Websites and applications must be usable by everyone, including individuals with visual, auditory, cognitive, or motor disabilities. That’s where accessibility testing comes in.
To make this process efficient, QA teams are increasingly turning to automation. While Selenium WebDriver is best known for functional testing, it can also play a valuable role in identifying accessibility issues early in the development cycle.
This article will cover how to get started with accessibility automation testing using Selenium, from learning the principles of accessibility testing to creating and running test scripts.
What is Website Accessibility?
Accessibility means ensuring that someone with disabilities can use a site the same way as anyone else. It involves presenting web pages in a way that all users can understand, operate, and perceive.
Think of a user who cannot use a mouse or someone who can only depend on high-contrast themes because they have some vision challenges. Accessibility ensures that these users are not excluded from using the site. Without accessibility, users would have difficulties reading content, navigating menus, or completing forms. That will lead to a bad user experience and, in some case,s can even cause legal trouble.
Understanding Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG)
The Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) are internationally recognized as the standard for accessibility. It was created by the W3, and the guidelines explain how to make digital content more accessible for people with disabilities.
WCAG has four principles, which can be remembered by the acronym POUR:
- Perceivable: Users should be able to see or hear the content.
- Operable: Users must be able to navigate and interact with the site.
- Understandable: Content and interfaces should be readable or understandable.
- Robust: Users should be able to access the website on different devices, platforms, and assistive technologies.
WCAG has three levels of compliance:
- Level A (minimum),
- Level AA (recommended),
- Level AAA (highest).
Most companies aim for Level AA as it addresses a large number of accessibility issues.
Read More: Top 15 Accessibility Automation Tools
Ways to perform Website Accessibility Testing
Accessibility testing can be completely manual, fully automated, or a combination of both.
Manual Accessibility Testing
Manual testing is the process where human testers manually use assistive technologies (e.g., screen readers, NVDA or JAWS), keyboard navigation, and browser developer tools to identify accessibility barriers.
Manual tests are great for:
- Verifying screen reader output
- Checking keyboard-only navigation
- Validating logical focus order
However, manual testing is time-consuming and may overlook some issues that are repetitive or deeper.
Automated Accessibility Testing
Automated tools are able to scan pages for common issues like a missing alt text, poor color contrast, and invalid ARIA roles.
Automated Accessibility Testing allows for quicker testing, especially across large websites and ensures accessibility is tracked during all development cycles. But automated testing should not be expected to replace manual testing entirely.
Read More: How to Automate Accessibility Testing
How to perform Accessibility Automation Testing with Selenium?
Selenium WebDriver is not designed for accessibility testing. However, when it is combined with another tool, it can assist in performing accessibility automation testing.
Given below is the process of how to set up accessibility automation testing with Selenium.
Installing and Configuring Selenium WebDriver
Install Eclipse and configure Selenium in the pom.xml file.
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.seleniumhq.selenium</groupId> <artifactId>selenium-java</artifactId> <version>4.31.0</version> </dependency> </dependencies>
Install the browser driver and set up the Selenium test.
System.setProperty("webdriver.chrome.driver", "*Path*");
WebDriver driver = new ChromeDriver();
driver.get("https://www.bstackdemo.com");Integrating BrowserStack With Selenium
Connect Selenium with BrowserStack Automate to run accessibility tests across real devices and browsers.
Follow the instructions below for the setup.
- Create a BrowserStack account and get the Username and Access key.
- Then create a new class and use the below sample code.
