designed directives can lead to errors during schema composition.
- Testing Complexity: Ensuring end-to-end reliability is harder when queries touch several subgraphs, making integration and contract testing critical.
- Debugging & Observability: Tracing issues across distributed subgraphs and the gateway can be challenging without robust logging and monitoring tools.
- Security Concerns: Managing authentication, authorization, and data privacy across multiple services adds another layer of risk.
These risks don’t outweigh the benefits, but they highlight the need for solid design principles, monitoring practices, and testing strategies when adopting federation.
Read More: Top 10 Python REST API Frameworks in 2024
Testing in Federated Systems
Testing becomes more complex in a federated setup, since a single client query may span multiple subgraphs and the gateway. To ensure reliability, teams need a layered testing approach:
- Unit Tests for Subgraphs: Validate schema definitions and resolver logic within each subgraph independently.
- Contract & Schema Validation: Ensure changes in one subgraph don’t break the overall supergraph by running schema compatibility checks.
- Integration Tests: Test interactions across multiple subgraphs through the gateway, verifying query plans and stitched responses.
- Mocking & Simulation: Use mocks for unavailable subgraphs or simulate failure scenarios to validate resilience.
- CI/CD Pipeline Testing: Automate federated schema checks and regression tests as part of continuous integration to catch issues early.
By combining local subgraph testing with end-to-end federation tests, teams can strike a balance between fast feedback and comprehensive coverage, which is critical for avoiding regressions in large-scale GraphQL systems.
When Not to Use Federation
While GraphQL Federation solves many scaling challenges, it isn’t always the right choice. In some cases, the added complexity can outweigh the benefits:
- Small Projects: A single GraphQL server is simpler and easier to manage when the API surface is limited.
- Tightly Coupled Domains: If most data and logic live within one domain, federation adds unnecessary overhead.
- Performance-Critical APIs: For systems where every millisecond counts, the extra network hops introduced by a gateway may be unacceptable.
- Limited Team Size: If only one or two teams manage the entire API, the autonomy benefits of federation don’t provide much value.
In these scenarios, a monolithic GraphQL server, or even a hybrid approach combining GraphQL with REST, can be more practical.
Best Practices & Guidelines
Adopting GraphQL Federation successfully requires strong design and operational discipline. The following best practices help ensure scalability and reliability:
- Design Subgraphs Around Domains: Use domain-driven design to define clear ownership boundaries and avoid overlapping responsibilities.
- Apply Schema Directives Consistently: Use federation directives like @key, @extends, and @requires with clear patterns to prevent confusion.
- Prioritize Backwards Compatibility: Evolve schemas carefully to avoid breaking existing queries; use deprecation and versioning strategies.
- Strengthen Testing Practices: Combine unit, integration, and contract tests to validate both subgraphs and the federated schema.
- Implement Robust Monitoring: Add tracing, logging, and performance metrics across the gateway and subgraphs for faster debugging.
- Plan for Incremental Deployment: Roll out subgraph updates gradually and validate them in staging before pushing to production.
By following these guidelines, teams can reduce risks, accelerate development, and ensure their federated GraphQL architecture scales smoothly.
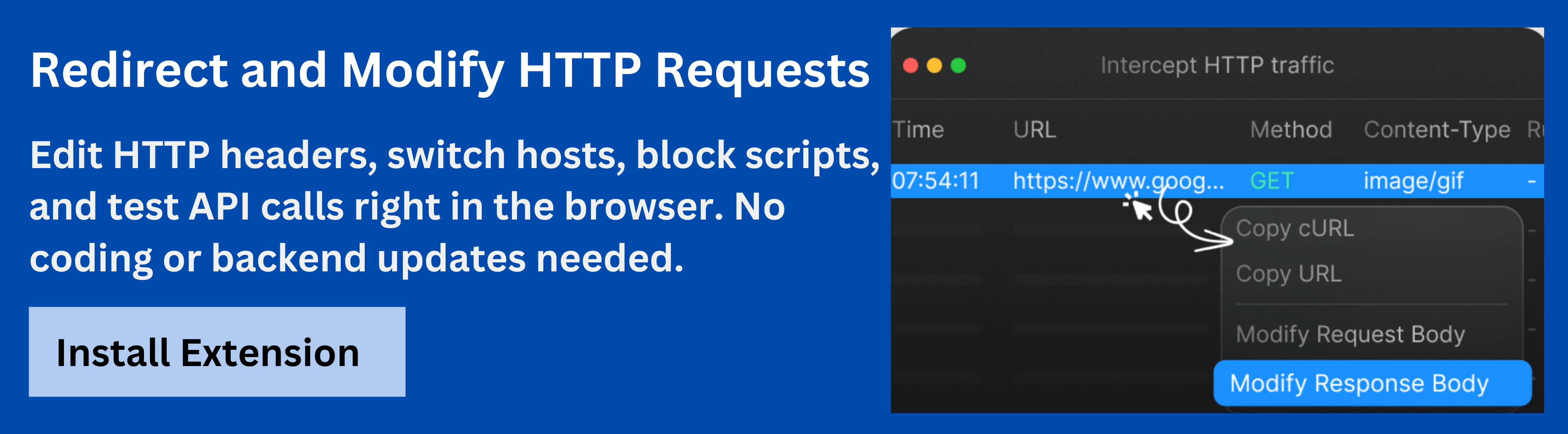
Debugging Federated APIs with Requestly
Federated GraphQL systems add complexity to debugging, since a single client query may pass through the gateway and multiple subgraphs before producing a response. Tools like Requestly HTTP Interceptor help simplify this process by giving developers control over network traffic in real time.
With Requestly, teams can:
- Intercept and Inspect GraphQL Requests: Capture live requests passing through the gateway to analyze headers, payloads, and responses.
- Mock Responses Easily: Simulate subgraph outputs without deploying services, speeding up testing and troubleshooting.
- Rewrite Requests On-the-Fly: Modify query parameters, URLs, or headers to reproduce edge cases and validate error handling.
- Simulate Failures: Test system resilience by injecting controlled failures or latency before they occur in production.
By integrating Requestly by BrowserStack into the debugging workflow, teams working with GraphQL Federation can resolve issues faster, validate resilience, and shorten the feedback loop between development and testing.
Conclusion
GraphQL Federation provides a powerful way to scale APIs across teams and domains, combining the flexibility of distributed ownership with the simplicity of a unified endpoint for clients. While it unlocks autonomy, modularity, and faster development, it also introduces challenges around testing, observability, and performance that teams must manage carefully.
By following best practices in schema design, testing strategies, and monitoring, and by leveraging tools like Requestly for debugging, organizations can adopt federation with confidence. Ultimately, the key is to evaluate when federation truly fits your needs and implement it thoughtfully to maximize long-term value.