Low-code and no-code platforms make development easier by reducing or removing the need for coding.
Overview
Low-code helps developers create advanced applications with minimal coding, while no-code allows users to build applications using visual tools. Both options speed up development and improve efficiency, reducing dependence on traditional coding.
Key Differences:
- Coding Requirement: Low-code requires minimal coding, while no-code requires none.
- Flexibility: Low-code offers customization, whereas no-code is limited to predefined functions.
- Target Users: Low-code suits developers, whereas no-code is for non-technical users.
- Use Cases: Low-code for complex applications, while no-code for simple workflows.
- Scalability: Low Code supports enterprise apps, whereas no-code is best for small-scale projects.
Knowing the differences between low-code and no-code helps teams pick the right platform. The choice depends on technical needs and business goals.
This article breaks down Low Code vs No Code, their differences, benefits, use cases, and how they compare to traditional automation. It also covers choosing the right approach for development and testing
What is Low-Code?
Low-code is a software development method that allows users to develop applications with minimal coding and technical expertise. It uses visual interfaces, drag-and-drop features, and pre-built templates to accelerate application development.
Low-code platforms empower professional developers and business users to build and test applications without deep programming knowledge.
The core concept of low-code is to simplify the development and testing process by reducing the complexity and time typically required for traditional coding. Low-code platforms simplify application creation by abstracting code and providing visual tools for designing interfaces, workflows, and data models.
Read More: Comprehensive Guide to Low-Code Development
Examples of Low-Code Development Platforms:
- OutSystems: A powerful platform for quickly building web and mobile applications with full-stack development tools.
- Mendix: A cloud-based platform enabling rapid app development, integration, and collaboration for both business users and developers.
- Appian: A low-code platform focused on process automation, allowing users to build apps, automate workflows, and integrate systems with minimal coding.
What is No-Code?
No-code code is an approach that allows users to create and test applications without writing any code.
No-code platforms enable users, often business professionals or citizen developers, to build fully functional applications without needing programming skills by using visual interfaces, drag-and-drop components, and pre-built templates.
Unlike low-code platforms, which may still require some coding for complex features, no-code platforms are designed to be entirely code-free, making them accessible to non-technical users.
Read More: Why is no-code the future of testing?
Examples of No-Code Platforms
- Webflow: A no-code platform for building responsive websites with a visual interface. It is ideal for users with no programming experience.
- Bubble: Allows users to create fully interactive web applications through a drag-and-drop interface without writing code.
- Adalo: Provides an intuitive drag-and-drop interface for designing and deploying mobile apps for Android and iOS.
Difference between Low-code and No-code
The table below shows the difference between Low-Code and No-Code
| Aspect | Low-Code | No-Code |
|---|---|---|
| Target Users | Helps developers streamline the development process by reducing coding effort, enabling focus on more complex tasks. | Designed for business users with little or no coding skills, simplifying automation and app creation. |
| Use Cases | Ideal for applications requiring complex logic, API integrations, and enterprise-level functionality. | Best suited for front-end applications, internal tools, and simple business automation tasks. |
| Speed | Faster than traditional coding but requires some training for effective customization. | Extremely fast, with intuitive drag-and-drop functionality. |
| System Type | Open system, allowing code extensions, custom plugins, and greater flexibility. | Closed system, with limited customization options, relying on templates and built-in tools. |
| End-to-End Development | Full development capabilities, offering a wide range of customization and integration options. | Some platforms may have limited features, especially in areas like back-end customization. |
| Shadow IT Risk | Lower risk as IT teams generally manage security, governance, and compliance. | Higher risk due to non-IT users creating unsecured apps without oversight. |
| Scalability & Architecture | Supports large-scale applications, works across multiple platforms, and offers better customization options. | Limited scalability, best suited for small, standalone applications or internal tools. |
Benefits of Low-Code Platforms
Low-code platforms empower developers to accelerate application development by minimizing the need for manual coding. They combine flexibility with simplicity, allowing teams to build robust applications faster and more efficiently.
- Faster Development: Low-code platforms speed up the development process by automating repetitive tasks and providing pre-built components, enabling teams to launch applications more quickly.
