React Native initially felt simple to me because so much of it resembled ReactJS, and the shared components made cross-platform builds look easy.
But device and OS fragmentation changed that quickly.
One Android model ran perfectly while another froze, and an iOS flow that passed on the latest version failed on older devices many users still depended on.
It pushed me to ask tougher questions: would the app stay consistent on new hardware, and could it support older versions without unpredictable behavior?
Overview
Methods to Test React Native Apps on iOS and Android Devices
- Method 1: Testing React Native Apps on Emulators and Simulators (iOS and Android)
- Method 2: Testing React Native Apps on Physical Devices (iOS and Android)
- Method 3: Testing Reactive Native Apps on a Real Device Cloud
In this article, I’ll walk through the exact process that helped achieve reliable testing for React Native apps across both iOS and Android devices.
What is React Native Framework?
React Native is an open-source framework developed by Facebook for developing native iOS and Android mobile application code.
It is a cross-platform JavaScript-based framework. With React Native, you can use the same codebase to develop applications for iOS and Android.
Here are some of the benefits of React Native framework:
- React Native streamlines cross-platform development by allowing teams to share most of the codebase across iOS and Android, reducing build time while maintaining consistent app behavior across devices.
- Hot Reloading accelerates iteration by showing UI and logic updates instantly without a full rebuild, making debugging and development cycles significantly faster.
- The framework delivers near-native performance by rendering UI through native components instead of WebViews, resulting in smoother animations and faster load times.
- Its foundation in JavaScript gives developers access to a vast ecosystem of libraries, tools, and existing expertise, improving productivity and reducing onboarding efforts.
- React Native’s modular architecture makes it easier to scale apps, update individual components independently, and support multiple contributors across large projects.
- A strong and active community provides solutions for navigation, animations, state management, deep linking, and more, helping teams adopt best practices and proven patterns.
- Native modules written in Swift, Objective-C, Java, or Kotlin can be integrated whenever deeper platform-level access is needed, offering flexibility for advanced functionality.
- The ability to reuse code across platforms and rely on widely used JavaScript skills makes React Native a cost-effective option for development and long-term maintenance.
- Rapid prototyping is easier because of flexible UI components and fast refresh cycles, enabling teams to build MVPs quickly and shorten time-to-market.
Methods to Test React Native Apps on iOS and Android Devices
React Native projects can be tested through three primary methods: emulators/simulators, physical devices, and real device clouds. Each method uncovers different types of issues and serves a distinct purpose in the development and QA cycle. The sections below break down each method in depth.
Method 1: Testing React Native Apps on Emulators and Simulators (iOS and Android)
Testing on emulators and simulators is the quickest way to validate your React Native app during development without relying on physical devices.
While they don’t fully replicate real device behaviour—especially around performance, sensors, hardware variations, and network conditions—they remain ideal for early-stage functional checks, UI validation, rapid debugging, and iterative development before moving to physical or cloud devices.
Testing React Native Apps Using Expo
Expo enables fast testing without configuring native code.
- Install platform tools: Xcode for iOS simulators, Android Studio for Android emulators.
- Navigate to the React Native project directory and run
npm start
Or
expo start
to launch the development server.
- For iOS, press i to open the simulator where Expo Go launches automatically. For Android, press a to open the selected AVD.
- The app loads within Expo Go, allowing developers to check UI rendering, navigation, basic interactions, and component behavior across both platforms.
Read More: UI Testing of React Native Apps
Testing React Native Apps Using React Native CLI
React Native CLI allows testing of native builds, making it essential for features unavailable in Expo.
- Install Xcode and Android Studio to enable device simulation.
- For iOS, run:
npx react-native run-ios
for Android:
npx react-native run-android
to compile and launch the app.
The simulator/emulator provides access to native modules, permission flows, navigation transitions, and platform-level behaviours that must be tested before moving to real devices.
Method 2: Testing React Native Apps on Physical Devices (iOS and Android)
Physical device testing is critical because simulators cannot replicate hardware variability, sensor behavior, OEM customizations, or real-world performance patterns. Android and iOS require different setup steps to install and run React Native apps on actual devices.
