CAPTCHA serves as a critical safeguard, protecting platforms from automated abuse like ticket scalping and spam attacks. Acting as a digital gatekeeper, it ensures a secure and fair experience for users.
While essential for security, testing CAPTCHA can be tricky due to its anti-automation design.
Overview
What is CAPTCHA?
CAPTCHA (Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart) is a security test that confirms a user is human by requiring them to solve tasks like identifying objects or typing distorted text.
How CAPTCHAs Work:
- Challenge-Response: CAPTCHAs use a challenge-response test that humans can easily solve but automated scripts struggle with.
- Distorted Text: Users must decipher letters or numbers in a distorted image, a format difficult for bots to decode accurately.
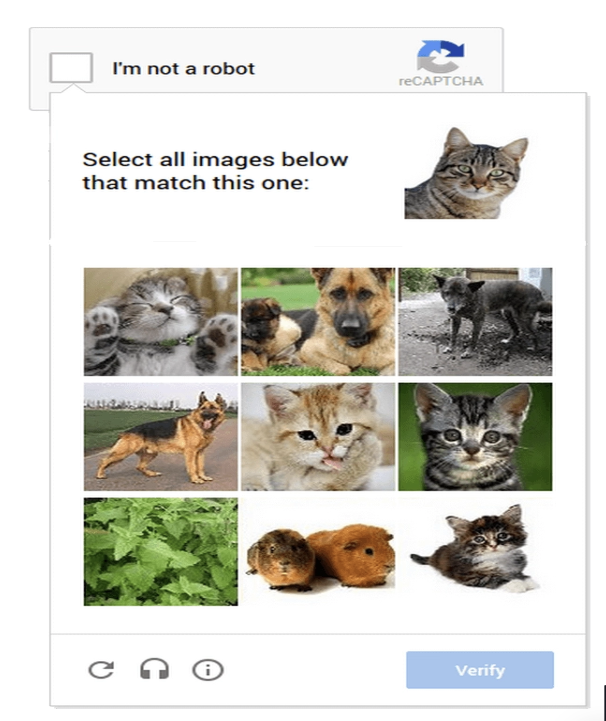
- Image Recognition: Some CAPTCHAs ask users to select specific items from a grid of images (e.g., crosswalks, buses).
- Audio CAPTCHAs: These offer an audio challenge where users transcribe distorted spoken characters or words.
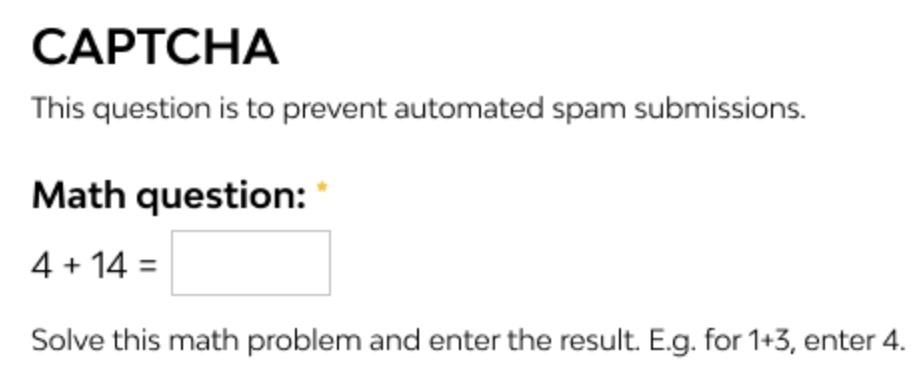
- Question-Based CAPTCHAs: Users answer simple math problems or logical questions, which bots typically cannot solve.
Purpose of CAPTCHAs:
- Prevent Spam: CAPTCHAs block bots from submitting fake forms, creating spam accounts, or posting malicious content.
- Protect Resources: They help defend websites from being overwhelmed by automated traffic and repetitive requests.
- Enhance Security: CAPTCHAs are a barrier against brute-force attacks and unauthorized data scraping.
