JavaScript powers dynamic, interactive websites, but poorly optimized scripts can slow down rendering and frustrate users.
Overview
JavaScript rendering refers to how browsers process and execute scripts to display interactive elements on a webpage. When this process is delayed or blocked, users experience slow loading, unresponsive pages, or incomplete content.
Common Causes:
- Long-running scripts blocking the main thread.
- Errors or bugs in JavaScript code preventing proper execution.
- Unoptimized or excessive DOM manipulation.
- Incorrect or missing dependencies.
- Rendering delays due to heavy JavaScript frameworks.
Troubleshooting and Fixing JavaScript Rendering Issues:
- Identify Slow Scripts: Use browser developer tools (e.g., Chrome DevTools) to pinpoint slow or blocking scripts.
- Minimize JavaScript Execution: Optimize and defer non-essential scripts to improve page load speed.
- Check for Errors: Use error logs and console outputs to identify and fix any JavaScript errors.
- Reduce DOM Manipulation: Limit excessive or inefficient DOM updates to speed up rendering.
- Optimize Dependencies: Ensure only necessary dependencies are loaded, and avoid large libraries unless needed.
- Async and Defer: Implement async and defer attributes for non-essential scripts to prevent blocking the render process.
- Use Web Workers: Offload heavy JavaScript tasks to Web Workers to keep the UI responsive.
This article explains common JavaScript rendering issues, their impact on performance, and proven ways to fix them while ensuring smooth, fast-loading experiences.
What Are JavaScript Rendering Issues?
JavaScript rendering issues refer to problems that occur when browsers struggle to process, execute, or display site content as intended due to the way JavaScript interacts with the page.
These problems are often rooted in how JavaScript modifies the Document Object Model (DOM) during or after initial load, causing pauses and delays in rendering that negatively impact both site speed and user experience.
Indicators of JavaScript Rendering Issues
- Delayed or incomplete display of page elements, such as text, images, or entire sections.
- Blank pages, broken layouts, or distorted formatting resulting from errors in JS code execution.
- Conflicting directives between raw HTML and rendered HTML, leading to missing or misplaced critical elements.
- Poor performance in tools like Google Search Console, including failed indexing, slow load times, and invalid internal links due to inaccessible content.
- Main thread activity bottlenecks, where heavy JavaScript processing stalls rendering and user interaction.
Read More: Top 9 JavaScript Testing Frameworks
Common Causes of JavaScript Rendering Problems
JavaScript rendering problems are typically caused by a variety of technical pitfalls related to how scripts are loaded, executed, or blocked within web applications. Here are the most common causes, explained in precise technical terms:
- Blocked JavaScript resources: When key JavaScript files or directories are restricted via robots.txt, browsers and search engine crawlers cannot access or execute these scripts, resulting in incomplete or failed rendering of essential page elements.
- Critical JavaScript errors: Syntax errors, missing dependencies, or incompatibilities within scripts can halt parsing or execution, leading to content not being displayed or certain interactive features failing entirely.
- Large and unoptimized JavaScript bundles: Excessive or monolithic scripts increase network load times and monopolize the main thread, significantly delaying DOM construction, interaction readiness, and visual completeness.
- Default client-side rendering (CSR): Many modern frameworks default to CSR, which shifts full rendering responsibility to the browser and can result in blank or incomplete pages for both users and crawlers if hydration is delayed or fails.
- Conflicting directives and dynamic metadata: Discrepancies between the raw HTML and JavaScript-modified content (such as noindex/nofollow directives or missing canonical/meta tags) can confuse search engines and misrepresent the intended structure of the page.
- Non-renderable or broken internal links: Navigation or linking elements generated entirely via JavaScript may not be included in the final DOM, preventing search engines from discovering critical content or internal pages.
- Improperly configured lazy loading or deferred scripts: Content or resources set to load only after specific user actions or asynchronous triggers may fail to appear during the initial browser or crawler render, reducing accessibility and indexation potential.
