Healthcare domain testing ensures that medical applications are compliant, secure, and reliable. It focuses on validating data privacy, system accuracy, and complex clinical workflows.
Overview
What is Healthcare Domain Testing?
Healthcare domain testing is the process of validating healthcare applications and systems against industry standards, regulations, and clinical requirements. It checks data security, workflow accuracy, and interoperability to ensure safe and compliant use in real-world healthcare environments.
Why is Healthcare Domain Testing Important?
- Protects patient data by enforcing strict privacy and security measures.
- Ensures compliance with healthcare regulations such as HIPAA, GDPR, and regional laws.
- Validates clinical workflows so doctors, nurses, and staff can perform tasks without disruptions.
- Improves reliability by testing performance, availability, and error handling under load.
- Builds trust with patients and providers by ensuring accurate and consistent system behavior.
This article explains healthcare domain testing in more detail, including the types, challenges, and best practices.
What is Healthcare Domain Testing?
Healthcare domain testing refers to the systematic evaluation of healthcare software applications to verify that they comply with regulatory standards and fulfill user requirements.
Different aspects, such as functionality, data management, security, and administrative processes, such as billing and patient record management, are validated via healthcare domain testing.
Read More: Top 15 Test Data Management Tools
The primary goal of healthcare domain testing is to validate that software solutions are reliable, secure, and capable of enhancing patient care while aligning with legal and safety requirements. This involves not only technical testing but also a deep analysis of healthcare workflows and regulations.
Healthcare Business Entities and Process
There are multiple entities involved in finalizing the process of the healthcare mechanism, which is explained below.
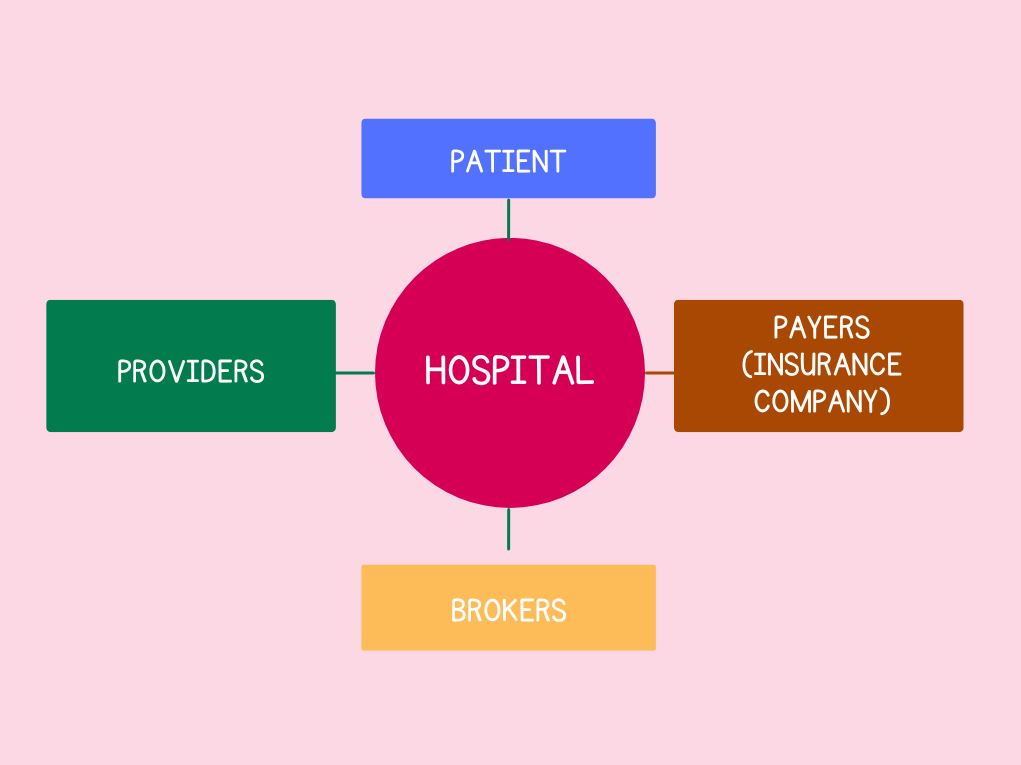
Healthcare Domain Entities
The healthcare system comprises multiple entities that engage with one another within a complex network. Here are some of the key entities:
- Patients: They receive healthcare services.
- Providers: They are the healthcare organizations or professionals who provide healthcare related services.
- Payers: Insurance companies or government programs that finance healthcare services.
- Brokers: Intermediaries facilitating insurance coverage for patients.