- Differentiate Humans from Bots: CAPTCHAs filter out bots, ensuring that only real users can access certain site features.
This article delves into what CAPTCHA is, its role in online security, and how it works to maintain order in the online ecosystem.
What is CAPTCHA?
CAPTCHA stands for Completely Automated Public Turing test to tell Computers and Humans Apart. It is a challenge-response test used to verify that a user is human.
CAPTCHAs often involve tasks such as selecting specific images, entering distorted text, or identifying simple patterns for humans but difficult for bots. These tests act as a digital checkpoint, ensuring that only real users can proceed while keeping automated bots at bay.
In a way, CAPTCHA is like a puzzle where the solution reveals whether you’re a trusted human or an unwanted robot.
Example: A user may be asked to identify all images containing traffic lights in a grid—a task easy for humans but tricky for machines.
What is CAPTCHA Used For?
CAPTCHA has one main job: to outsmart bots and keep the internet safe for humans. Here’s how it works its magic:
- Preventing Spam Effectively: From preventing fake account registrations to blocking spam in comment sections, CAPTCHA serves as an essential line of defense.
- Securing Online Transactions: Whether it’s online shopping or banking, CAPTCHA ensures that only genuine users can perform sensitive actions, safeguarding against automated bots.
- Guarding Content: Ever wondered why bots don’t steal your favorite articles or data? You can thank CAPTCHA for protecting intellectual property.
- Fair Play Online: Whether securing votes in online polls or ensuring fair ticket bookings, CAPTCHA keeps the playing field even.
- Preventing Credential Stuffing: Bots often try to use stolen usernames and passwords to break into accounts. CAPTCHA blocks these attacks by ensuring only humans can log in, keeping your accounts safe from hackers.
Benefits of Using CAPTCHA
Some of the benefits include:
- Keeps Hackers Out: Acts as a digital bodyguard, blocking bots from sneaking into login systems and protecting your accounts.
- Reduces Spam: Keeps comment sections, forms, and emails free from bot-generated spam.
- Ensures a Level Playing Field: This prevents bots from hoarding tickets, dominating polls, or unfairly claiming resources meant for humans.
- Secures Your Wallet: Adds an extra checkpoint to verify transactions, ensuring your online payments and activities stay safe.
- Guards Your Digital Treasure: Protects sensitive data and prevents bots from stealing or scraping valuable information.
- Improves Website Performance: Reduces the strain caused by bot traffic, ensuring websites run smoothly and efficiently for real users.
Different Types of CAPTCHA
Following are the different types of CAPTCHA:
- Text CAPTCHA: Users enter distorted or scrambled text shown in an image.
- Image CAPTCHA: Tasks like selecting images containing specific objects (e.g., traffic lights or cars).
- Audio CAPTCHA: An audio clip with spoken characters for visually impaired users.
- Math CAPTCHA: Solving simple math problems, such as “5 + 3 = ?”.
- Behavioral CAPTCHA: Monitors user actions like mouse movement or typing speed to detect bots.
- Invisible CAPTCHA: Works in the background without the user noticing, analyzing behavior and interactions.
- Puzzle CAPTCHA: Requires users to complete tasks like dragging and dropping puzzle pieces to fit correctly.
- Logical CAPTCHA: Poses logic-based challenges like “Which number is larger: 5 or 8?”
How Does CAPTCHA Work?
CAPTCHA works through a step-by-step process that helps separate human users from bots. Here’s how it functions:
Challenge Creation
When a user tries to access a protected feature, such as a form or login, the system presents a CAPTCHA challenge. This could be a task like reading distorted text, clicking on certain images, or interacting with a checkbox.
User Interaction
The user completes the challenge by responding to the prompt. Some CAPTCHAs rely on visible tasks, while others observe how the user moves the mouse or types, making decisions based on behavioral patterns.
Response Submission
The user’s input is submitted to the server along with details like response accuracy, time taken, and interaction behavior.
Validation Process
The server analyzes the response to determine whether it matches the expected pattern of a human user. It checks both the accuracy of the input and any behavioral signals.