Addressing these causes requires a combination of robust coding standards, careful configuration of technical SEO settings, and ongoing monitoring using developer tools and search performance analytics.
How JavaScript Rendering Issues Affect Website Performance
JavaScript rendering issues have a significant impact on website performance by affecting page load speed, interactivity, and overall user experience. These issues primarily slow down critical performance metrics that modern web standards emphasize:
- Increased Time to First Paint (TTFP) and Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Excessive or blocking JavaScript delays the rendering of the largest visible content elements, causing users to wait longer before meaningful content appears on the screen. This poor loading experience can increase bounce rates.
- Delayed Time to Interactive (TTI): Heavy JavaScript processing blocks the browser’s main thread, postponing the moment when a page becomes fully interactive. Users may see the page visually but experience unresponsive buttons, menus, or forms until scripts finish executing.
- Increased Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Render-blocking or late-loading JavaScript can cause elements to suddenly move or resize during page load, resulting in layout instability and a jarring experience. This impacts perceived quality and is penalized by Google’s Core Web Vitals.
- Long Main-Thread Blocking Times: JavaScript parsing and execution often monopolize the browser’s main thread, preventing it from handling rendering, user input, or other critical tasks efficiently. This leads to sluggish animations, input delays, and degraded page responsiveness.
- Core Web Vitals Degradation: JavaScript rendering issues negatively affect all three Core Web Vitals metrics, LCP, FID (First Input Delay), and CLS, which are key ranking factors in search engines, thereby harming SEO and organic traffic.
- Higher Network Load and Data Usage: Large JavaScript bundles increase download times and data consumption, especially problematic for users on slow or metered connections. This can discourage users from continuing to load or interact with the site.
Effective management and optimization of JavaScript delivery and execution help overcome these performance penalties, leading to faster, smoother, and more accessible websites that benefit both users and search engines.
Proven Ways to Fix JavaScript Rendering Issues
Fixing JavaScript rendering issues requires a combination of strategies designed to optimize script loading, execution, and impact on the critical rendering path. Here are well-established techniques with practical benefits:
1. Minimize Render-Blocking JavaScript
- Use the defer or async attribute on script tags to prevent JavaScript from blocking HTML parsing and rendering. defer ensures scripts execute after parsing, while async allows scripts to download and execute asynchronously.
- Preload critical JavaScript resources with
or
to prioritize essential scripts without blocking render.
2. Split and Lazy-Load Code
- Implement code splitting to load only necessary JavaScript for the current page or route, reducing initial bundle size and speeding up load times.
- Lazy-load non-critical scripts and third-party tags so they do not delay the initial render. Load them asynchronously or on-demand when needed.
3. Optimize Critical Rendering Path
- Minify and compress JavaScript files to reduce download times and parsing cost.
- Remove unused or redundant scripts and dependencies with tree shaking and bundle analysis tools.
- Combine related JavaScript files where it reduces HTTP requests without negatively impacting parallel loading.
4. Adopt Modern Rendering Techniques
- Use Server-Side Rendering (SSR) or static site generation to send fully or partially rendered HTML to clients, reducing client-side JS processing.
- Implement hydration strategies to progressively enable interactivity without blocking rendering or causing layout shifts.
5. Improve Runtime Efficiency
- Optimize DOM manipulation by batching updates and using efficient selectors like getElementById instead of slower query selectors.
- Prefer CSS animations over JavaScript where possible, since browsers natively optimize CSS for rendering performance.
- Employ requestAnimationFrame() for JS-driven animations to synchronize updates with browser repaint cycles.
6. Use Performance Monitoring and Diagnostic Tools
- Regularly audit JavaScript performance to locate bottlenecks.
- Implement continuous performance regression detection in development workflows to prevent regressions.
Applying these proven methods helps drastically reduce JavaScript-induced rendering delays, improving both user-perceived speed and overall site performance metrics critical for SEO and usability.
