Ever had a Selenium test suddenly freeze because an unexpected alert or popup appeared?
I’ve seen entire suites come to a halt from a single popup, forcing reruns and time-consuming log checks just to understand what broke.
These interruptions don’t just slow things down; they lead to flaky builds, delayed feedback, and frustration across the team.
The real challenge is that not all alerts and popups behave the same, and treating them as identical often creates more issues than it solves.
Once you understand the different types and how Selenium interacts with each, handling them becomes far more predictable.
Overview
Alerts and popups are messages or dialog boxes that interrupt the normal workflow of a webpage. In Selenium, alerts are browser-generated (JavaScript alerts), while popups can be browser dialogs or HTML-based modals built into the webpage.
How to Handle Alerts in Selenium
- Use driver.switchTo().alert() to access the alert.
- accept() confirms the alert; dismiss() cancels it.
- getText() reads the alert message.
- sendKeys() enters text into prompt alerts.
- Works only for JavaScript alerts, not HTML popups.
How to Handle Popups in
- HTML popups / modal dialogs: Treat them as regular DOM elements; locate them using XPath, CSS, or IDs and interact normally.
- Child windows / browser popups: Capture window handles using getWindowHandles(), switch using switchTo().window(handle), and perform actions.
- Close popups with driver.close() or switch back to the main window afterward.
This article explores how to handle alerts and popups in Selenium, covering key configurations, best practices, and troubleshooting tips.
What are Alerts in Selenium?
Alerts in Selenium are browser-generated dialog boxes that appear on a webpage to convey information or request user action.
They interrupt the normal flow of the page and must be handled before you can continue interacting with other elements.
These alerts are triggered using JavaScript and appear as native browser popups—not as part of the HTML DOM.
Since Selenium cannot interact with the page until an alert is addressed, handling them correctly is essential for preventing test failures and stuck executions.
Software testing expert Crissy Joshua emphasize that context switching—whether it’s dealing with popups, alerts, or multiple tabs—is a foundational skill for building stable UI automation.
Understanding how to manage different browser contexts ensures smoother test execution and prevents issues from arising in complex web applications.
Common reasons alerts appear include:
- Confirming an action (e.g., delete, submit, navigate away)
- Showing warnings or errors
- Requesting user input
- Displaying simple information messages
Since alerts are outside the DOM, Selenium uses the switchTo().alert() interface to identify and interact with them.
Alerts behave differently across browsers and must be handled before a test can continue, it’s important to validate your alert interactions in real user environments.
Platforms like BrowserStack Automate makes this easier by letting you run Selenium tests on 3,500+ real browser and device combinations, ensuring your alert-handling logic works reliably everywhere.
Types of Alerts in Selenium
There are three types of Alert in Selenium, described as follows:
- Simple Alert
- Prompt Alert
- Confirmation Alert
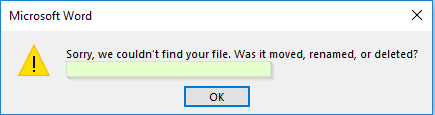
1. Simple Alert
This alert is used to notify a simple warning message with an ‘OK’ button, as shown in the below snapshot.
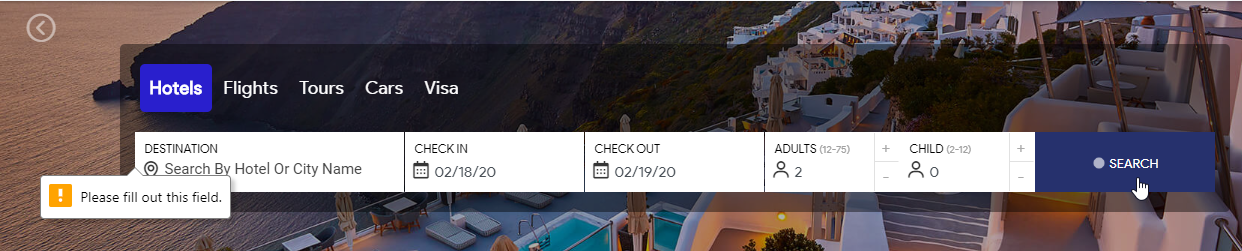
2. Prompt Alert
This alert will ask the user to input the required information to complete the task. In the below snapshot, you can see that without entering the destination for Hotel, you are not allowed to hit the search button.
Now, this input can be entered with the help of sendKeys(“input_text”) method in Selenium Webdriver.
3. Confirmation Alert
This alert is basically used for the confirmation of some tasks. For Example: Do you wish to continue a particular task? Yes or No? The snapshot below depicts the same.