Testing on Physical iOS Devices
iPhones enforce strict signing, provisioning, and security rules, making on-device testing a necessary step before production.
- Connect the iPhone to a Mac and open the project’s ios folder in Xcode.
- Select the device in the target menu and configure Signing & Capabilities by assigning a development team and enabling automatic signing.
- Press the Run button to build and deploy the app to the device.
- If the device displays an “Untrusted Developer” message, navigate to Settings > General > VPN & Device Management on the iPhone and trust the associated certificate.
- Once trusted, the app launches normally, allowing performance tests, gesture validation, native animation checks, and real hardware behavior analysis.
Read More: End-to-End React Native Testing
Testing on Physical Android Devices
Due to OEM diversity, physical testing on Android helps surface issues that emulators often miss.
- Install Android Studio and connect an Android device with USB Debugging enabled.
- Verify connectivity using adb devices.
- Run
npx react-native run-android
to build and deploy the app.
- Physical Android testing exposes issues related to CPU throttling, custom manufacturer skins, varied permission behaviors, network rules, and adaptive UI scaling.
Testing Expo Projects on Physical Devices
Expo also supports quick testing on hardware.
- Install the Expo Go app on the iPhone or Android device.
- Run npm start or expo start to display a QR code.
- Scan the QR code from the Expo Go app to instantly load and test the app without building native binaries.
Read More: End-to-End React Native Testing
Method 3: Testing Reactive Native Apps on a Real Device Cloud
Real-device cloud offered by testing platforms like BrowserStack, provide most accurate and maximum test coverage. With manufacturers releasing new devices constantly, maintaining an in-house device lab is expensive and incomplete. Testing on a cloud platform ensures that React Native apps work across a wide range of real-world conditions, OS versions, and device models.
Why Test on a Real Device Cloud?
Testing on real devices hosted in the cloud helps address questions like:
- Will the app function consistently across the latest Android and iOS devices?
- Will it remain stable on older OS versions that a significant user base still depends on?
- How does the app behave on devices from different OEMs like Samsung, Google, Xiaomi, and Apple?
Using BrowserStack for React Native Testing
A real device cloud exposes React Native apps to the diversity of actual iPhones and Android phones—different OS versions, hardware specs, screen sizes, and manufacturers. BrowserStack ensures accurate, real-world results by offering a wide device range, eliminating emulator gaps, and helping teams ship stable builds with confidence.
One can test React Native apps manually using BrowserStack App Live or by automated testing using BrowserStack App Automate.
BrowserStack helps you to test React Native apps across real devices offering these benefits:
- Install and test multiple app versions in one session.
- Switch between portrait and landscape instantly.
- Run geolocation tests across global regions.
- Simulate poor or variable network conditions.
- Validate localisation by changing device language.
- Capture precise screenshots for UI and security checks.
Follow these steps to test React Native apps in manual method using BrowserStack App Live:
To get started, one just needs to Signup on BrowserStack App Live and follow the steps below:
Step 1 – Upload the desired version of the React-Native app (iOS or Android) i.e, the .apk or .ipa file.