Result Outcome
If the system is confident the user is human, it allows the action to proceed. Otherwise, it may block access or prompt the user with a new challenge.
What is a CAPTCHA Test Case?
A CAPTCHA test case is a specific scenario designed to test the functionality, usability, and effectiveness of CAPTCHA implementation on a website or application.
It ensures that the CAPTCHA:
- Works as intended for human users.
- Accurately blocks automated bots.
- Is accessible to all users, including those with disabilities.
Importance of CAPTCHA Test Affirmation
The CAPTCHA test affirmation ensures that the CAPTCHA is working as intended, offering both security and usability. It verifies that the CAPTCHA is human-friendly while effectively blocking bots.
It serves as a quality checkpoint verifying that the system is easy for humans to navigate while effectively blocking bots. By maintaining this balance, CAPTCHA test affirmation safeguards sensitive processes, enhances user experience, and reinforces trust in online platforms.
Here’s why CAPTCHA Test Affirmation Matter:
- Ensures Functional Accuracy: Confirms the CAPTCHA performs as designed, solving tasks accurately for humans while deterring bots.
- Enhances Security: Validates that sensitive areas, like login pages and payment gateways, are secure against automated attacks.
- Supports Accessibility Compliance: Ensures users with disabilities can access alternatives like audio CAPTCHAs.
- Improves User Experience: Guarantees that CAPTCHA challenges are neither too simple (vulnerable to bots) nor too complex (frustrating for users).
- Prevents Errors: Identifies bugs or implementation gaps that could allow unauthorized access or deny access to valid users.
- Ensures Scalability: CAPTCHA systems can handle high traffic without compromising performance or user experience.
Test Cases for CAPTCHA
Testing CAPTCHA involves validating its functionality across different types to ensure it effectively distinguishes between human and automated users. Below are the test cases categorized by CAPTCHA type:
General CAPTCHA Test Cases
These test cases apply to all CAPTCHA types:
- Verify that CAPTCHA appears on the relevant pages (e.g., login, signup, feedback forms).
- Verify that CAPTCHA is displayed properly and is legible.
- Verify that the CAPTCHA challenge changes with each page refresh.
- Verify that the CAPTCHA expires after a set time or number of attempts.
- Verify that submitting the form without solving CAPTCHA shows an appropriate error message.
- Verify that CAPTCHA validation occurs both on the client-side (optional) and the server-side (mandatory).
- Verify that the CAPTCHA can be refreshed or regenerated.
- Verify accessibility compliance (keyboard navigation, ARIA labels, alt text).
- Verify CAPTCHA works across different devices, browsers, and screen resolutions.
Test Cases for Text-Based CAPTCHA
The following test cases focus on CAPTCHA challenges where users must enter text or characters displayed in an image:
- Verify that the text CAPTCHA is displayed clearly and is not distorted beyond readability.
- Verify that the case sensitivity of text CAPTCHA (if applicable) is handled correctly.
- Verify that entering the correct text passes validation.
- Verify that entering an incorrect or partial CAPTCHA text shows an error.
- Verify that no spaces or special characters are required unless specified.
Test Cases for Image-Based CAPTCHA
These test cases ensure that image-based CAPTCHA, such as selecting images from a grid, functions as intended:
- Verify that the image CAPTCHA displays a clear image challenge (e.g., select all squares with traffic lights).
- Verify that image challenges are appropriately randomized.
- Verify that clicking the correct images passes validation.
- Verify that selecting incorrect images triggers an error message.
- Verify the ability to refresh the image challenge.
- Verify images are of high quality and load within acceptable time limits.
Test Cases for Audio CAPTCHA
These test cases validate the functionality of audio CAPTCHA, ensuring accessibility for visually impaired users:
- Verify that an audio CAPTCHA option is available for users who cannot solve visual CAPTCHAs.
- Verify that the audio CAPTCHA is clear, with minimal background noise.
- Verify that the user can play, pause, and replay the audio.
- Verify that entering the correct characters from the audio passes validation.
- Verify that incorrect input triggers an error message.