- Greater Flexibility and Customization: Unlike no-code platforms, low-code tools allow developers to write custom code when necessary, offering more control over the application’s functionality and appearance.
- Reduced Development Costs: By automating manual coding tasks and enabling collaboration between business users and developers, low-code platforms help reduce the need for large development teams, lowering costs.
- Seamless Integration: Low-code platforms allow easy integration with existing systems and third-party services, ensuring the application works well with other tools used by the business.
- Improved Collaboration: These platforms enable collaboration between IT teams and business users, fostering innovation and making it easier to align technical solutions with business needs.
Benefits of No-Code Platforms
No-code platforms offer a streamlined approach to application development, allowing non-technical users to create apps without writing any code. This opens up new possibilities for business teams to rapidly prototype and deploy solutions.
- Empowerment for Non-Technical Users: No-code platforms democratize app development by enabling business users or “citizen developers” to create applications without relying on developers.
- Faster Prototyping and Deployment: These platforms allow for rapid prototyping, enabling teams to quickly turn ideas into fully functional applications without waiting for development cycles.
- Cost Savings: With no need for professional coding expertise, businesses can save on development and maintenance costs. Non-technical users can independently create and modify applications, reducing the reliance on development teams.
- Increased Agility: No-code platforms allow businesses to adapt quickly to changing needs by enabling fast modifications and iterations to applications, enhancing organizational agility.
- Simple Maintenance: Applications built on no-code platforms are easier to maintain, as non-technical teams can update and modify the app without the need for a specialized developer.
Read More: AI Automation and Testing
Low-Code vs No-Code: Similarities
Both low-code and no-code platforms offer simplified ways to build applications, aiming to reduce the need for manual coding. While they cater to different user needs, they share several similarities that make them appealing for businesses looking to accelerate development.
| Feature | Low-Code | No-Code |
|---|---|---|
| Target Users | Developers with limited coding skills | Non-technical users, “citizen developers” |
| Ease of Use | Drag-and-drop interface, with custom code options | Drag-and-drop interface, no coding required |
| Development Speed | Fast, but with the option for advanced customization | Very fast, ideal for rapid prototyping |
| Integration with External Tools | Seamless integration with APIs and systems | Limited, but includes pre-built integrations |
| Automation | Automates repetitive tasks, some manual intervention required | Fully automated, no manual coding needed |
| Customization | Custom coding available for complex functionality | Limited customization, mostly for simple applications |
Low-Code vs. No-Code: What to Choose for Development?
The right choice depends on project complexity, customization, and scalability. Here’s a comparison to help you determine which platform suits your development needs:
- For Simple Applications: No-code platforms are ideal for quickly building simple apps or automating basic processes with minimal learning. They’re perfect for business users and small, front-end applications.
- For More Complex Applications: Low-code platforms provide more customization, advanced logic, and integrations. They balance simplicity and flexibility, allowing developers to add custom code for complex workflows.
- Skillset Consideration: No-code is best for non-technical teams needing quick prototypes. Low-code is suitable for teams with technical expertise or those requiring custom features.
- Project Scale and Growth: Low-code platforms offer better scalability and integration for larger projects. No-code works well for smaller apps but may struggle with scaling.
Must Read: Why No Code is the Future of Testing
Low-Code vs. No-Code: What to Choose for Testing?
The choice between low-code and no-code for testing depends on your project’s complexity and your team’s expertise:
- For Simple Testing: No-code platforms are ideal for basic tests, like UI testing or automating repetitive tasks. These platforms are user-friendly and great for non-technical testers or teams needing quick results.
- For Advanced Testing: Low-code platforms are better suited for complex testing scenarios, such as load testing, performance testing, or testing applications with complex logic and integrations. They provide more flexibility and control, allowing testers to customize scripts and integrate with other testing tools.
- Skillset Consideration: No-code is great for testers with limited technical knowledge, while low-code platforms require more technical expertise but offer greater customization.
- Scalability: Low-code platforms are better for large-scale, enterprise-level testing that requires extensive automation and integration. No-code platforms, while fast and easy to use, may not scale well for more complex or resource-intensive testing.