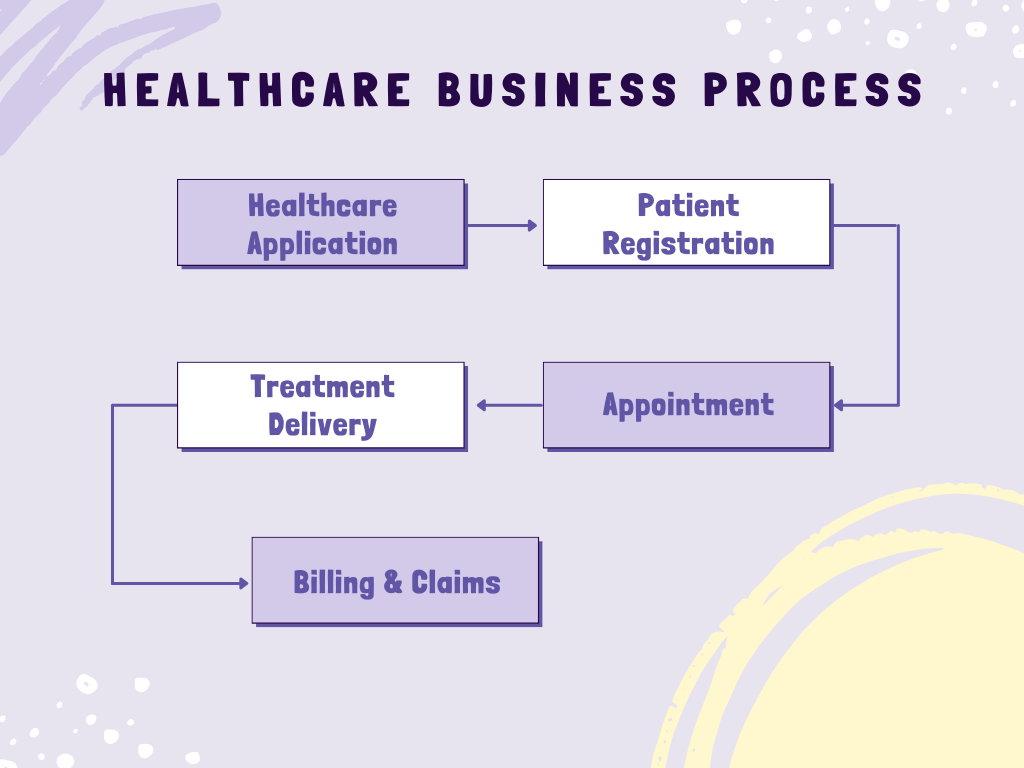
Healthcare Business Process
Healthcare processes are often sophisticated and contain multiple steps to facilitate quality services. Here’s a look into the process:
- Patient Registration: Patient details are gathered and saved for record-keeping.
- Appointment Scheduling: Managing provider availability and scheduling patient appointments.
- Treatment Delivery: Medical services are provided according to the patients’ requirements.
- Billings and Claims Processing: Handling payments and insurance claims.
Why is Healthcare Testing important?
Healthcare testing is important for several reasons such as:
- Patient Safety: Ensures that the software apps function responsibly and do not compromise with patient health.
- Regulatory Compliance: Follows the laws like HIPAA, ensuring data protection.
- Data Accuracy: Validates the accuracy and relevance of patient records.
- Operational Efficiency: Improves the usability of applications for healthcare professionals.
- Risk Mitigation: Decreases the probability of software failures that could lead to expensive errors.
Read More: How to Perform Software Risk Assessment
Types of Testing for Healthcare Applications
Different kinds of testing are important to fulfill the unique but critical demands of the healthcare industry. This often includes sensitive patient details and sophisticated workflows.
Here are the main types of testing for healthcare applications:
1. Functionality Testing
This type of testing sees to it that every feature of the healthcare application works according to expectations. It evaluates end-to-end processes and makes sure that user engagement yields the intended outputs.
2. Data Accuracy Testing
This type of testing validates the accuracy and reliability of information. Even minor
discrepancies can cause significant consequences, so validating data integrity is important for patient safety and operational efficiency.
3. Security Testing
Security testing is all about protecting sensitive patient information from unauthorized access and breaches. For example, assessing encryption methods, vulnerability assessments, etc.
4. Compliance Testing
It verifies that the software meets legal and regulatory standards requirements, helping organizations to establish a reputation in the industry.
Read More: 508 Compliance Testing Tools
5. Device Integration Testing
The objective of device integration testing is to allow seamless data transfer between devices and applications by making sure that the integrations with medical devices work correctly.