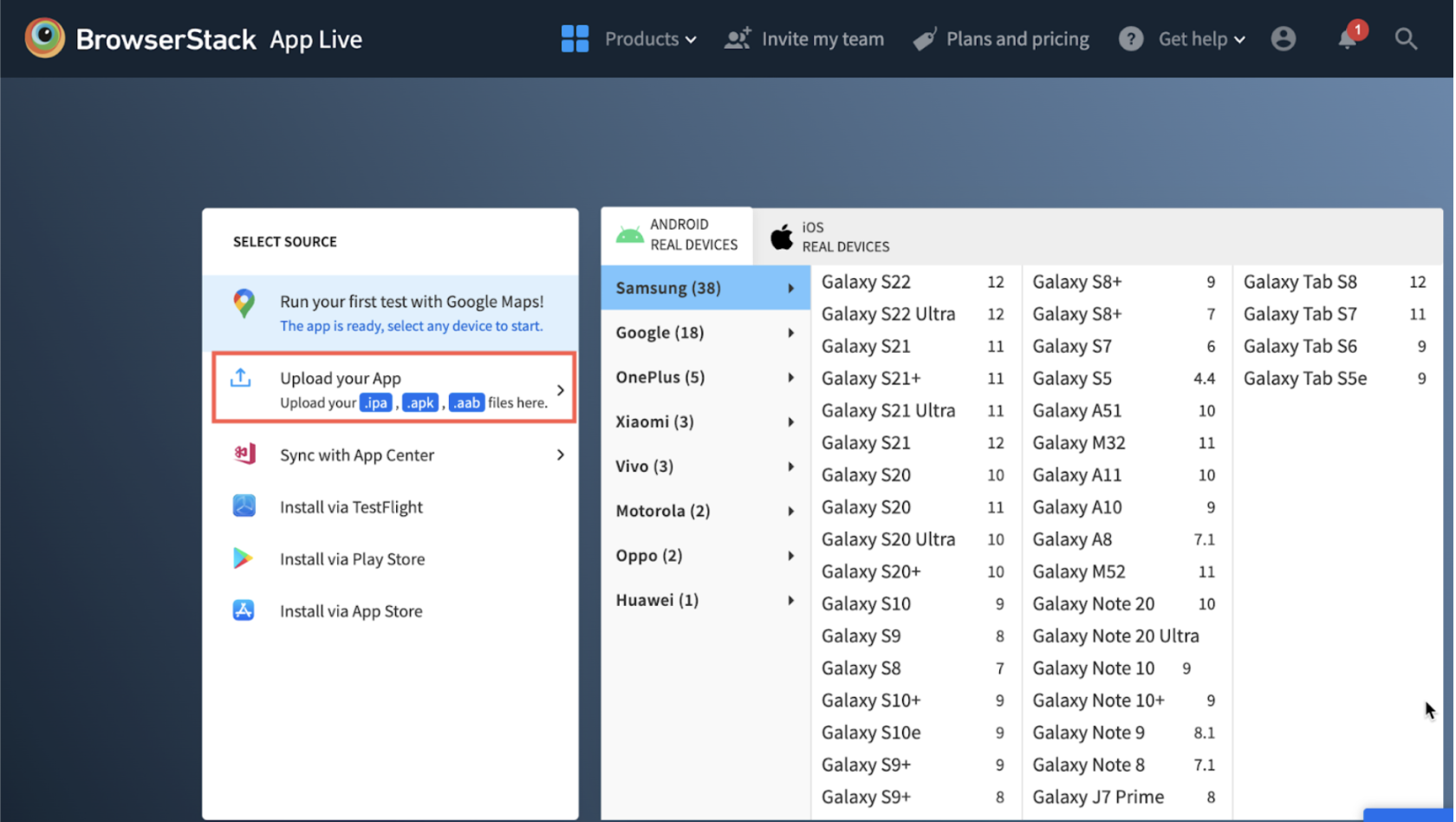
Note: One can also install the particular app directly from App Store or Play Store for testing.
Step 2 – Based on the type of app you upload (Android or iOS), choose the desired mobile device to test. To simplify, choose an Android device if you upload a .apk file or choose a specific iPhone/iPad if you upload a .ipa file. (In this case, consider testing a sample.apk file on Galaxy S22 Ultra).