In short, no-code platforms are best for simple, quick tests, while low-code platforms are ideal for advanced, scalable testing needs.
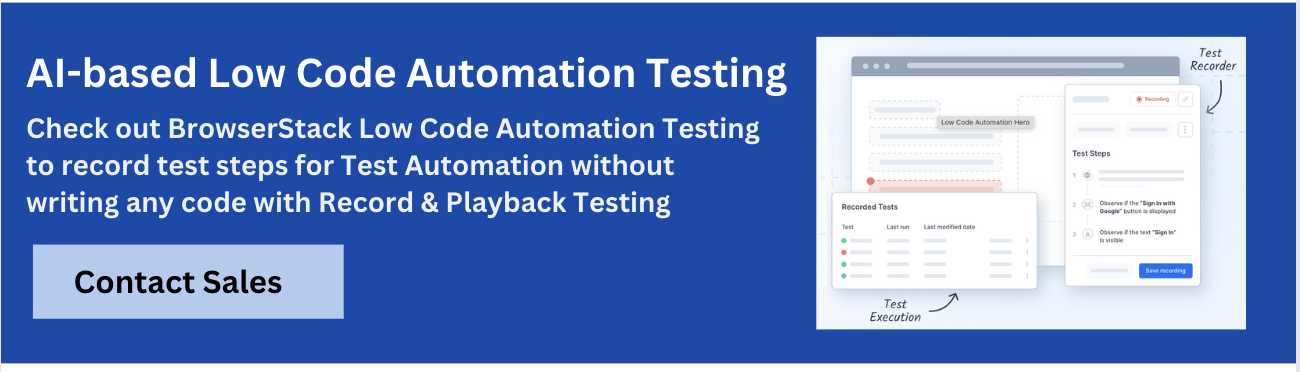
To ensure seamless test execution, BrowserStack offers a Low-Code Automation platform that reduces coding efforts while maintaining flexibility. It allows users to create and run AI-driven automated tests without coding, ensuring seamless execution on the BrowserStack cloud.
Why Use BrowserStack for Low-Code Automation?
BrowserStack Low-Code Automation enables teams to create, execute, and manage automated tests without requiring any complex coding.
It combines an interactive test recorder, AI-powered self-healing, and real-device cloud testing, making it easy to start automation and scale across different browsers and devices.
With AI-powered self-healing and low-code authoring agents, it accelerates test creation by up to 10x and reduces build failures by 40%, delivering faster, more stable automation for both technical and non-technical users.
Key Features of BrowserStack Low-Code Automation:
- Test Recorder: Capture user actions such as clicks and form inputs, which are automatically transformed into automated tests. This recorder supports complex functional validations, including both visual and text checks.
- Readable Test Steps: Actions are recorded and converted into simple, human-readable English instructions, making it easy for anyone to understand and modify tests.
- Visual Validation: Testers can add checkpoints during recording to verify that UI components and screens display correctly, ensuring visual elements meet expectations.
- AI-Powered Self-Healing: Uses AI to detect when UI elements change and automatically update the test, preventing failures and reducing the need for manual maintenance.
- Low-Code Authoring Agent: Leverages AI to turn natural language prompts into executable test steps, simplifying the process for non-technical users to automate tasks from simple instructions.
- Cross-Browser & Mobile Testing: Runs tests on real desktop browsers and mobile devices across a wide range of operating systems and devices, leveraging the BrowserStack cloud for seamless coverage.
- Data-Driven Testing: Allows the same test to be executed with different input values, expanding coverage across various test scenarios without duplicating efforts.
- Reusable Modules: Teams can save commonly used sequences of steps as reusable modules, reducing duplication and making test maintenance simpler.
- API Step Integration: Adds flexibility by enabling testers to call APIs within tests for tasks like generating data, setting up conditions, or cleaning up databases.
- Test Scheduling and CI/CD Integration: Enables automated tests to run on a set schedule or trigger directly from build pipelines via REST APIs or CI tools, ensuring continuous validation without manual intervention.
