GraphQL has become a popular choice for modern API development, offering flexibility and efficiency over traditional REST APIs.
Overview
Integrating GraphQL with Spring Boot enables developers to build flexible, efficient, and high-performance APIs that handle complex queries with ease, improving the overall development experience and performance.
Key Steps for GraphQL Integration in Spring Boot:
- Set up a Spring Boot project using Spring Initializr with GraphQL dependencies.
- Define a GraphQL schema using Schema Definition Language (SDL).
- Implement resolvers to handle queries and mutations.
- Configure data sources (e.g., databases) and repositories.
- Set up security and authentication for GraphQL endpoints.
- Write unit and integration tests for the GraphQL API.
- Optimize performance with batching, caching, and error handling.
Benefits of Using Spring for GraphQL:
- Seamless integration with existing Spring ecosystem (e.g., Spring Data, Spring Security).
- Simplified configuration with Spring Boot’s auto-configuration capabilities.
- High scalability and maintainability for large applications.
- Strong support for testing, security, and performance optimization.
- Access to powerful Spring features like dependency injection and AOP.
This article explores the process of building, securing, optimizing, and deploying GraphQL APIs with Spring Boot for efficient and scalable applications.
Understanding GraphQL and Spring Boot
GraphQL is a query language and runtime for executing queries by using a type system. It allows clients to request exactly the data they need, reducing over-fetching and under-fetching of data.
Spring Boot is a framework built on top of the Spring framework that simplifies the development of Java-based applications. It offers rapid application development with minimal configuration, making it easy to build stand-alone, production-grade Spring applications.
Integrating GraphQL with Spring Boot allows developers to combine the power of Spring’s robust ecosystem with GraphQL’s flexibility and efficiency. By doing so, applications can handle complex queries in a structured manner, enabling more dynamic data fetching, reducing server load, and improving client performance.
Spring Boot’s ease of configuration, combined with GraphQL’s ability to query and mutate data on demand, creates a powerful combination for modern web and mobile applications.
Key Advantages of Using GraphQL with Spring Boot:
- Efficient Data Fetching: GraphQL allows clients to request only the data they need, eliminating the problem of over-fetching and under-fetching.
- Single Endpoint for Multiple Queries: Unlike REST APIs that require multiple endpoints, GraphQL uses a single endpoint for all queries and mutations.
- Strong Type System: GraphQL’s type system enables introspection, ensuring that clients know exactly what data they can query.
- Integration with Spring Boot Features: Spring Boot provides a streamlined way to integrate GraphQL, with auto-configuration, security, and database integration already built-in.
Setting Up Your Spring Boot Project
Setting up a Spring Boot project to integrate GraphQL involves a few essential steps. Follow the instructions below to quickly get started with a GraphQL-powered Spring Boot application.
1. Generate the Spring Boot Project
The quickest way to generate a Spring Boot project is by using the Spring Initializr. Select the following options:
- Project: Maven or Gradle (depending on your preference).
- Language: Java.
- Spring Boot Version: Choose the latest stable version.
- Dependencies: Add Spring Web, Spring Boot DevTools, Spring Data JPA, and GraphQL (You may need to add the GraphQL starter manually later if not available in the list).
After filling out the form, click Generate to download a zip file containing your Spring Boot project.
2. Add Required Dependencies
To enable GraphQL functionality, you need to add the appropriate dependencies to your pom.xml or build.gradle file. Below are the necessary dependencies for Maven and Gradle:
For Maven (Add to your pom.xml):
com.graphql-java
graphql-java
17.3com.graphql-java
graphql-java-spring-boot-starter
11.0org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-data-jpa
For Gradle (Add to your build.gradle):
dependencies {
implementation ‘com.graphql-java:graphql-java:17.3’
implementation ‘com.graphql-java:graphql-java-spring-boot-starter:11.0’
implementation ‘org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-jpa’
}3. Configure Application Properties
In src/main/resources/application.properties, configure the database connection and GraphQL endpoint. For example, if using an in-memory H2 database:
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:mem:testdb
spring.datasource.driverClassName=org.h2.Driver
spring.datasource.username=sa
spring.datasource.password=password
spring.jpa.database-platform=org.hibernate.dialect.H2Dialect# GraphQL endpoint configuration
graphql.servlet.mapping=/graphql
graphql.servlet.enabled=true
graphql.servlet.corsEnabled=true
For production environments, replace the H2 database configuration with the connection details for MySQL, PostgreSQL, or any other preferred database.