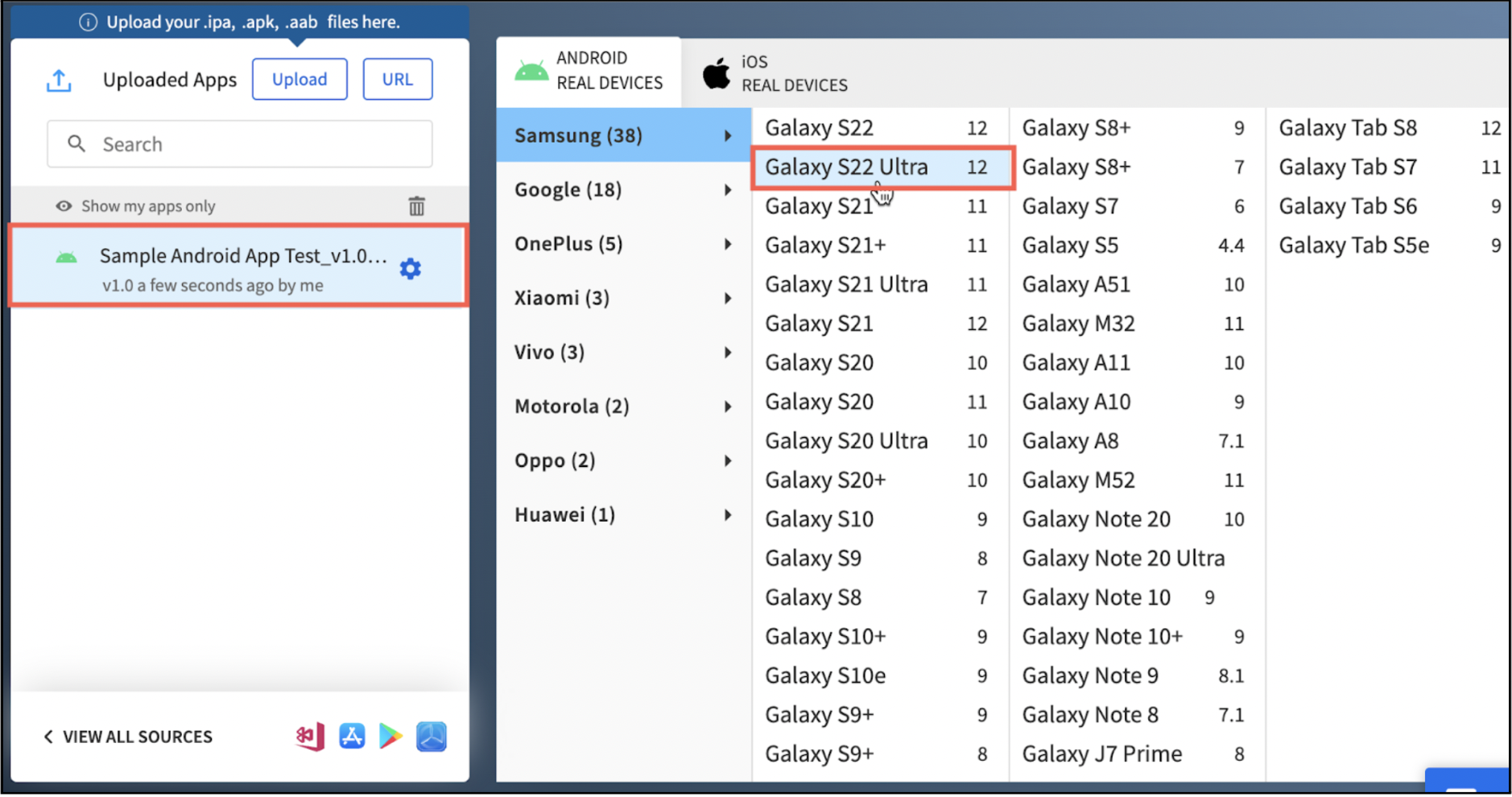
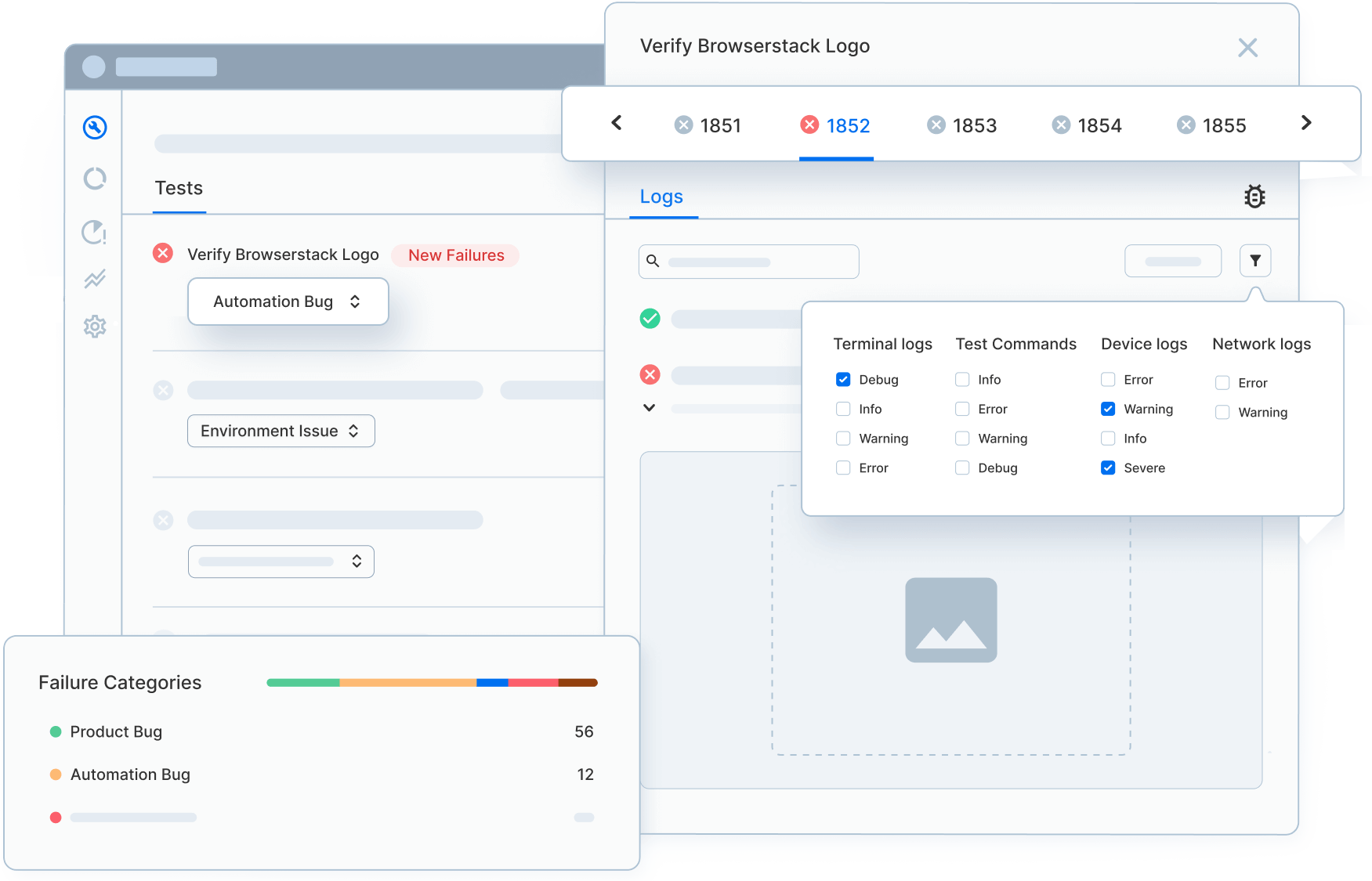
Step 3 – After uploading the app and selecting the desired mobile device (iOS or Android), an App-live session starts instantly on the selected device (Galaxy S22 Ultra in this case). Once the app is successfully installed, QAs can proceed to test and debug their apps in real user conditions. Here is an App Automate test session on a real Galaxy S22 Ultra.