Now that you know what are alerts in selenium and its types, let’s move further and understand how to handle alerts in selenium.
How to Handle Alerts in Selenium?
Handling alerts manually is a tedious task. To reduce human intervention and ease this task, Selenium provides a wide range of functionalities and methods to handle alerts.
The following methods are useful to handle alerts in Selenium:
1. Void dismiss(): This method is used when the ‘Cancel’ button is clicked in the alert box.
driver.switchTo().alert().dismiss();
2. Void accept(): This method is used to click on the ‘OK’ button of the alert.
driver.switchTo().alert().accept();
3. String getText(): This method is used to capture the alert message.
driver.switchTo().alert().getText();
4. Void sendKeys(String stringToSend): This method is used to send data to the alert box.
driver.switchTo().alert().sendKeys("Text");Tip of the day: 5 Selenium tricks to make your life easier
Now let’s understand how exactly alerts in selenium work with the help of an example.
Real-time Example of Alert Handling
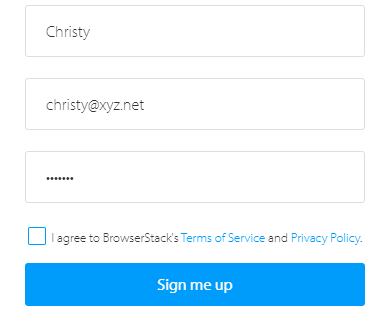
Let’s take the example of the BrowserStack website. Using the Browserstack sign up page for alert handling. Initially, enter the requested details as shown in the below snapshot.
Now, without checking the box of Terms of Service, click on the “Sign me up” button. As it is necessary to accept Terms of Service, it will throw an Alert to check the box of Privacy Policy. The snapshot below depicts the same.
The task here is to handle this alert. Let’s write a Selenium test script to handle alerts.
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.NoAlertPresentException;
import org.openqa.selenium.Alert;
public class AlertHandlingDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws NoAlertPresentException,InterruptedException {
System.setProperty("webdriver.chrome.driver","Path_of_Chrome_Driver"); //mention dummy path or variable that stores chrome driver path
WebDriver driver = new ChromeDriver(); driver.get("https://www.browserstack.com/users/sign_up");
driver.findElement(By.id("user_full_name")).sendKeys("username"); driver.findElement(By.id("input-lg text user_email_ajax")).sendKeys("username.xyz.net");
driver.findElement(By.id("user_password")).sendKeys("Your_Password");
driver.findElement(By.id("user_submit")).click();
Thread.sleep(5000);
Alert alert = driver.switchTo().alert(); // switch to alert
String alertMessage= driver.switchTo().alert().getText(); // capture alert message
System.out.println(alertMessage); // Print Alert Message
Thread.sleep(5000);
alert.accept();
}
}When you execute the above code, it navigates through the Sign up page, inputs the necessary details, hits the Sign me up button and throws the alert.
Next, the driver will switch to alert, try to capture the alert message, and then display the message.
Note: To cross-verify or handle alerts manually, one can paste the below command.
driver.findElement(By.xpath("//a[@class='bs-alert-close']")).click();That’s all about how to handle alerts in selenium. With this, let’s move further with this article and understand the fundamentals of pop-ups in selenium.
In case you are facing any issues, read about how to handle common exceptions in Selenium Webdriver.
Pro Tip: Want to dive deeper into Selenium implementation on BrowserStack with free interactive courses and lab exercises? Visit Test University
What are Popups in Selenium?
Popup is a window that displays or pops up on the screen due to some activity. If one wishes to know about the various scenarios of pop-ups and how to handle them, read the documentation page.
How to handle popups in Selenium
In Selenium Webdriver, there are multiple methods to handle popups:
1. Driver.getWindowHandles();
In order to handle the opened windows by Selenium Webdriver, you can use Driver.getWindowHandles() to switch between the windows.
2. Driver.getWindowHandle();
When the webpage is loaded, you can handle the main window by using driver.getWindowHandle(). It will handle the current window that uniquely identifies within the driver instance.
Also Read: How to handle multiple windows in Selenium
Now let’s move further and understand how to handle a web dialog box or a pop up window using Selenium Webdriver with the help of an example.
Handling Web Dialog Box/Popup Window using Selenium
In Selenium, a robot class is used to handle the keyboard and mouse functions. It is used to close the pop-up window. You can get the window handle of the pop-up window using the WindowHandle() function.
I have created my own webpage to demonstrate popup handling in Selenium. You can copy the same code and paste in notepad and save it as .html file to proceed with testing.
