A test case defines the steps, inputs, and expected results to verify a specific software feature. It helps QA teams validate functionality and determine if the feature works correctly.
Overview
Components of a Test Case
- Test Case ID: Unique identifier for the test case.
- Test Priority: Execution order (Low, Medium, High).
- Module Name: Name of the module being tested.
- Test Designed By / Reviewed By: Author and approver of the test case.
- Test Designed Date / Execution Date: Dates for creation and execution.
- Test Executed By: Name of the tester performing the test.
- Test Title/Name: Name or title of the test case.
- Test Summary/Description: Brief description of the test case objective.
- Pre-Requisites: Conditions to be met before execution.
- Dependencies: Links to other related test cases or requirements.
- Test Steps: Ordered steps to execute the test.
- Test Data: Input values required for the test.
- Expected Result: Outcome expected from the test.
- Post-Condition: System state after execution.
- Actual Result: Observed outcome of the test.
- Status (Pass/Fail): Indicates if the test passed or failed.
- Attachments: Screenshots or supporting files.
- Notes/Comments: Additional observations or clarifications.
Creating effective test cases is essential for ensuring software quality. This article explores various test case templates and provides practical examples to help streamline your testing process.
What is a Test Case?
A test case refers to the actions needed to verify a specific functionality or feature in software testing. The purpose of a test case is to detail the data, steps, prerequisites, and post-conditions necessary to substantiate a feature.
In other words, a test case intends to lay out particular variables used by the QA team members to compare actual and expected results, determine the application’s health, and conclude whether the feature works.
What Are the Components of a Test Case?
The components of a Test Case include the required input, execution process, and expected output. It guides testers and developers on what to do, how to do it, and the intended results.
A Test Case consists of the following components:
- Test Case ID: Every test case has a unique ID. It’s good to practice a naming convention for it. For example, TC_UI_1 indicates “User Interface Test Case #1.”
- Test Priority determines the order of executing the tests. Depending on the business requirements, test priority can be low, medium, or high.
- Module Name: This is the name of the module or sub-module being tested.
- Test Designed by: The name of the tester who designed the test case.
- Test Reviewed By: The person who reviewed and approved the test case.
- Test Designed date: The date when the test case was designed.
- Test Executed by: The name of the tester who executed the test. This field is populated after the test execution is completed.
- Test Execution date: The date when the test case was executed.
- Test Title/Name: Test case title/name
- Test Summary/Description: A summary of the test case and what it intends to cover.
- Pre-Requisites: This covers all the requirements to be catered to before the test case is executed. It’s good to list all the prerequisites to execute the test case successfully.
- Dependencies: This Identifies and determines all the dependencies, if any, on other test cases or requirements
- Test Steps: Here, all the test steps are listed with details and in their order of test execution.
- Test Data: Input for the test cases is defined here. You can provide different data sets with their exact values for input.
- Expected Result: Here, the expected result of the test case is mentioned, including messages or any errors that should appear on the screen.
- Post-Condition: This captures the state of the system after running the test case
- Actual Result: This captures the Actual result obtained after the test case execution is completed.
- Status (Pass/Fail): The test case status is captured here: Pass if the actual and expected results match and Fail if they don’t.
- Bug Details (optional): If a bug is identified, the details about it and the steps to reproduce it can be captured here.
- Attachments: Any relevant screenshots, files, or document links associated with the test case are mentioned here.
- Notes/Questions/Comments: This section captures any special information/insights or queries related to the test case that are also mentioned here.
Also Read: Fundamentals of Writing Good Test Cases
What is a Test Case Template?
A test case template is a predefined structure intended to provide a standardized way to create and document test cases. It captures all the necessary information about a test scenario to ensure consistency and clarity. A well-designed template helps testers systematically outline a test’s objectives, steps, and expected outcomes, making execution and review more efficient.
Test Case Templates with Examples
Predefined test case templates provide a structured format to document test scenarios, inputs, and expected outcomes. Here are some test case templates with examples:
General
The general test case planning and execution template can help capture all major details of test scenarios. Using this, test cases can be tracked through their Test Case ID and description. The prerequisites of the test case and their date of execution are also captured. Testers also have the expected and actual results captured, which determines the status of the test and additional notes for the cases, if any. This complete template can be used for any kind of test.
