Low-code development simplifies application building with visual tools and a drag-and-drop interface, minimizing the need for traditional coding.
It accelerates development by automating backend tasks, enabling users to create apps quickly with pre-built components.
Overview
Key Features of Low-Code Development
- Visual Development: Drag-and-drop interfaces for easy design.
- Pre-built Components: Ready-made modules and templates for quick app assembly.
- Reduced Coding: Automates backend coding, reducing manual effort.
- Faster Development: Speeds up app creation and deployment.
- Increased Accessibility: Enables non-developers to build apps, expanding development potential.
- Improved Collaboration: Facilitates teamwork between business and IT departments.
Top Low Code Development Tools
- BrowserStack Low-Code Automation: Offers AI-powered test automation with no coding required, using real devices and cross-browser testing in the cloud.
- Selenium IDE: A browser extension for recording and playing back web interactions for automated testing.
- Robot Framework: An open-source automation framework for acceptance testing with a keyword-driven approach.
- Gauge: A lightweight, open-source test automation framework designed for simplicity and supporting multiple languages.
- Karate: A versatile testing framework for API, UI, and performance testing with easy setup and no dependencies.
This guide explores low-code development, explaining its advantages, distinct characteristics, limitations, and upcoming scope in the current era.
What is Low-Code Development?
Low-code development is an effective software development approach that enables developers to build applications via a visual interface and requires minimal coding efforts.
It allows developers and non-developers alike to build and customize applications by combining pre-built components, automating workflows, and managing integrations, reducing the complexity of traditional coding.
It is one of the easiest alternatives to traditional software application development.
Also Read: 12 Open source Low Code Testing Tools
Benefits of Low-code Development
Low-code development empowers organizations to accelerate application delivery and streamline workflows, allowing developers to focus on high-value tasks.
According to a survey, 80% of respondents agree that low-code platforms free up developer time, enabling them to work on more strategic projects.
Key Benefits of Low-Code Development
- Speedy Development: Low-code platforms enable faster application development, reducing backlogs and speeding time-to-market.
- Flexibility and Scalability: Easily adaptable to changing business needs, low-code platforms scale with minimal development effort.
- Increased Agility: Quickly design and deploy applications without extensive coding knowledge, enabling faster responses to market demands.
- Reduced Development Costs: With less manual coding and simplified workflows, low-code development lowers development expenses and maximizes ROI.
- Captivating UI/UX: Easily design engaging user interfaces using pre-built templates, ensuring a balance between functionality and design.
- Better Collaboration: Business stakeholders can actively participate in development, ensuring the final product meets their needs and speeding up the SDLC.
- Streamlined Updates and Maintenance: Low-code applications are easier to maintain and update, reducing long-term upkeep costs.
- Innovation and Digital Transformation: Facilitates digital transformation by enabling quick, innovative solutions to meet evolving business needs.
- Improved Productivity: By simplifying the development process, low-code platforms allow more applications to be created faster, boosting overall productivity.
Also Read: How to Accelerate Product Release Velocity
Differences between Low Code and No Code
Both low-code and no-code development platforms empower citizen developers and professional developers to build apps. Such platforms’ significance lies in allowing users with little to zero coding experience to build apps that address multiple business challenges.
- Low-code platforms offer visual development tools and pre-built elements to accelerate app development.
- No-code development needs no coding at all. Novice users can use no-code platforms to create apps by easily dragging and dropping components and configuring settings.