- Verify that the audio CAPTCHA can be refreshed or changed.
Test Cases for Video CAPTCHA
These test cases ensure the accuracy and functionality of CAPTCHA that uses video content for user verification:
- Verify that the video CAPTCHA loads and plays without delays or errors.
- Verify that the video content is clear and understandable (e.g., “select all objects shown in the video”).
- Verify that the user can control playback (play, pause, restart).
- Verify that answering the question based on the video content passes validation.
- Verify that incorrect answers trigger an error message.
- Verify that the video CAPTCHA can be refreshed or changed.
Test Cases for Puzzle CAPTCHA
These test cases validate the functionality of CAPTCHA which requires users to solve visual or interactive puzzles:
- Verify that the puzzle CAPTCHA loads correctly and displays all necessary elements.
- Verify that solving the puzzle successfully allows form submission.
- Verify that an incomplete or incorrect puzzle solution shows an error message.
- Verify the ability to refresh or regenerate the puzzle.
- Verify that the puzzle CAPTCHA works across different browsers, devices, and screen sizes.
- Verify that the puzzle CAPTCHA is intuitive and accessible for all users.
To ensure CAPTCHA works seamlessly across all environments, testing must cover a wide range of devices and browsers. BrowserStack Live provides real-device access, helping teams manually verify CAPTCHA rendering, responsiveness, and user flows on real browsers and devices.
Steps to Write a CAPTCHA Test Case
Here’s how you can test CAPTCHA step-by-step:
Step 1: Define the Test Objective
Clearly state the purpose of the test.
Example: Validate the CAPTCHA system allows humans to pass but blocks bots.
Step 2: Choose a CAPTCHA Type
Determine the CAPTCHA type to test (e.g., text-based, image-based).
Step 3: Simulate User Interaction
Write code to simulate user inputs.
Take an example code (Javascript) for testing the Text CAPTCHA:
let captcha;
function generate() {
// Clear old input
document.getElementById("submit").value = "";
// Access the element to store
// the generated captcha
captcha = document.getElementById("image");
let uniquechar = "";
const randomchar =
"ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZabcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz0123456789";
// Generate captcha for length of 4 with random character
for (let i = 1; i < 5; i++) {
uniquechar += randomchar.charAt(
Math.random() * randomchar.length)
}
// Store generated input
captcha.innerHTML = uniquechar;
}
function printmsg() {
const usr_input = document
.getElementById("submit").value;
// Check whether the input is equal
// to generated captcha or not
if (usr_input == captcha.innerHTML) {
let s = document.getElementById("key")
.innerHTML = "Matched";
generate();
}
else {
let s = document.getElementById("key")
.innerHTML = "Not Matched";
generate();
}
}Step 4: Run Tests
Simulate scenarios:
- Enter the correct text to verify the Passed output.
- Enter incorrect text to confirm Failed output.
Step 5: Verify Output
Correct Input:
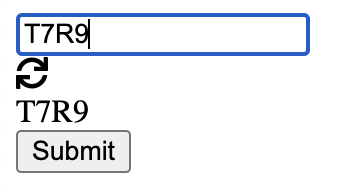
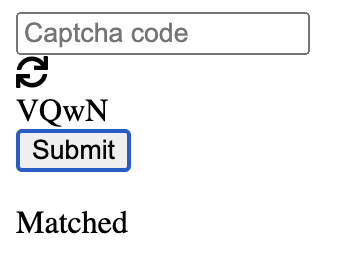
Incorrect Input:
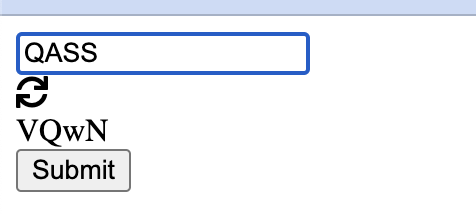

Read More: Top 9 JavaScript Testing Frameworks
Different Cases of CAPTCHA
CAPTCHA is widely used across various online platforms to enhance security, prevent abuse & ensure fair usage. Below are common use cases:
- Login Security: Protects accounts by verifying human users and blocking brute force attacks on login pages.