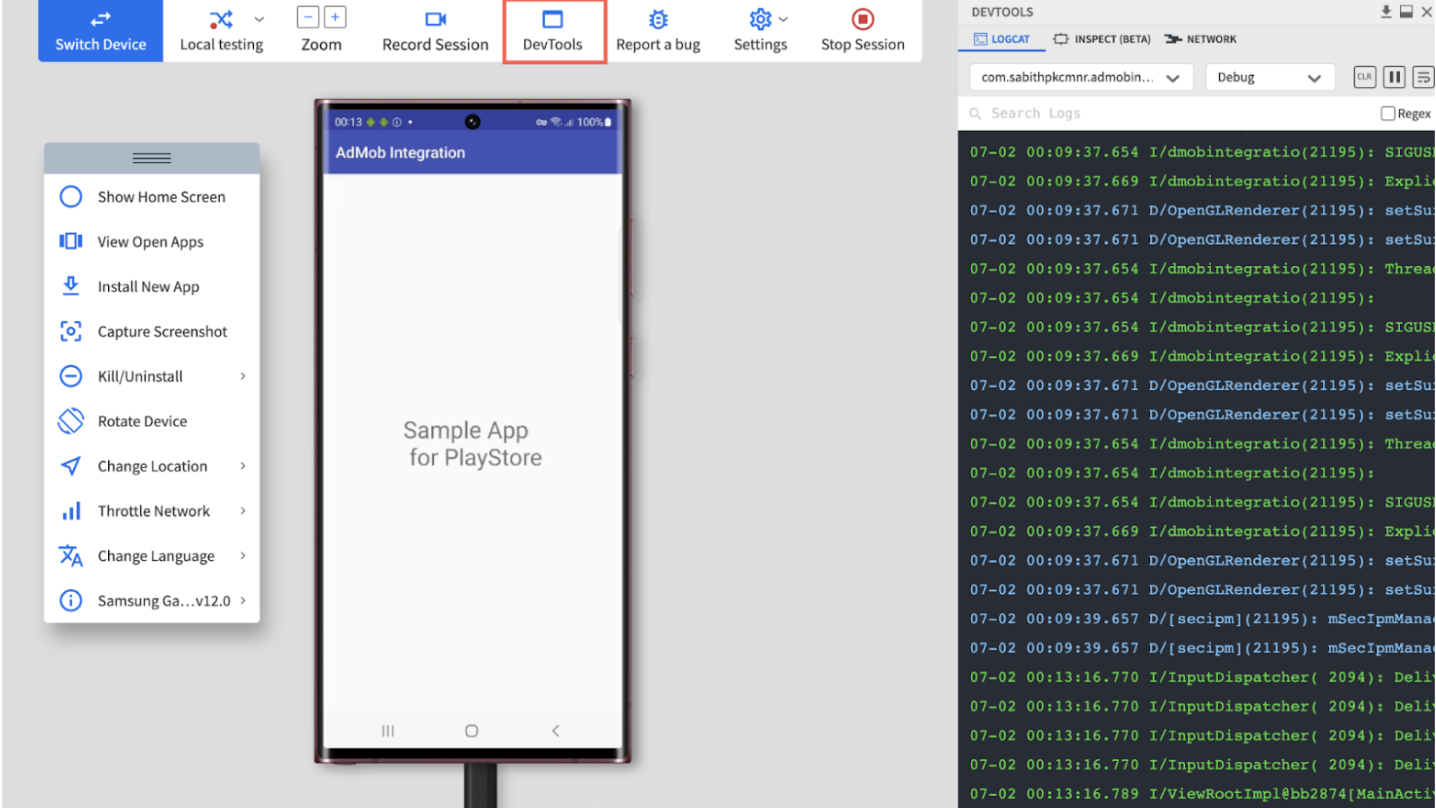
When to Use Manual Testing of React Native Apps using BrowserStack App Live?
- Validating UI layouts, animations, and visual consistency across devices.
- Exploring new features or early builds where test cases aren’t finalized.
- Reproducing and debugging device-specific or environment-specific issues.
- Checking usability, accessibility, gestures, and real-world interactions.
- Testing localization, geolocation, network conditions, and quick visual checks.
Follow these steps to test React Native apps in automated method using BrowserStack App Automate:
Automating React Native testing with BrowserStack App Automate allows teams to run reliable, repeatable test suites on real iOS and Android devices without maintaining internal device labs. The process follows a clear sequence that integrates smoothly into existing workflows.