Code:
WebDriver driver;
@Test
public void accessTest() throws Exception {
String USERNAME = "USERNAME";
String ACCESS_KEY = "ACCESS_KEY";
String URL = "https://" + USERNAME + ":" + ACCESS_KEY + "@hub-cloud.browserstack.com/wd/hub";
System.out.println(URL);
URL browserstackURL = URI.create(URL).toURL();
MutableCapabilities capabilities = new MutableCapabilities();
capabilities.setCapability("browserName", "Chrome");
capabilities.setCapability("browserVersion", "latest");
MutableCapabilities bstackOptions = new MutableCapabilities();
bstackOptions.setCapability("os", "Windows");
bstackOptions.setCapability("osVersion", "10");
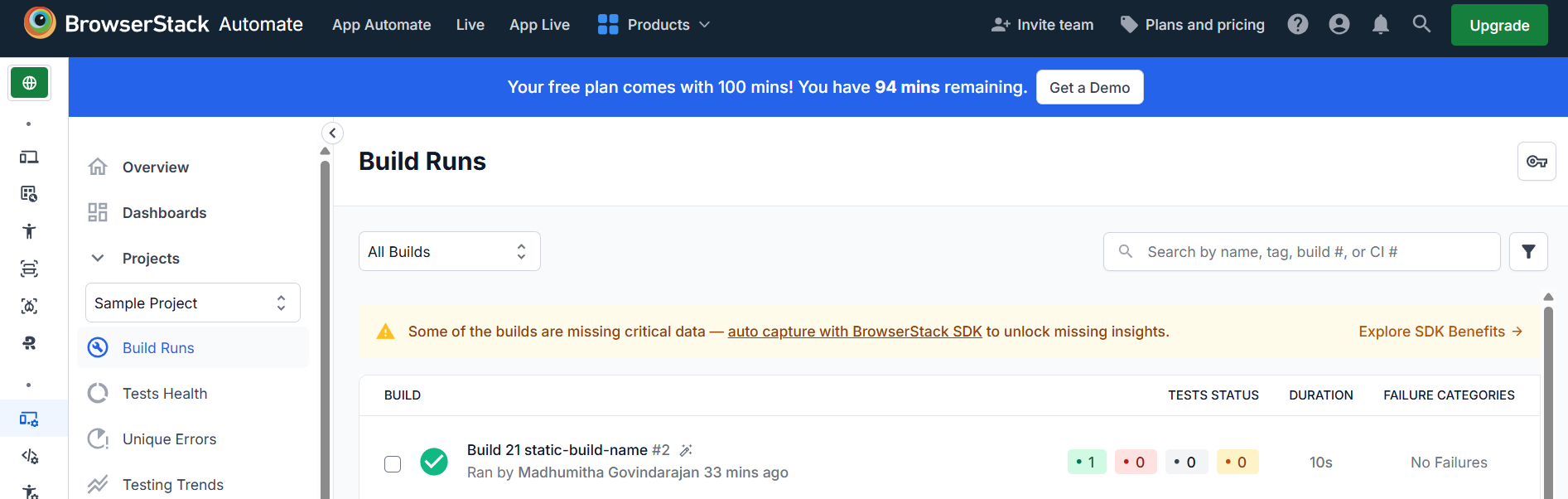
bstackOptions.setCapability("projectName", "Sample Project");
bstackOptions.setCapability("buildName", "Build 21");
bstackOptions.setCapability("sessionName", "TestNG Demo");
bstackOptions.setCapability("buildIdentifier", "static-build-name");
capabilities.setCapability("bstack:options", bstackOptions);
driver = new RemoteWebDriver(browserstackURL, capabilities);
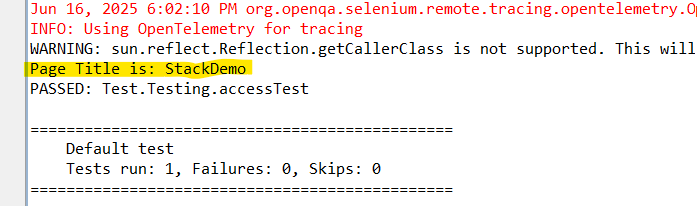
driver.get("https://www.bstackdemo.com");
System.out.println("Page Title is: " + driver.getTitle());
}
@AfterMethod
public void tearDown(ITestResult result) {
String status = result.isSuccess() ? "passed" : "failed";
String reason = result.isSuccess() ? "Test passed" : "Test failed: " + result.getThrowable();
((JavascriptExecutor) driver).executeScript("browserstack_executor: {\"action\": \"setSessionStatus\", "
+ "\"arguments\": {\"status\":\"" + status + "\", \"reason\": \"" + reason + "\"}}");
driver.quit();
}Output:
BrowserStack allows the user to test accessibility on real devices with varying screen sizes, OS versions, and browsers and guarantees a wider coverage.