- Preventing Spam: Safeguards forms, comment sections & email systems from automated spam submissions.
- E-commerce: Ensures fair access during ticket bookings, flash sales, and limited-time offers by blocking bots.
- Data Protection: Prevents unauthorized bots from scraping sensitive or proprietary information from websites.
- Preventing Fake Account Creation: Stops bots from creating multiple fake accounts during registrations.
- Online Polls: Maintains fairness by restricting participation to legitimate users, preventing bots from influencing results.
What is reCAPTCHA?
reCAPTCHA is an advanced form of CAPTCHA designed to help distinguish human users from automated bots.
Developed by researchers at Carnegie Mellon University and later acquired by Google in 2009, reCAPTCHA offers a more advanced & effective alternative to traditional CAPTCHA.
While traditional CAPTCHAs typically ask users to identify distorted letters or numbers, reCAPTCHA leverages real-world content such as text from scanned books, historical newspapers, or street addresses.
By asking users to decipher these images, reCAPTCHA helps digitize and improve machine-learning models while ensuring the user is human. This system protects websites from bots and contributes to projects involving data processing like improving optical character recognition (OCR) technology.
Types of reCAPTCHA:
Below are the main types of reCAPTCHA:
- reCAPTCHA v2: This is the most common type, requiring users to click a checkbox (“I’m not a robot”) or solve image-based puzzles to confirm they are human.
- Invisible reCAPTCHA: Operates seamlessly in the background without requiring user interaction unless suspicious behavior is detected.
- reCAPTCHA v3: An advanced version that assigns a score (ranging from 0 to 1) based on user behavior to determine the likelihood of bot activity, empowering site owners to customize responses.
- Enterprise reCAPTCHA: Specifically designed for businesses offering enhanced security features & integration with enterprise-level applications.
- Audio reCAPTCHA: This option provides accessibility by presenting audio challenges instead of visual ones for visually impaired users to complete.
Read More: JavaScript Unit Testing Tutorial
Test Cases for reCAPTCHA
Below are the key test cases to validate its functionality:
- Verify that reCAPTCHA is displayed on relevant pages (e.g., login, registration, or contact forms).
- Verify that reCAPTCHA does not block form submission when solved correctly.
- Verify that reCAPTCHA prevents form submission when not solved or if validation fails.
- Verify that the reCAPTCHA checkbox (v2) is clickable and shows the green checkmark upon successful verification.
- Verify that the reCAPTCHA challenge (e.g., image selection) appears when the system detects suspicious activity.
- Verify that solving the challenge correctly passes validation.
- Verify that incorrect responses or skipping the CAPTCHA show an appropriate error message.
- Verify that the reCAPTCHA script loads without errors in the browser console.
- Verify that reCAPTCHA works across different browsers, devices, and screen resolutions.
- Verify that reCAPTCHA does not significantly impact page load time.
- Verify that reCAPTCHA can be refreshed if the challenge is too difficult.
- Verify that reCAPTCHA times out after a reasonable period of inactivity and requires re-validation.
- Verify accessibility compliance, such as keyboard navigation and screen reader support.
- For reCAPTCHA v3:
- Verify that a valid score is generated for user interactions.
- Verify that low scores (indicating likely bot activity) trigger appropriate actions (e.g., additional verification, blocking submission).
Read More: How to Write Test Cases for Login Page
Limitations of Using CAPTCHA
Below are some of the key limitations associated with using CAPTCHA systems:
- Accessibility Challenges: It may be complex for users with disabilities even with alternatives like audio CAPTCHAs.
- User Frustration: Complex or repetitive challenges can lead to poor user experience.
- False Positives: Legitimate users may be flagged as bots due to unexpected behavior.
- Bypass Techniques: Advanced bots or CAPTCHA-solving services can sometimes circumvent them.
- Performance Impact: Can slow down page load times or create unnecessary user barriers.
Best Practices for Using CAPTCHA
To effectively utilize CAPTCHA without compromising user experience, it’s important to follow best practices.