4. Create GraphQL Schema
In the root directory of src/main/resources, create a file named schema.graphqls to define your GraphQL schema. This file will describe the types, queries, and mutations available in your API.
Example:
type Query {
books: [Book]
}
type Book {
id: ID
title: String
author: String
}
5. Create Resolvers
Resolvers define how to fetch data for the fields in your GraphQL schema. For example, in the BookResolver class, you can fetch data from a database or a service layer.
Example:
@Component
public class BookResolver implements GraphQLQueryResolver {
private final BookRepository bookRepository;public BookResolver(BookRepository bookRepository) {
this.bookRepository = bookRepository;
}public List getBooks() {
return bookRepository.findAll();
}
}
6. Create Data Entities and Repositories
Use Spring Data JPA to define your data model and repositories. For instance, the Book entity:
@Entity
public class Book {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String title;
private String author;// Getters and setters
}
And the corresponding repository:
public interface BookRepository extends JpaRepository {
}7. Running the Application
Once all dependencies are added, and configurations are in place, run your Spring Boot application by executing the mvn spring-boot:run command for Maven or ./gradlew bootRun for Gradle.
The application will start on http://localhost:8080, and you can interact with the GraphQL API using the /graphql endpoint.
By following these steps, you’ll have successfully set up a Spring Boot project with GraphQL, ready for further development and integration.
Defining the GraphQL Schema
In GraphQL, the schema is the foundation of the API, defining how clients can interact with the server. It describes the types of data available, the queries to fetch data, and the mutations to modify data. A well-structured schema ensures that the API is flexible, scalable, and easy to maintain.
1. Schema Definition Language (SDL)
The schema is written using Schema Definition Language (SDL), a simple syntax that describes the types, queries, and mutations in the API. It defines the structure of data and operations that can be executed on that data.
2. Types
Types are used to define the structure of the data. For example, a Book type can represent a book with fields like title, author, and publishedYear. Types are the building blocks of the schema.
type Book {
id: ID
title: String
author: String
publishedYear: Int
}3. Queries
Queries are the read operations in GraphQL. They allow clients to request data from the server. Each query corresponds to a specific operation, such as fetching a list of books or retrieving a single book by ID.
type Query {
books: [Book]
book(id: ID): Book
}4. Mutations
Mutations are used for modifying data, such as creating, updating, or deleting resources. For example, a createBook mutation might be used to add a new book to the system.
type Mutation {
createBook(title: String, author: String, publishedYear: Int): Book
}5. Resolving Data
Each query or mutation in the schema is linked to a resolver function in the Spring Boot application. The resolver contains the logic to fetch or modify data based on the request.
By defining the schema correctly, you set clear expectations for both the client and the server on how data should be structured and accessed.
Implementing CRUD Operations
Once the GraphQL schema is defined, the next step is to implement the CRUD (Create, Read, Update, Delete) operations. These operations allow clients to interact with the data and modify it as needed. In this section, we will walk through how to implement these operations in a Spring Boot application using GraphQL.
1. Create Operation (Mutation)
The Create operation allows clients to add new resources, such as creating a new entry in the database. In GraphQL, this is done through a mutation, which defines how new data is inserted into the system. In the Spring Boot application, the corresponding resolver will handle the logic for saving new data to the database.
2. Read Operation (Query)
The Read operation is used to fetch data from the server. This is typically done through queries, which allow clients to request one or more resources. A query can be used to retrieve specific data based on parameters (such as an ID) or fetch a list of resources. In the resolver, the query is mapped to a method that fetches the data from the database and returns it.
3. Update Operation (Mutation)
The Update operation allows clients to modify existing resources. In GraphQL, this is also handled through mutations. The mutation will receive the necessary parameters, including an identifier, and update the corresponding resource. The Spring Boot resolver will handle the logic for retrieving the resource, modifying it, and saving the changes back to the database.