Read More: What is System Integration Testing
6. Performance Testing
Performance testing evaluates how well a healthcare application performs under various conditions, including normal and peak loads. It ensures that the application remains stable and responsive during high traffic or unexpected situations.
Health Care Domain Testing: Workflow [with Examples of Test Cases]
The workflow follows various testing phases that validate the functionality and performance of systems used by healthcare providers, insurers, and patients.
This is required to maintain the integrity of sensitive patient information and facilitate a seamless flow of healthcare services.
1. Testing of Member System
Test Scenario and Test Case Examples: Member (Patient) System
| Test Scenario | Test Cases |
|---|---|
| 1. Member system | Validate the member registration process works smoothly. |
| 2. Positive flow system testing | Ensure members can view their health records without errors. |
| 3. Negative flow system testing | Check how the system responds to invalid member login attempts. |
2. Testing of Provider System
Test Scenario and Test Case Examples: Provider System
| Test Scenario | Test Cases |
|---|---|
| 1. Access to the provider system | Verify that authorized providers can log in successfully. |
| 2. Positive flow system testing | Ensure that a provider can access patient records without errors. |
| 3. Negative flow system testing | Attempt to access the system with invalid credentials and check for denial. |
| 4. System integration testing | Validate that the provider system integrates correctly with billing systems. |
| 5. Positive flow providers portal | Confirm that providers can submit treatment plans without issues. |
| 6. Negative flow providers portal | Check how the system handles incorrect data submissions from providers. |
3. Testing of Broker System
Test Scenario and Test Case Examples: Broker System
| Test Scenario | Test Cases |
|---|---|
| 1. Broker system | Ensure brokers can access their dashboards without issues. |
| 2. Positive flow system testing | Verify that brokers can retrieve insurance plans accurately. |
| 3. Negative flow system testing | Attempt to access restricted areas and confirm access is denied. |
4. Testing of Claims System
Test Scenario and Test Case Examples: Claims System
| Test Scenario | Test Cases |
|---|---|
| 1. Claims system | Confirm that claims can be submitted correctly through the application. |
| 2. Positive flow system testing | Check claim processing reflects accurate payment information. |
| 3. Negative flow system testing | Attempt to submit a claim with missing information and check for rejection. |
5. Testing of the Finance System
Test Scenario and Test Case Examples: Finance System
| Test Scenario | Test Cases |
|---|---|
| 1. Finance system | Ensure financial transactions are recorded accurately in the ledger. |
| 2. Positive flow system testing | Checks that correct account details are used during payment processing. |
| 3. Negative flow system testing | Check how the system handles incorrect payment information entries. |
6. Testing for Regulatory Compliance
Test Scenario and Test Case Examples: Regulatory Compliance
| Test Scenario | Test Cases |
|---|---|
| 1. User’s Authentication | Ensure that only authorized users are logging in to the application. |
| 2. Information disclosure | Ensure access to patient information is restricted based on user roles. |
| 3. Data transfer | Confirm that all data transfers are encrypted to ensure patient privacy protection. |
Why use BrowserStack for Healthcare Domain Testing?
Healthcare apps demand rigorous testing because they manage sensitive patient data and must meet strict compliance standards. Teams need a secure and dedicated environment to validate features like telehealth consultations, patient records, online payments, and e-prescriptions without risking data exposure.
BrowserStack’s Private Device Cloud provides this environment by giving QA teams secure access to dedicated real devices for end-to-end testing. It allows healthcare organizations to replicate real-world usage while keeping sensitive data protected.
Key Benefits for Healthcare App Testing with BrowserStack Private Device Cloud
- App Persistence Testing: Confirm that login states, user preferences, and session continuity remain intact across app launches.
- SIM-Based Testing: Validate two-factor authentication, SMS notifications, and region-specific login flows on real SIM networks.
- Offline and Network Simulation: Assess how healthcare apps perform during low bandwidth, unstable connectivity, or complete offline use.
- Custom Device Configurations: Use catalog, non-catalog, or custom devices to match target user environments and hardware.
- Automation Support: Automate regression and functional test cases such as login, scheduling, and payment flows with Appium or Espresso.
- Logs and Performance Metrics: Gather detailed reports on crashes, latency, and app responsiveness to optimize performance.
- Flexible Cleanup Controls: Retain or reset test data between sessions depending on the QA workflow.