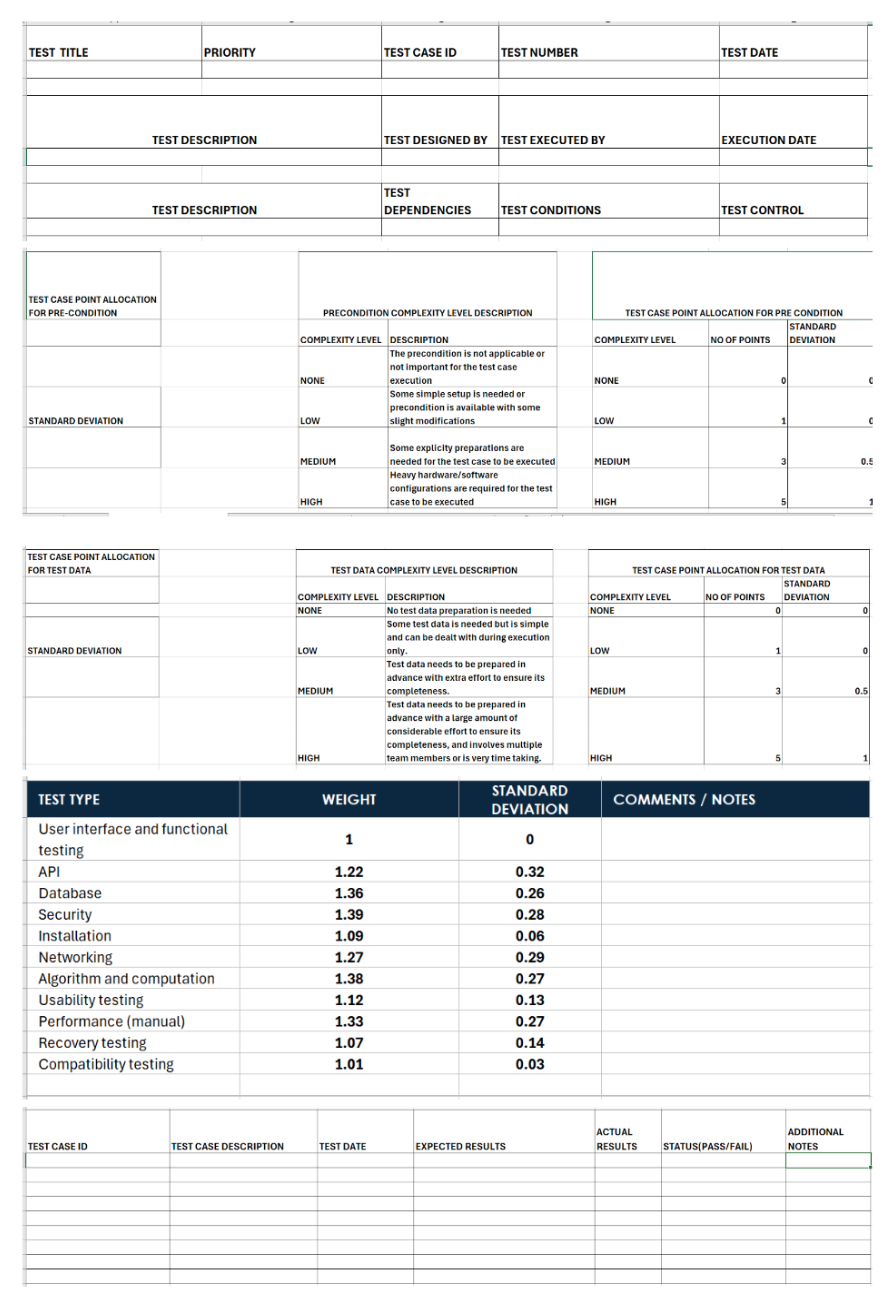
Test Case Point Estimate Template
The test case point estimate template assesses the approach being used to test the application and determines the preconditions and checkpoints, followed by a detailed test result analysis. Using the above template, testers can allocate the time needed for each specific step, rate the priorities, and determine the amount of work needed for each test.