Step 1: Prepare your automation framework: Set up or reuse existing automated tests built with Appium, WebdriverIO, or any supported framework. This ensures React Native workflows can be scripted without changing your test stack.
Step 2: Upload the React Native app to BrowserStack:Upload the Android (.apk/.aab) or iOS (.ipa) build to App Automate. Each uploaded build gets a unique identifier that can be referenced directly in your test scripts.
Step 3: Configure desired capabilities: Define device name, OS version, app ID, and other required capabilities in your test scripts. This tells App Automate which real devices to run your tests on.
Step 4: Run tests on real devices: Execute your automated test suite across real Android and iOS devices. BrowserStack handles device provisioning, OS updates, and availability, ensuring stable test environments.
Step 5: Enable parallel execution: Configure parallel test runs to significantly reduce the total execution time of large regression suites. Running tests simultaneously across devices accelerates CI/CD feedback loops.
Step 6: Integrate with CI/CD pipelines: Plug App Automate into Jenkins, GitHub Actions, GitLab CI, Azure DevOps, or other CI tools to trigger automated tests on every commit, PR, or release build.
Step 7: Analyze detailed debugging insights: Review videos, screenshots, Appium logs, device logs, and network data for each session. These insights help quickly identify failures caused by UI changes, timing issues, or device-specific behavior.
When to Use Automated Testing for React Native Apps using BrowserStack App Automate?
- Running repetitive regression tests across Android and iOS at scale.
- Ensuring stability during continuous integration and release cycles.
- Validating complex workflows that must run consistently across devices.
- Achieving faster execution through parallel test runs on real devices.
- Maintaining long-term test coverage with scripted, repeatable test suites.
Why Testing React Native Apps on Real Device Cloud is Important?
It is best to test React Native Apps on iOS and Android using real device cloud like BrowserStack for these reasons:
- Provides instant access to a wide range of real iOS and Android devices, covering new releases and legacy OS versions that are difficult to maintain in-house.
- Detects hardware-specific issues such as GPU rendering glitches, sensor inaccuracies, thermal throttling, battery impact, and memory constraints that emulators cannot replicate.
- Eliminates device lab maintenance by offering ready-to-test devices that are constantly updated, charged, and available for multiple team members in parallel.
- Surfaces OEM-specific behaviors across Samsung, Google, Xiaomi, and other manufacturers, including custom permission flows, UI variations, and background process rules.
- Enables realistic testing of gestures, animations, camera modules, push notifications, network fluctuations, and OS-level interruptions in real user conditions.
- Accelerates debugging with built-in logs, video recordings, screenshots, and network traffic insights that simplify root-cause analysis for React Native issues.
- Supports fast release cycles by allowing teams to switch between devices instantly, test regressions quickly, and validate compatibility across multiple environments.
- Integrates manual and automated testing workflows, making it easy to run exploratory tests on App Live and automated suites on App Automate using Appium or Detox.
A real device cloud exposes React Native apps to the full spectrum of iPhones and Android devices users actually own—older OS versions, new releases, varied chipsets, and different screen profiles.
BrowserStack makes this coverage effortless by offering instant access to real hardware, removing emulator blind spots, and revealing issues that surface only under true device conditions. This leads to more reliable builds and fewer surprises in production.
Useful Resources for React Native
- How to make React Native App Responsive?
- Top 5 React Native UI Components
- UI Testing of React Native Apps
- End-to-End React Native Testing
- React Native and Appium Tutorial
- Test React Native Apps with Cypress
Conclusion
With the ever-increasing fragmentation, teams are bound to face the challenge of testing apps across latest devices with the change in mobile usage trends. Naturally, teams need a scalable and feasible method that allows them to meet their testing goals speedily.
Adopting a real device cloud like BrowserStack for app testing is one such feasible method that eliminates the burden of setting up test infrastructure for teams. It eliminates the overhead of maintaining the digital labs. This way team can purely focus on testing and delivery of robust apps.