4. Delete Operation (Mutation)
The Delete operation allows clients to remove resources from the system. This is performed through a mutation that accepts an identifier for the resource to be deleted. In the Spring Boot application, the resolver will execute the deletion process in the database, ensuring the resource is removed.
Integrating with Databases
Integrating a database with GraphQL in Spring Boot involves configuring the data source, defining JPA entities, and linking them to GraphQL queries and mutations.
- Configure Database: Set up the database connection in application.properties with the relevant URL, username, password, and dialect.
- Define JPA Entities: Create entity classes to represent database tables, using annotations like @Entity and @Id.
- Create Repositories: Use Spring Data JPA to create repositories for CRUD operations. These repositories provide ready-made methods like save(), findById(), and findAll().
- Implement Resolvers: In GraphQL, resolvers interact with the repositories to fetch and manipulate data based on client queries and mutations.
- Pagination and Sorting: Implement pagination and sorting by utilizing Spring Data’s Pageable and Sort objects to handle large datasets efficiently.
By following these steps, you can easily integrate a database with your Spring Boot GraphQL application, ensuring data persistence and efficient querying.
Testing Your GraphQL API
Testing is a crucial part of developing any API. For a GraphQL API in Spring Boot, it’s essential to ensure both unit and integration tests are implemented to validate the behavior and correctness of queries, mutations, and database interactions.
1. Unit Testing with @GraphQlTest
Spring Boot provides the @GraphQlTest annotation to test GraphQL queries and mutations in isolation. It focuses on testing the GraphQL resolvers and schema without needing to start the entire Spring context.
- Test GraphQL Queries: Use @GraphQlTest to test specific queries and mutations by providing mock data or using an in-memory database.
- Mock Dependencies: Use @MockBean to mock services or repositories used within your resolvers.
Example:
@GraphQlTest
public class BookQueryResolverTest {@Autowired
private GraphQlTester graphQlTester;@MockBean
private BookRepository bookRepository;@Test
void testGetBooks() {
List books = List.of(new Book(1L, “Title”, “Author”));
when(bookRepository.findAll()).thenReturn(books);graphQlTester.query(“{ books { id title author } }”)
.execute()
.path(“books[0].title”).entity(String.class).isEqualTo(“Title”);
}
}
2. Integration Testing with HttpGraphQlTester
For end-to-end testing, use HttpGraphQlTester to send actual GraphQL queries over HTTP, mimicking real-world scenarios. This test ensures that the entire stack (from controller to database) works correctly.
- Set Up an Embedded Database: Use an embedded database like H2 for testing, ensuring that real data interactions are tested.
- Test Full Requests: Send full GraphQL queries and mutations to validate that the server responds correctly and integrates with the database.
Example:
@SpringBootTest
@AutoConfigureMockMvc
public class BookIntegrationTest {@Autowired
private MockMvc mockMvc;@Test
void testCreateBook() throws Exception {
String query = “{ “query”: “mutation { createBook(title: “New Book”, author: “Author”) { title author } }” }”;mockMvc.perform(post(“/graphql”)
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
.content(query))
.andExpect(status().isOk())
.andExpect(jsonPath(“$.data.createBook.title”).value(“New Book”));
}
}
3. Mocking Data
During unit testing, it’s common to mock database calls or external services. Use @MockBean to mock the BookRepository or any other service, ensuring that your resolver methods are tested in isolation without actual database interactions.
4. Best Practices for GraphQL Testing
- Test Resolvers Independently: Use unit tests to verify each resolver method and ensure it’s functioning as expected.
- Test Query and Mutation Combinations: Ensure that multiple queries or mutations within a single request work as intended.
- Mock Database Responses: Mock database queries where possible to test the logic without needing an actual database.
Effective testing ensures your GraphQL API behaves as expected. By leveraging @GraphQlTest for unit testing and HttpGraphQlTester for integration testing, you can verify both the individual resolver logic and the complete request-response cycle.
Securing Your GraphQL API
Securing your GraphQL API in Spring Boot involves implementing authentication, authorization, input validation, and other protective measures to ensure data safety.