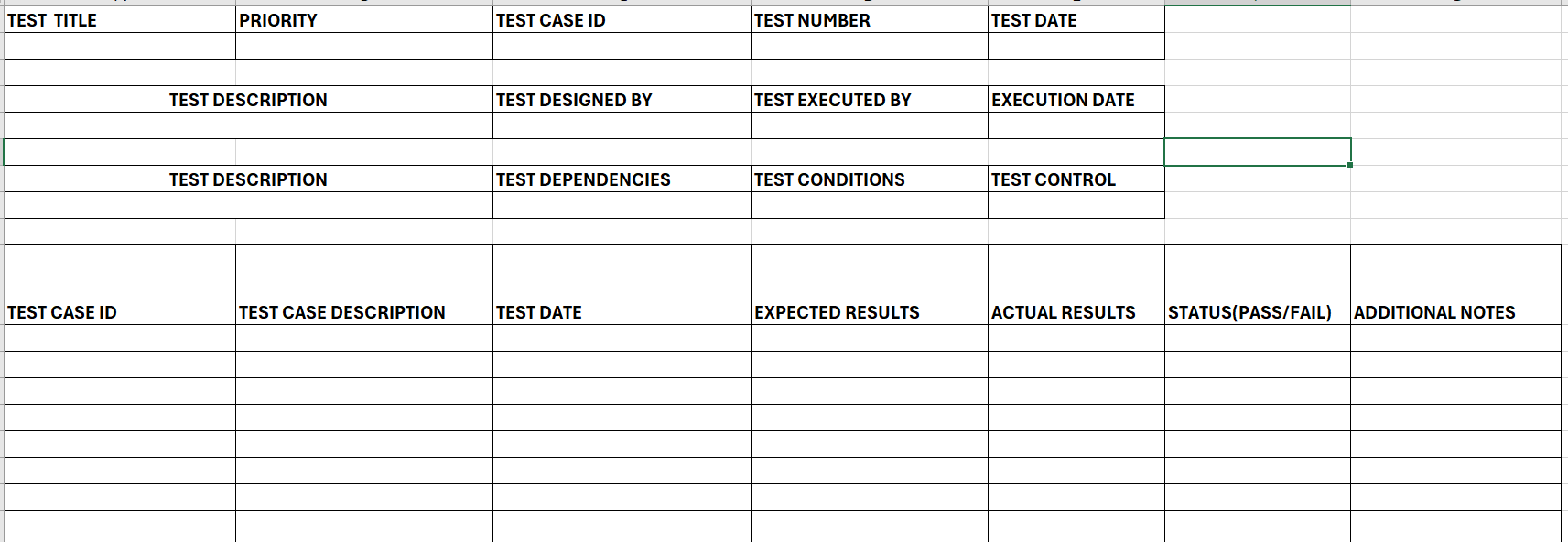
Manual Testing Test Case Template
The manual testing test case template can be used to record the test cases using their IDs, descriptions, the date of their execution, their priority, and dependencies, if any. This can also be used to analyze the expected results versus the actual results and figure out whether the test case passed or failed. This template helps in a very detailed inspection of the test cases.
Learn More: Manual Testing vs Automation Testing
Automation Testing Test Case Template
The automation testing test case template can be used to assess the status of automated test cases. Along with the Test case ID, description, and date of execution, testers also need to capture the test duration, which helps in analyzing the automation health. A very high or very low number in Test Duration would let the testers know which case needs fixing and identify automation bottlenecks. The Automation as Yes/No column helps determine the number of automated test cases.
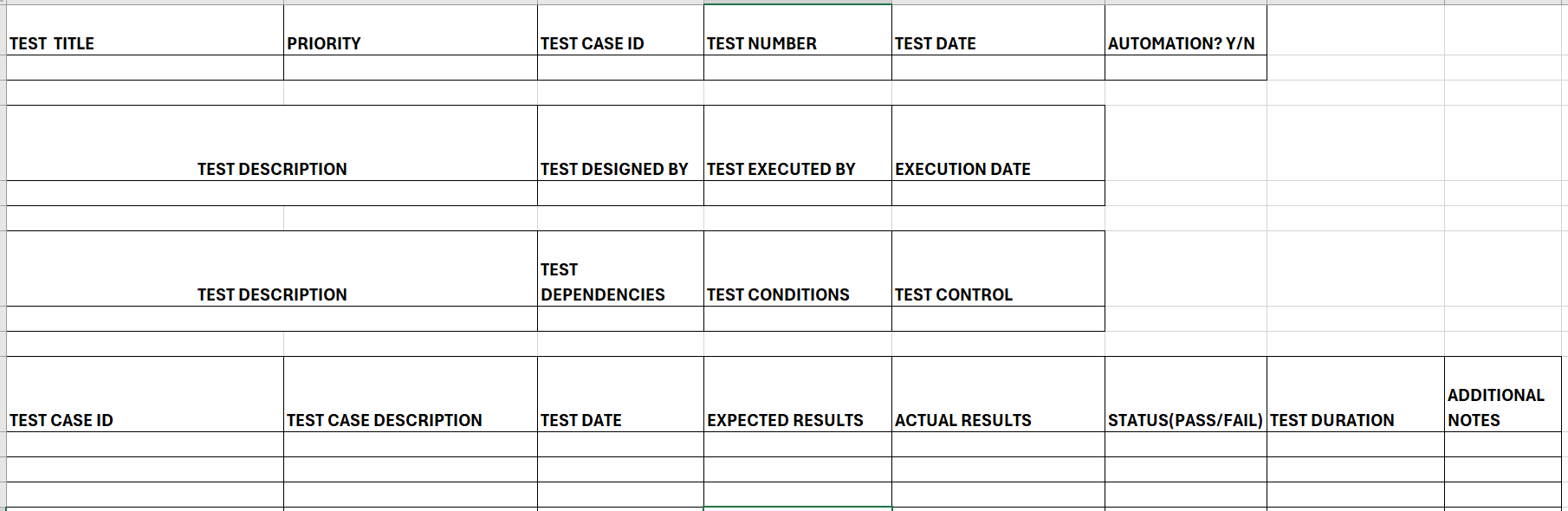
Cross Browser Testing Test Case Template
With this cross-browser testing test case template, along with the general test case details, including their Name, ID, Description, and Prerequisites/Dependencies, if any, testers must also capture the browser type in which the test case was executed. This helps keep track of the different browsers that were covered in testing and analyzes their results.

What Makes a Good Test Case Template?
A good test case template is essential for effective software testing. It provides a structured framework for documenting the test cases consistently and efficiently.
Here are some key characteristics that make a test case template effective:
Characteristics of a Good Test Case Template
- Clarity and Simplicity: The template should be straightforward to understand, with clear instructions to avoid confusion.
- Completeness: It should cover all necessary details and scenarios, including edge cases and negative testing.
- Consistency: Ensure uniformity in format and content across all test cases to maintain organization and readability.
- Reusability: Test cases should be designed to be reusable in future testing cycles or projects, saving time and effort.
- Traceability: The ability to link test cases to specific requirements or defects, facilitating tracking and impact analysis.
- Flexibility: The template should be adaptable to different projects or testing types, accommodating changes without major revisions.
- Measurability: Clearly define success and failure criteria to measure test results accurately.
- Maintainability: Easy to update and maintain as the application or requirements evolve, ensuring the test cases remain relevant.