Writing Test Scripts to Detect Accessibility Issues
To test for accessibility, integrate axe-core with Selenium tests.
- Download axe.min.js file from:
https://cdnjs.cloudflare.com/ajax/libs/axe-core/4.7.2/axe.min.js
- Save it at: src/test/resources/axe.min.js
Sample code to run an accessibility audit:
System.setProperty("webdriver.chrome.driver", System.getProperty("user.dir") + "\\src\\main\\resources\\Driver\\chromedriver.exe");
driver = new ChromeDriver();
driver.get("https://www.bstackdemo.com");
driver.manage().window().maximize();
String axeScript = new String(Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("src/test/resources/axe.min.js")));
((JavascriptExecutor) driver).executeScript(axeScript);
String axeTest = "var callback = arguments[arguments.length - 1];" + "if (typeof axe === 'undefined') {"
+ " callback({ error: 'axe not loaded' });" + "} else {"
+ " axe.run().then(results => callback(results))"
+ " .catch(err => callback({ error: err.message }));" + "}";
Object rawResult = ((JavascriptExecutor) driver).executeAsyncScript(axeTest);
Gson gson = new Gson();
JsonObject result = gson.toJsonTree(rawResult).getAsJsonObject();
if (result.has("error")) {
System.out.println("Axe Error: " + result.get("error").getAsString());
} else if (result.has("violations")) {
JsonArray violations = result.getAsJsonArray("violations");
System.out.println("Violations Found: " + violations.size());
for (int i = 0; i < violations.size(); i++) {
JsonObject violation = violations.get(i).getAsJsonObject();
System.out.println("🚫 " + violation.get("help").getAsString());
System.out.println(" → " + violation.get("description").getAsString());
}
} else {
System.out.println("⚠️ No violations or unexpected result:\n" + result.toString());
}
driver.quit();Sample Output:
Executing Tests Across Different Browsers and Devices
Using BrowserStack Automate, users can run the above scripts across:
- Desktop browsers (Chrome, Firefox, Edge, Safari)
- Mobile browsers (on iOS and Android)
- Different OS versions and screen sizes
This guarantees that an app or site properly addresses accessibility requirements in the real world.
Read More: Web Accessibility Best Practices
Best Practices in Accessibility Automation Testing With Selenium
Here are some useful tips to get the best value from accessibility tests:
- Use both manual and automated tests, as automation does not catch everything.
- Conduct accessibility checks early in the development lifecycle.
- Set up CI/CD pipelines with accessibility gates.
- Use updated and consistent WCAG rules.
- Provide developers with a clear report so fixes are easy.
- Do not limit to testing a single page and validate all templates, forms, and key user journeys.
Why choose BrowserStack for Accessibility Automation Testing with Selenium?
BrowserStack enhances Selenium testing by making it easier, faster, and more reliable. A few reasons to consider BrowserStack for accessibility testing are:
- Real Devices Testing: Since accessibility can vary on devices, tests can be run on 3500+ real browsers and devices.
- Parallel Testing: Run many accessibility scripts at the same time.
- Easy Integration: Works easily with Selenium, Appium, and many CI tools such as Jenkins.
- Team Collaboration: Share the test results, logs, and accessibility reports across teams.
In BrowserStack Automate, a user can scale the accessibility efforts without needing to build and maintain an in-house testing grid.
Conclusion
Accessibility can no longer be ignored. It is one of the fundamental aspects of delivering engaging user experiences. Manual checks are still vitally important, but using Selenium WebDriver for automated accessibility testing can help identify accessibility issues early and fix them quickly.
Platforms like BrowserStack can help extend those checks to real devices and browsers, making sure the digital experiences delivered are inclusive and usable for all people.
All accessibility tests on BrowserStack will be run on real browsers and devices – both the latest and older models. Start testing web accessibility today and create a site approachable by everyone.