Challenges of Healthcare Domain Testing and Its Solutions
Healthcare software testing comes with unique demands. Systems must remain safe, compliant, and reliable while handling sensitive data, complex workflows, and critical integrations. Below are the major hurdles and how teams can address them.
1. Regulatory compliance and audits
Healthcare applications must meet strict requirements such as HIPAA, GDPR, and regional laws. Even a minor gap in documentation can lead to failed audits or penalties.
To handle this, you can maintain a compliance matrix that maps regulations to test cases. Keep requirements traceability, signed test plans, and execution records together, and automate evidence capture in your CI pipeline to make audits smoother.
2. PHI privacy and safe test data
Real patient data cannot be used in testing, and simple masking often breaks workflows. To avoid this, you can generate synthetic test data that mirrors real-world distributions. Apply irreversible de-identification, preserve referential integrity, and run automated checks to ensure your anonymized data is still valid for end-to-end scenarios.
3. Interoperability across standards
Healthcare systems rely on standards like HL7 v2, FHIR, DICOM, and e-prescriptions to share information. Even small variations in format or schema can disrupt workflows.
To prevent this, you can use conformance profiles and schema checks to keep data structures consistent and create golden message suites that serve as repeatable test cases to catch issues early. Validating medical codes such as LOINC, SNOMED CT, and RxNorm also ensures the meaning of data is preserved across systems.
4. Complex clinical workflows
Patient journeys often span intake, triage, orders, results, billing, and follow-ups. A small change in one step can affect the entire process. To cover this, you can design end-to-end scenarios that mirror real clinical workflows. Include role-based testing for nurses, physicians, lab technicians, and administrators to make sure handoffs and permissions work as expected.
5. Legacy systems and integrations
Hospitals often depend on older EHRs, PACS, RIS, and billing systems that may be unstable or unavailable in test environments.
To deal with this, you can use service virtualization to simulate external systems and apply contract testing to verify integrations. Versioned mocks and standardized test data profiles help you keep testing consistent even when partner systems change.
6. Safety and accuracy risks
Mistakes in dosage calculations or decision support can directly affect patient safety. To minimize this risk, you can apply risk-based testing that gives deeper coverage to safety-critical features. Use trusted reference datasets for dosage adjustments, pediatrics, and clinical alerts, and add negative test cases to confirm the system fails safely when errors occur.
7. Availability and performance under load
Systems face heavy spikes during clinic hours, telehealth sessions, or mass results releases. Without preparation, this can cause downtime or delays in care.
To prevent bottlenecks, you can run capacity tests with realistic concurrency, device mixes, and network conditions. Test failover, read-only modes, and queue handling so the system remains reliable even under stress.
Best Practices for Healthcare Domain Testing
Healthcare testing requires accuracy, compliance, and reliability at every step. These practices help you stay consistent, audit-ready, and aligned with clinical needs:
- Start with a risk register: Identify safety, privacy, and financial risks so you know where to apply deeper coverage. A focused register helps prioritize areas where errors could cause serious harm.
- Maintain requirements traceability: Map every regulation and requirement to a test case and result. This keeps audits simple and ensures no critical rule is missed.
Read More: Importance of Traceability Matrix in Testing
- Use realistic synthetic data: Replace real PHI with synthetic records that reflect real-world distributions and edge cases. This preserves workflow accuracy without exposing sensitive data.
- Include role-aware end-to-end tests: Simulate workflows for nurses, doctors, lab staff, admins, and patients. Role-based testing confirms permissions, handoffs, and clinical journeys work smoothly.
- Shift left on security and privacy: Add code scans, dependency checks, and consent-flow validation early in your pipeline. Finding issues early reduces risk and fixes costs.
- Continuously validate performance: Run regular load and capacity tests that mirror real clinic usage. This ensures the system remains stable during peak demand.
Conclusion
Healthcare domain testing is essential for building applications that meet compliance standards, protect patient data, and support complex clinical workflows. covers compliance, data privacy, interoperability, and workflow accuracy, giving you a clear roadmap to build dependable healthcare applications.
With BrowserStack’s Private Device Cloud, you can test healthcare apps securely on real, dedicated devices, validate interoperability across platforms, and ensure performance under real-world conditions. This helps you meet regulatory requirements and deliver applications that healthcare providers can trust.
Try BrowserStack Private Device Cloud
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the six domains of healthcare?
The six domains of healthcare include
- Clinical health services
- Health information systems
- Public health services
- Health financing,
- Governance
- Health workforce development
2. What is domain-specific testing?
Domain-specific testing refers to the evaluation process focused on meeting the unique requirements and standards of a particular industry or field, such as healthcare, finance, or education.