By incorporating these elements and characteristics, a test case template can significantly improve the efficiency and effectiveness of your testing process, leading to higher software quality and reduced defect risk.
Differences Between Test Cases and Test Scenarios
Understanding the differences between a test case and a test scenario is crucial for effective software testing, as they serve distinct purposes and play different roles in the testing process.
| Test Case | Test Scenario |
|---|---|
| Offers detailed information on what to test, steps required for testing, and the accurate result to be expected | Only detailed information on what feature is to be tested and the user story associated with the feature. |
| Required keeping testers and developers in sync | Required so that testers know what their task is on a high level |
| It consists of low-level, individual actions testers have to undertake | Consists of high-level information (usually a one-liner) about what feature should be tested |
| It is derived from test scenarios | It is derived from the requirements document |
| Creating test cases is a one-time effort since test cases can be reused, especially during regression testing. | Test scenarios may need to be changed as the software evolves to align with newly developed features. |
| It is mostly helpful for guiding individual testers on how to progress in a certain project | Most helpful in reducing complexity by listing out everything that must be tested and helping testers create test cases for each scenario |
How Can You Write a Test Case?
To create comprehensive and detailed test cases and make the most of them, one must keep in mind the pointers below.
- Make the test steps clear and precise, and avoid any vague directions or objectives.
- Mention the test case name and a unique test case ID to keep the tests segregated.
- Include a detailed description of the scenario being tested so that anyone else can understand it.
- To avoid confusion, ensure that there are no more than 15 steps. If there are more than 15 steps, bifurcate the tests into multiple tests.
- Always write the test cases, keeping the end user in mind to build better software.
- Always follow the peer review process for the test cases and incorporate suggestions from the team members who participated in it.
- Capture the actual and expected result of the test case so that the status can be determined after the execution.
- Try to make the test cases atomic and avoid repetition of the same steps across multiple cases.
If you would like to learn in detail about creating and managing test cases, refer to our guide on how to write test cases.