Here is a comparison of Low-Code and No-Code development:
| Parameters | Low-Code Development | No-Code Development |
|---|---|---|
| Target Users | Citizen and Technical Developers | Citizen Developers |
| Coding Knowledge | Low-code is introduced for developers and a little coding is needed to utilize them. The platform delivers modes of automating things rapidly, but only for persons with tangible coding expertise. | No-code is mainly designed for business executives/ citizen developers; zero coding know-how is required. |
| Projects Complexity | Ideal for moderate to complicated projects. | Suited for easy projects. |
| Customization | Offers greater custom choices. | Offers restricted customization capabilities |
| Development Time | Speedy development due to some coding. | Rapid development without coding. |
| Flexibility | Higher flexibility in designing workflows. | Restricted flexibility in workflows. |
| App complexity | Can build complex apps. | Can build simple and easy-to-use apps |
| Learning Curve | Moderate learning curve for users. | Simple to use with minimal learning |
| Scalability | Ideal for scaling big projects | Suitable for smaller projects. |
| Control | Offers more control over the process. | Less control, automated approach. |
| Integration Capabilities | Robust integration with other systems. | Restricted integration possibilities. |
Key Components/Features of Low-code Development
The best low-code development platforms have a comprehensive suite of components and features designed to fast-track your journey to success.
Key Components of Low Code Development
- Visual development environment
- Drag-and-Drop interfaces
- Pre-built templates and components
- Mobile-first design
- Integration capabilities
- Cross-platform accessibility
- Security and compliance
- Workflow automation
Here is a deep dive into the essential elements that make up the foundation of low-code development.
- Visual Development Environment: Low-code platforms give a visual development surrounding with drag-and-drop functionality, letting software developers build apps without immense coding.
- Drag-and-Drop Interfaces: Drag-and-drop must be at the top of your listing regarding necessities in a low-code platform. This is not merely a convenience; it’s highly significant. Citizen developers require this to build their apps.
- Pre-Built Templates and Components: Low-code platforms also proffers a library of reusable elements and pre-built templates, letting app developers accelerate app development.
- Mobile-First Design: Low-code platforms prioritize mobile optimization, confirming that apps are responsive and accessible across multiple devices.
- Integration Capabilities: Low-code platforms provide seamless integration with numerous third-party databases, solutions, and APIs, letting developers build robust and interconnected apps.
- Cross-Platform Accessibility: If you are building an app using one of the low-code platforms available on the marketplace, this is a great trait to have. Building an app with multi-channel compatibility, which lets your manpower access it from any place, makes things simple.
- Security and Compliance: Low-code platforms execute robust safety measures and compliance standards to protect confidential or sensitive info and guarantee regulatory adherence.
- Workflow Automation: Low-code platforms allow the automation of recurring jobs and business procedures, enhancing productivity and efficiency.
Read More: How to build Cross-Platform Mobile Apps
Real-World Use Cases of Low Code Development
Some low-code use development in enterprise settings include:
- HR Management: Big enterprises use low-code platforms to build comprehensive HR management systems that automate employee recruitment, onboarding, performance assessments, and training.
- Financial Management: Low-code solutions generate financial management apps that handle budgeting, financial expense tracking, invoicing, and reporting.
- Supply Chain Management: Low-code platforms are also leveraged to build supply chain management apps that manage inventory, track shipments, and confirm seamless logistics operations.
- CRM (Customer Relationship Management): Enterprises deploy low-code Customer Relationship Management solutions to organize customer info, enhance customer engagement, and streamline marketing and sales processes.
How do Low Code Development Tools Work?
Low-code development tools work by providing a platform with visual, drag-and-drop interfaces and pre-built components. It allows users to build applications quickly and with minimal coding. Here is how low code development works:
Step 1: Design with Drag-and-Drop
Arrange components visually using a drag-and-drop interface. This allows users to build layouts without coding.
Step 2: Use Pre-built Modules
Choose from a library of ready-made templates and modules. Customize these as needed to speed up development.
Step 3: Automate Workflows
Set up automated processes. Define business logic with easy-to-use, conditional workflows.
Step 4: Integrate Data Sources
Connect to external databases and APIs. Use built-in connectors for seamless data flow.
Step 5: Customize with Code (Optional)
Add custom code for unique features not covered by built-in options. This enables a hybrid approach.
Step 6: Test and Deploy
Simulate app behavior before launch. Deploy with single-click options, which often automate versioning and scaling.