- Authentication: Authenticate users using methods like Basic Authentication or JWT (JSON Web Token) to verify the user’s identity before accessing the API.
- Authorization: Control access to queries and mutations with role-based access control (RBAC). Use annotations like @PreAuthorize or @Secured to restrict access based on user roles (e.g., ADMIN or USER).
- Input Validation: Ensure that only valid data is processed by using Spring’s validation annotations (e.g., @NotNull, @Size) on resolver method parameters to prevent malicious inputs.
- Rate Limiting: Protect your API from abuse by limiting the number of requests per user within a given time period using libraries like Bucket4j or Resilience4j.
- Securing the GraphQL Endpoint: Configure Spring Security to secure the /graphql endpoint, allowing access only to authenticated users. This can be done via Spring Boot’s default security configurations or custom settings.
- CORS (Cross-Origin Resource Sharing): Restrict cross-origin requests by defining trusted domains for accessing the GraphQL API, reducing CSRF risks.
- Logging and Monitoring: Track security events like unauthorized access using logging and integrate with tools like Prometheus or ELK stack for monitoring.
Optimizing Performance
To ensure your GraphQL API performs efficiently, it’s important to implement strategies that improve query execution, reduce server load, and optimize data retrieval. Here are some key techniques to optimize the performance of your Spring Boot-based GraphQL API.
1. Batching Queries
Batching allows multiple queries to be sent together in a single request, reducing the number of database calls. Tools like DataLoader can be used to batch database queries, especially when resolving multiple fields that require the same data.
2. Caching
Implement caching to store frequently requested data and reduce repetitive database queries. Use tools like Spring Cache or Redis to cache query results or specific data fields. Cache query responses for certain time intervals to reduce latency.
3. Pagination
For queries returning large datasets, implement pagination to limit the number of records returned in each query. This reduces the load on both the server and the database by returning only a subset of the data.
Example:
type Query {
books(page: Int, size: Int): [Book]
}4. Query Complexity Analysis
Limit the complexity of queries by analyzing incoming queries for depth and size. Complex or deeply nested queries can be throttled or rejected to prevent excessive resource usage.
5. Avoiding N+1 Query Problem
The N+1 query problem occurs when multiple database queries are executed for related data. Use techniques like JOINs in SQL or batch fetching with Hibernate to avoid unnecessary queries.
6. Optimizing Resolvers
Resolvers should be efficient and avoid heavy logic or complex database operations. Offload heavy processing tasks, such as image or file processing, to background jobs instead of handling them in the resolver.
7. Error Handling and Graceful Degradation
Ensure that errors are handled efficiently, preventing the entire API from failing under heavy load. Implement fallback mechanisms where appropriate, and allow the system to degrade gracefully.
8. Monitoring and Profiling
Use performance monitoring tools like Prometheus or Spring Boot Actuator to identify bottlenecks and track the performance of GraphQL queries. Profiling tools can help optimize database interactions and query execution time.
Deploying Your Application
Once your GraphQL API is developed and optimized, the next step is deployment. Deploying a Spring Boot application with GraphQL can be done easily to various platforms like cloud services or on-premise servers. Here’s a concise guide on deploying your Spring Boot GraphQL application.
1. Packaging the Application
First, package your application into a deployable format:
JAR File: Use Maven or Gradle to build a standalone executable JAR file that contains all dependencies. You can build it with the command:
- For Maven: mvn clean package
- For Gradle: ./gradlew build
This creates a target or build/libs directory with the packaged JAR file.
2. Choosing a Deployment Platform
You can deploy your application to various platforms:
- Cloud Platforms: Popular platforms like AWS, Google Cloud, and Microsoft Azure offer simple ways to deploy Java applications.
- Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS): Platforms like Heroku allow quick deployment with minimal configuration. Simply push your app to a Git repository, and Heroku will handle the rest.
- On-Premise Servers: You can deploy the JAR file directly to an on-premise server using a tool like Docker for containerization or by running the JAR as a background process.