- Test Editing Without Re-Recording: Testers can modify existing tests by adding, inserting, or deleting steps without having to re-record the entire test, saving time and effort during maintenance.
How is Low-code and No-code different from Traditional Automation?
Low-code, no-code, and traditional automation differ significantly in their approach, complexity, and accessibility:
1. Development Approach:
- Low-Code/No-Code: These platforms use pre-built components and visual interfaces, allowing users to drag and drop elements to build applications or workflows. Minimal coding is required, making them accessible to both technical and non-technical users.
- Traditional Automation: Traditional automation relies heavily on coding, requiring skilled developers to write scripts or use specialized tools to automate processes, which demands more technical expertise.
2. Complexity and Flexibility:
- Low-Code/No-Code: These platforms are designed to simplify development and automate tasks with less customization. While they provide flexibility, they may not support the complex workflows or custom logic required for more intricate processes.
- Traditional Automation: Traditional automation offers more flexibility and customization, allowing developers to create highly complex automation scripts tailored to specific needs. However, it comes at the cost of higher complexity and longer development time.
3. User Accessibility:
- Low-Code/No-Code: They empower non-technical users to build applications and automate workflows without needing coding skills, making them accessible to a wide range of users within an organization.
- Traditional Automation: This typically requires technical expertise and is usually performed by experienced developers or engineers, limiting its accessibility to a smaller pool of users.
4. Speed of Development:
- Low-Code/No-Code: These platforms accelerate the development process by simplifying tasks and reducing the need for custom coding. Users can quickly create and deploy automation workflows with minimal effort.
- Traditional Automation: It usually takes longer, as it involves coding, testing, and debugging, making the process more time-consuming.
5. Customization:
- Low-Code/No-Code: While these platforms offer some customization, they may be limited in handling complex automation scenarios that require custom logic or integration with specialized systems.
- Traditional Automation: Customization is more extensive in traditional automation, as developers have full control over the code, allowing for deep integrations and highly tailored solutions.
Limitations of Low-Code/No-Code Platforms
While low-code/no-code platforms offer significant benefits, they also come with several limitations that organizations should be aware of before fully relying on them. These include:
- Customization Constraints: Limited ability to implement complex features or advanced business logic, making them unsuitable for highly customized applications.
- Scalability Issues: As applications grow, these platforms may face performance issues, limiting their scalability and flexibility for large projects.
- Vendor Lock-In: These platforms often create dependency on specific vendors, making it challenging to migrate or integrate with other systems in the future.
- Security Risks: Limited control over infrastructure and data security can pose risks, particularly for applications dealing with sensitive information.
- Limited Integration: Integration options with legacy systems or third-party tools may be restricted, affecting functionality and workflow.
Best Practices of Low-Code/No-Code Platforms
To get the most value out of low-code/no-code platforms, it’s important to follow best practices that ensure success and avoid common pitfalls. Here are some key best practices:
- Define Clear Objectives: Clearly outline your project’s requirements and limitations to avoid overloading the platform’s capabilities and ensure realistic expectations.
- Governance and Security: Implement strong governance and security measures, especially when handling sensitive data or business-critical processes.
- Regular Testing: Continuously test and iterate on applications to ensure that they perform well and scale effectively as needs change.
- User Training: Provide adequate training for both technical and non-technical users to ensure smooth development and maintenance.
- Combine with Traditional Development: For complex projects, integrate low-code/no-code platforms with traditional development practices to fill any functionality gaps.
Also Read: 12 Open source Low Code Testing Tools
Conclusion
Choosing between Low-Code and No-Code development platforms depends on project needs and user expertise. No-code platforms are ideal for business users, enabling quick automation and app development without IT support. However, they may have limitations in customization and scalability.
Low-code platforms, on the other hand, offer greater flexibility. Developers can build complex applications faster while integrating custom features and scaling efficiently. Understanding both options helps teams make the right choice for speed, control, and efficiency.
BrowserStack provides a low-code automation platform to ensure seamless testing. With real device testing, cross-browser compatibility, and seamless CI/CD integrations, BrowserStack helps teams validate applications effortlessly, ensuring development quality, speed, and reliability.