Step 7: Collaborate and Manage Roles
Allow team collaboration by assigning roles and access levels. This lets both technical and non-technical users contribute.
How to choose a Low Code Development Platform?
Here are some essential factors to consider on how to choose a low-code development platform:
- Relevance to the Use Case: Choose a platform suited to your project type (for example, web, mobile, or internal tool).
- Easy to Use: Ensure the platform is intuitive for both technical and non-technical users.
- Customization: Look for options to add custom code if unique features are required.
- Integration Capabilities: Make sure it connects easily with the databases, APIs, and services you need.
- Scalability: Verify the platform’s performance as usage grows.
- Security: Confirm it meets your security standards and compliance needs.
- Support: Look for team support and solid customer service.
- Cost: Compare pricing with the features offered to ensure good ROI.
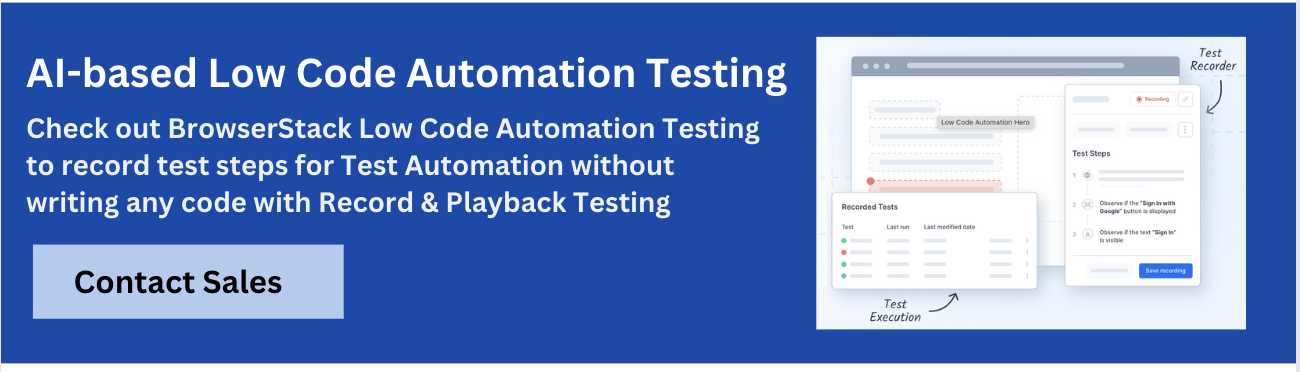
Why Choose BrowserStack Low Code Automation?
BrowserStack Low-Code Automation allows teams to create, execute, and maintain automated tests without writing a single line of code.
It integrates an interactive test recorder, AI-powered self-healing, and real-device cloud testing, enabling teams to start automation in minutes and scale effortlessly across browsers and devices.
With features like AI-driven self-healing and low-code authoring agents, test creation becomes 10x faster and build failures decrease by up to 40%, delivering reliable and faster automation for both technical and non-technical teams.
Key Features of BrowserStack Low-Code Automation
- Test Recorder: Easily capture user actions like clicks and form inputs, converting them into automated tests with functional and visual validations.
- Readable Test Steps: Recorded actions are translated into simple, human-readable instructions for easy understanding and modification.
- Visual Validation: Add checkpoints to verify UI component displays and detect visual regressions.
- AI-Powered Self-Healing: Automatically detects and updates tests when UI elements change, reducing manual maintenance.
- Low-Code Authoring Agent: Converts natural language instructions into executable test steps, simplifying complex test creation.
- Cross-Browser & Mobile Testing: Run tests on real devices and browsers in the BrowserStack cloud for comprehensive cross-platform coverage.
- Data-Driven Testing: Run the same test with different input datasets for broader scenario coverage without duplicating tests.
- Reusable Modules: Save and reuse common sequences of steps across multiple test cases, simplifying maintenance.