Below are key recommendations for implementing CAPTCHA systems:
- Balance Usability and Security: Avoid overly complicated challenges to reduce user frustration.
- Offer Accessibility Options: Include audio or alternative CAPTCHAs for users with disabilities.
- Use Adaptive CAPTCHAs: Implement dynamic CAPTCHAs that adjust difficulty based on risk levels.
- Integrate with Behavior Analysis: Combine CAPTCHA with behavioral analysis for enhanced bot detection.
- Optimize for Mobile Devices: Ensure CAPTCHAs are responsive & easy to complete on smaller screens.
- Regularly Update CAPTCHA Solutions: Stay ahead of evolving bot technologies.
Manual vs. Automated Testing for CAPTCHA
Below are the key differences when it comes to manual testing and automated testing for CAPTCHA:
| Aspect | Manual Testing | Automated Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Validation Approach | Focuses on evaluating CAPTCHA usability from a real user’s perspective to ensure user-friendliness and accessibility. | Simulates multiple CAPTCHA interactions using scripts or tools for efficient scenario testing. |
| Accessibility | Verifies alternatives like audio CAPTCHAs to ensure they are accessible for users with disabilities. | Tests technical aspects of accessibility but may not fully replicate user interaction. |
| Edge Case Handling | Tests unusual inputs or extreme conditions, such as multiple failed attempts or uncommon user behaviors. | Assesses CAPTCHA resilience against automated scripts and tools attempting to bypass restrictions. |
| Speed | Time-intensive, requiring human intervention, which makes it slower and potentially prone to errors. | Highly efficient, capable of quickly executing tests on a large scale without manual involvement. |
| Consistency | Results may vary due to human error or subjective interpretation. | Provides consistent and repeatable test execution across all scenarios. |
| Tool Dependency | Relies on human testers, requiring minimal technological setup. | Requires specialized tools like Selenium or CAPTCHA-specific frameworks, which may have limitations. |
| Best Suited For | Usability testing, verifying CAPTCHA design, and checking visual or audio clarity. | Large-scale testing, stress testing under heavy loads, and validating technical robustness. |
While automated testing can verify CAPTCHA presence and integration, manual testing is essential for effectively validating CAPTCHA challenges. This is because manual testing allows you to:
- Verify CAPTCHA visibility, rendering, and responsiveness
- Check user interaction flows across different browsers, devices, and operating systems
- Ensure CAPTCHA accessibility features work across devices
BrowserStack Live offers real device access that empowers testers to perform these manual CAPTCHA validations seamlessly across real user conditions. It supports:
- Instant access to a wide range of real devices and browsers to verify CAPTCHA behavior in authentic environments
- Screenshot and video capture tools to document CAPTCHA interactions and troubleshoot issues effectively
- Network simulation capabilities to test CAPTCHA responsiveness under various connectivity conditions
Conclusion
CAPTCHA is like a digital gatekeeper, quietly working behind the scenes to keep online experiences safe and fair. It stops bots from spamming websites, stealing data, or causing chaos in online activities.
Even though it has some challenges, like being tough for some users, new versions like reCAPTCHA are making it smarter and easier.
CAPTCHA can help protect online spaces and ensure everything runs smoothly for real people.
Join Test Management Live Webinar
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What Triggers a CAPTCHA Test?
A CAPTCHA test is triggered when a website suspects unusual activity that might indicate a bot. Common triggers include:
- Repeated or rapid form submissions.
- Suspicious IP addresses or geolocations.
- Use of automated scripts or unusual browser behavior.
- Accessing secure areas of a site.
2. How to Enter CAPTCHA Correctly?
Here are the steps for the following:
- Text CAPTCHA: Carefully enter the letters or numbers shown, considering case sensitivity.
- Image CAPTCHA: Select the images that match the given prompt (e.g., “Select all squares with traffic lights”).
- Audio CAPTCHA: Listen to the audio and type the numbers or letters you hear.
- ReCAPTCHA: If prompted, click the checkbox confirming you’re not a robot.