Create and Manage Test Cases Using BrowserStack Test Management
BrowserStack Test Management is an AI-powered, unified platform designed to accelerate test case creation, execution, and automation with up to 90% faster test authoring and 50% improved coverage.
It offers seamless integrations, real-time visibility through customizable dashboards, and advanced AI agents that streamline testing workflows for both manual and automated tests.
Built for teams of all sizes, it ensures secure data handling while enabling high-quality, efficient software delivery.
Key Features of BrowserStack Test Management:
- AI-Powered Test Case Creation: Automatically generate comprehensive test cases from Product Requirement Documents (PRDs), user stories, or text prompts. AI also suggests enhancements to existing test cases, reducing manual effort significantly.
- Test Deduplication Agent: Detects exact or semantically similar test cases across your repository, providing intelligent recommendations for merging or removal to maintain a clean and efficient test suite.
- Low-Code Automated Test Authoring: Quickly convert manual test cases into low-code automated tests to accelerate automation adoption without requiring deep coding skills.
- Intelligent Test Selection Agent: Uses AI to identify and recommend the most relevant tests for execution, optimizing test runs and focusing on critical test coverage.
- Unified Test Management: Manage all manual and automated test cases in one centralized platform with full traceability from requirements to defects through seamless integrations with Jira, Azure DevOps, and more.
- Powerful Dashboard Analytics: Access customizable dashboards that offer real-time insights, track release status, monitor historical trends, and visualize testing metrics, including automation coverage.
- AI-Powered Jira App with Two-Way Binding: Synchronize test cases and runs between BrowserStack Test Management and Jira, allowing management from both platforms with AI-driven assistance.
- Streamlined Manual and Automated Test Runs: Plan and execute test runs across manual and automated tests. Supports dynamic test inclusion and uploading automation results from frameworks like JUnit and BDD-JSON.
- Support for Automation Frameworks & CI/CD Tools: Integrates with popular frameworks (Appium, Playwright, TestNG, etc.) and CI/CD platforms (Jenkins, Azure Pipelines, Bamboo), enabling scalable test automation workflows.
- Shared Steps for Reusability: Mark repetitive test steps as shared within test cases to enhance reusability and save effort when creating or maintaining test cases.
- Quick Import & Custom Field Mapping: Import test cases rapidly from CSV files or existing management tools with automatic field mapping and on-the-fly custom field creation.
- The free version of BrowserStack Test Management offers unlimited test cases, robust integrations, and real-time reporting capabilities for up to 10 users.
Try BrowserStack Test Management
Conclusion
The foundation of a successful testing cycle lies in creating well-structured, maintained, and comprehensive test cases.
This can be achieved by maintaining clean and detailed test case templates. The entire test management process also plays a major role in getting the desired results.
BrowserStack Test Management combines AI with enterprise-grade features to streamline test creation, management, and execution. It enables faster, more reliable software releases with better test coverage and improved efficiency.
Join Test Management Live Webinar
Useful Resources for Test Case
Understanding Test Case:
- What is a Test Suite & Test Case? (with Examples)
- What is Test Case Specification?
- Fundamentals of Writing Good Test Cases
- Understanding what is UI Test Cases (with Examples)
- Test Case Vs Test Script
- Test Plan vs Test Case: Core Differences
- Use Case vs Test Case: Core Differences
- Test Case Review Process
- Captcha Test Case
- Test Case Templates with Example
Tutorials and Best Practices:
- How to Write Test Cases for Login Page
- How to optimize test cases for Continuous Integration
- How to speed up UI Test Cases
- How to run parallel test cases in TestNG
- How to write JUnit test cases
- How to write Test Cases for Gmail
- How to write Test Cases for Mobile Applications
- How Automation of Regression Test Cases can be Cost Effective
- How to Create Test Cases for Automated tests?
- How to create Selenium test cases
- How to write Test Cases in Software Testing? (with Format & Example)
- How to write Test Case in Cypress: (with testing example)
- How to run failed test cases using TestNG in Selenium Webdriver?
- How to take Screenshot of Failed Test Cases in Cucumber
- How to run JUnit 4 Test Cases in JUnit 5
- How to create and manage test cases in Jira and BrowserStack Test Management
- How to make your Selenium test cases run faster
- How to Write Test Cases for Amazon Shopping?
- Test Cases for Search Functionality
- Test Cases for ECommerce Website
- Test Cases for Facebook Login Page
- Test Case Reduction and Techniques to Follow