Before running the code, one should do a quick check on 6 things to avoid while running selenium scrips. Check it out.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<style>
h1 {
color: blue;
margin-left: 60px;
}
button {
color: white;
margin-left: 60px;
background-color: black;
border: none;
padding: 15px 32px;
text-align: center;
text-decoration: none;
display: inline-block;
font-size: 16px;
}
button:hover {
background-color: grey;
color: black;
}
.column {
float: left;
width: 33.33%;
}
/* Clear floats after the columns */
.row:after {
content: "";
display: table;
clear: both;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class=column>
<div align="center"><alt="BrowserStack" width="400" height="80"></div>
<h1><center>Alerts and popups in Selenium</center></h1>
<div align="center"><button id="PopUp" onclick="return popup(this, 'notes')">PopUp</button></div>
<div align="center"><img src="sel.png" alt="BrowserStack" width="400" height="400"></div>
</div>
<script type="text/javascript">
function popup()
{
myWindow = window.open("", "myWindow", "width=400,height=200");
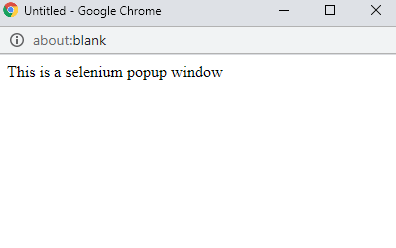
myWindow.document.write("<p>This is a selenium popup window</p>");
}
</script>
</body>
</html>Now when you execute this and click on Pop Up, a window will be displayed as shown below.
Now let’s write a code to handle this dialog box.
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.Set;
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.firefox.FirefoxDriver;
public class Popup_Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
WebDriver driver=new FirefoxDriver(); driver.get("Webpage link");
driver.manage().window().maximize();
Thread.sleep();
driver.findElement(By.id("PopUp")).click(); // Clicking on the popup button
Robot robot = new Robot();
robot.mouseMove(400.5); // Navigating through mouse hover. Note that the coordinates might differ, kindly check the coordinates of x and y axis and update it accordingly.
robot.mousePress(InputEvent.BUTTON1_DOWN_MASK);
Thread.sleep(2000);
robot.mouseRelease(InputEvent.BUTTON1_DOWN_MASK);
Thread.sleep(2000);
driver.quit();
}
}When you execute this, dialog or the pop-up box will be handled. This is how you need to handle popups in Selenium.
Note: Alerts and popup functions are widely used in online application forms and banking websites.
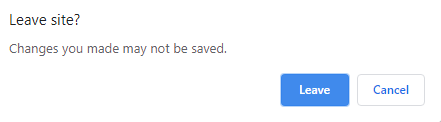
With these popup-handling techniques in place, the next step is making sure they behave consistently across different browsers and environments.
Since dialog boxes can appear and respond differently depending on the setup, it’s important to validate them under real conditions—something BrowserStack Automate helps you do effortlessly.
Test Alerts and Popups on Real Browsers with BrowserStack Automate
Handling alerts and popups reliably in Selenium depends heavily on how they appear and behave across different browsers and devices.
A JavaScript alert that opens instantly in Chrome might respond slower in Safari. HTML-based modals may render differently on desktop vs. mobile. Browser-specific quirks can also affect switching between windows or interacting with dialog boxes.
To ensure your alert and popup handling works consistently, it’s important to test in real user conditions—not just local setups.
BrowserStack Automate helps by providing:
- 3,500+ real browser and device combinations to validate alerts and popups under true user conditions.
- Accurate alert behavior since tests run on real browsers.
- Reliable validation of window switching, modal interactions, and JavaScript alert handling.
- Debugging support with video recordings, screenshots, console logs, and network logs to trace failures quickly.
- Parallel execution, allowing teams to test alert workflows across multiple environments at once for faster feedback.
By running your Selenium tests on real browsers and devices, BrowserStack Automate ensures your alert and popup handling remains stable, predictable, and aligned with how end users actually experience your application.
Conclusion
Handling alerts and popups in Selenium becomes much simpler once you understand the differences between JavaScript alerts, browser dialogs, and HTML-based popups. Each type requires a specific handling method, and choosing the right approach prevents flaky tests, hangs, and unexpected failures.
By combining Selenium’s alert-handling APIs with proper window switching and DOM-based interactions, you can create stable and predictable automation flows.
To ensure these interactions behave consistently across different browsers and devices, running your tests on real environments—such as those offered by BrowserStack Automate—provides the reliability and confidence needed for high-quality automation.