- API Step Integration: Add API calls directly into tests for tasks like data generation, test setup, and database cleanup.
- Test Scheduling & CI/CD Integration: Schedule automated tests or trigger them from CI pipelines via REST APIs, ensuring continuous validation.
- Test Editing Without Re-Recording: Modify test steps directly without re-recording the entire test, saving time during maintenance.
Challenges and Limitations of Low-Code Development
Even though low-code development brings myriad benefits, it also comes with certain limitations and challenges:
- Restricted Flexibility: One of the most significant challenges of low-code development is its partial flexibility. While low-code platforms offer pre-built modules and templates for speedy development, these elements might only sometimes be fully customizable to meet precise and intricate business requirements.
- Limited Control: Ease of usage comes at the cost of fine-grained control over the app development procedure. Advanced developers accustomed to old coding practices may find it tough to control the app’s complexities completely.
- Security Concerns: Security is a crucial consideration in development. Although reputable low-code providers implement strong security features, companies should remain vigilant and guarantee their apps are protected adequately from potential data breaches and cyber-security threats.
- Performance Limitations: While low-code platforms prioritize ease of development every so often, they might not optimize performance to a similar extent.
Best Practices and Tips for Successful Low-Code Development
To ensure successful low-code development, following key best practices is essential for efficient and reliable app delivery:
- Plan Before You Start: Define requirements, identify key features, and decide on the UI design upfront.
- Choose the Right Platform: Select a low-code platform that is easy to use, flexible, scalable, and integrates well with other systems.
- Keep It Simple: Leverage the simplicity of low-code development by avoiding unnecessary complexity in the app.
- Maintain Coding Standards: Even in low-code environments, follow best practices for readability, consistency, and maintainability of the codebase.
- Prioritize Security: Implement industry-standard security protocols to protect sensitive data and prevent vulnerabilities.
- Adopt Agile Methodologies: Use agile techniques to break the development process into manageable sprints for quicker bug detection and resolution.
- Document Your App: Ensure thorough documentation of the app’s features, functions, and customizations for easy management and collaboration.
- Rigorous Testing: Conduct extensive testing, including visual and cross-browser tests, to ensure the app functions well across different platforms. Low-code automation testing accelerates this process by minimizing manual coding, making it accessible to testers with limited programming experience.
Differences between Low Code and Traditional Application Development
Low-code development enables rapid application creation through visual interfaces, reducing the need for extensive coding, unlike traditional development.
While traditional development relies on professional developers’ custom coding providing highly customized solutions, Low code development allows both technical and non-technical users to participate in the development process.
Traditional development requires longer development times and deeper technical expertise compared to low code development.
| Aspect | Low-Code Development | Traditional Application Development |
|---|---|---|
| Coding Requirement | Minimal coding; uses visual tools | Extensive coding; relies on manual coding |
| Speed of Development | Faster; allows rapid prototyping and deployment | Slower; requires detailed, step-by-step coding |
| Target Users | Developers and non-developers | Primarily professional developers |
| Customization Flexibility | Limited to pre-built components | Highly customizable with full control |
| Maintenance | Easier updates through platform management | Manual updates and patch management |
| Cost | Generally lower; reduced development costs | Higher; involves extensive development resources |
| Application Complexity | Best suited for simpler, standard applications | Suitable for complex, custom solutions |
| Scalability | May have scalability limits due to platform | Highly scalable, depending on development choices |
Conclusion
Low-code development transforms how businesses build and deploy applications. It enables rapid, cost-effective solutions without heavy coding. It speeds up development, allowing teams to iterate faster, integrate smoothly, and deliver high-value features.
For teams embracing low-code development, BrowserStack’s Low Code tool is a powerful test automation platform to ensure quality at every stage of development. With its intuitive test recorder, simply specify your URL and perform actions to auto-capture steps.
Verify complex assertions using visual validation while intelligent timeouts ensure smooth execution. Experience self-healing tests, seamless cloud execution, and easy testing on dev environments.