3. Configuring Environment Variables
Before deploying, configure the application’s environment-specific properties (like database URLs or secret keys). You can set these in the application.properties or application.yml file, or inject them as environment variables:
Example:
spring.datasource.url=${DB_URL}
spring.datasource.username=${DB_USER}
spring.datasource.password=${DB_PASSWORD}4. Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)
Set up a CI/CD pipeline using tools like Jenkins, GitLab CI, or GitHub Actions. These tools automate the build, testing, and deployment process to ensure fast, consistent releases.
Steps:
- Push your code to a Git repository.
- The CI tool runs tests, builds the JAR file, and deploys it to the selected environment.
5. Monitoring and Logging
Once deployed, use tools like Spring Boot Actuator, Prometheus, or Grafana to monitor the performance and health of your application. Set up logging using ELK Stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana) or Logback to track issues and errors in production.
6. Scaling
For larger applications, you may need to scale your GraphQL API horizontally. This can be achieved by:
- Load Balancers: Distribute traffic between multiple instances of your application.
- Auto-Scaling: Automatically scale your application based on traffic demands, available on cloud platforms like AWS or Google Cloud.
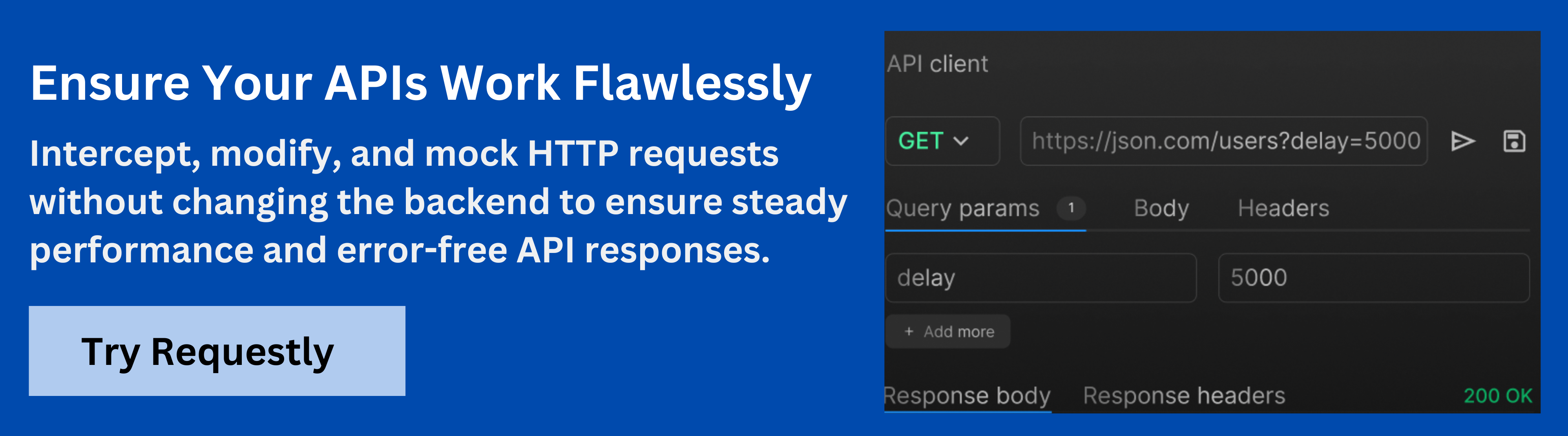
Enhance Your API Development and Testing with Requestly
To further streamline your GraphQL API development and testing process, Requestly is an excellent tool for mocking API responses, intercepting HTTP requests, and simulating different scenarios.
Whether you’re testing your GraphQL queries or ensuring that your API handles various edge cases, Requestly helps improve the efficiency of your workflow by allowing you to easily manage API interactions in real-time.
Conclusion
Integrating GraphQL with Spring Boot allows for the creation of flexible, efficient, and scalable APIs. From defining the schema to implementing CRUD operations, optimizing performance, and securing the API, each step plays a crucial role in building a robust application. With easy deployment options and the ability to scale as needed, Spring Boot and GraphQL together provide a powerful foundation for modern web and mobile applications.
By following the strategies outlined in this article, developers can build, test, and deploy high-performance GraphQL APIs, ensuring both seamless data interactions and a great user experience.