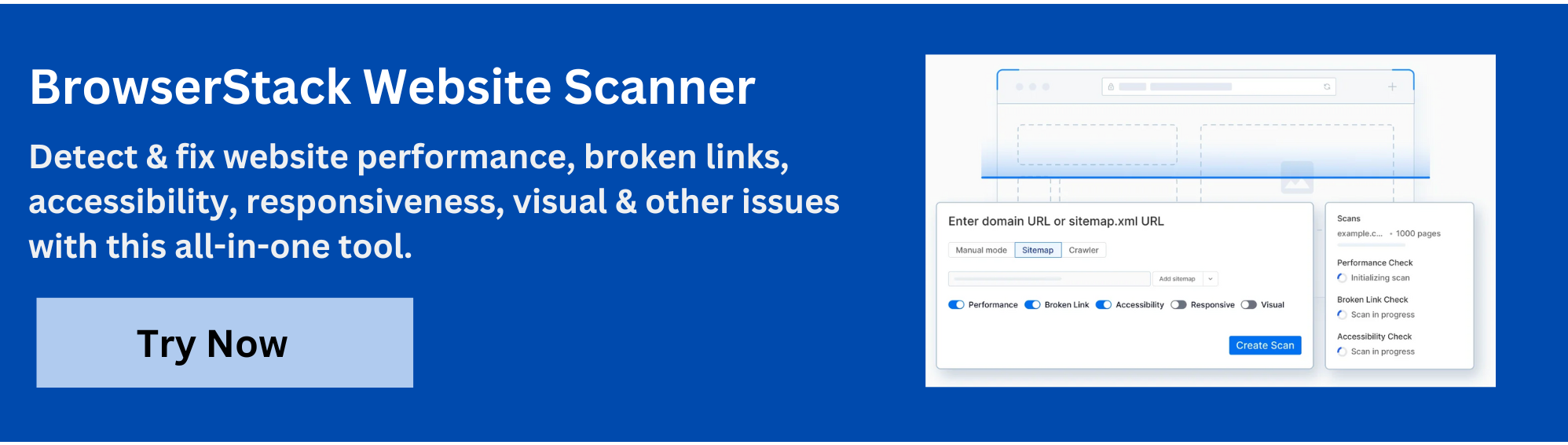
Diagnose JavaScript Rendering Issues with BrowserStack Website Scanner
BrowserStack Website Scanner is an automated, no-code tool designed to help developers and QA teams efficiently detect and fix JavaScript rendering issues that impact website performance and user experience.
By running comprehensive scans across your website, the tool automatically identifies common problems such as broken images, failed JavaScript execution, and missing CSS files, ensuring your pages render correctly and consistently across browsers.
Key Capabilities:
- Automated Detection: The scanner systematically crawls your web pages to spot JavaScript rendering failures, broken resource links, and CSS loading errors without any manual scripting or setup.
- Comprehensive Coverage: It scans every page URL you provide or extracts them directly from your sitemap, checking for visual defects, functionality errors, and accessibility compliance.
- Easy Diagnostics and Reporting: Detailed scan reports provide actionable insights into exactly which scripts failed, which resources are missing or blocked, and where layout or performance issues occur.
- Continuous Monitoring: Set up scheduled recurring scans to monitor your site over time, quickly identifying regressions or new issues caused by code changes or third-party updates.
By integrating the Website Scanner into your development and QA process, you can proactively diagnose and resolve JavaScript rendering problems before they reach end users, ensuring that your website functions as intended and delivers a flawless browsing experience across platforms.
Conclusion
JavaScript is essential for delivering dynamic, interactive experiences, but rendering issues can severely slow down websites and frustrate users. By identifying the root causes, applying proven optimization techniques, and validating fixes across browsers and devices, you can ensure fast, reliable performance.
To stay ahead, use tools like BrowserStack Website Scanner to automatically detect rendering problems, broken scripts, and other critical issues, helping you maintain a seamless user experience and stronger search visibility.