REST APIs connect front-end applications with backend services and enable data exchange across platforms. They are widely used in web and mobile apps for authentication, data transfer, content delivery, and third-party integrations.
Overview
Why Should You Secure Your REST API?
Unsecured REST APIs expose sensitive data, allow unauthorized access, and create entry points for attacks like injection or data tampering. Securing your REST API helps:
- Prevent data breaches: Unprotected APIs can leak sensitive user or business data to attackers.
- Avoid unauthorized access: Without strict access control, attackers can exploit endpoints and take actions they shouldn’t.
- Meet compliance standards: Regulations like GDPR or HIPAA require strong protections for APIs that handle personal data.
- Stop abuse and misuse: Lack of rate limits or auth checks can lead to scraping, spam, or DDoS attacks.
Best Practices to Secure Your REST API
Apply these techniques to protect your API from unauthorized access, data leaks, and misuse:
- Use HTTPS to encrypt all data in transit and prevent interception or tampering.
- Enforce authentication with API keys, tokens, or OAuth to block anonymous access.
- Apply role-based access control to restrict users to only the actions they’re allowed to perform.
- Validate and sanitize inputs to stop injection attacks and prevent logic manipulation.
- Limit request rates with throttling or rate limiting to defend against brute-force and abuse.
This article highlights key design principles and best practices to secure your REST API.
What Is a REST API?
A REST API (Representational State Transfer API) is a set of architectural rules that lets applications communicate over HTTP. It allows clients such as browsers, mobile apps, or external systems to interact with backend servers using standard methods like GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE.
REST APIs are stateless and resource-based, meaning each endpoint corresponds to a specific data object or operation. They are used in modern applications for tasks like user login, data access, updates, system integrations, and more.
Why Do You Need to Secure Your REST API?
Without proper security, your REST API becomes an easy entry point for attackers to access data, abuse functionality, or disrupt services.
Here’s what can go wrong if your API is not secured:
- Account takeovers: Weak or missing authentication controls allow attackers to log in as real users, access personal data, perform unauthorized actions, or escalate privileges across the system.
- Data leaks: APIs that return complete data objects without filtering can accidentally expose sensitive fields like user roles, internal flags, or email addresses, which attackers can use to map the system or plan privilege escalation.
Also Read: What is API Testing? (with Examples)
- System overloads: Without rate limiting or throttling, bots or malicious users can flood your API with requests, leading to performance degradation, increased server costs, or complete outages through denial-of-service attacks.
- Backend compromise: If your API accepts unvalidated inputs, attackers can craft payloads that trigger SQL, NoSQL, or command injections, which can expose data, modify records, or even let them run arbitrary code on your backend.
- Credential theft: Serving your API over plain HTTP or using misconfigured TLS exposes sensitive information like passwords and tokens during transmission, especially when using public or shared networks.
- Code exploitation: Using outdated libraries or frameworks leaves known vulnerabilities open, and attackers can use freely available tools and public exploit databases to compromise your API without much effort.
REST API Security Design Principles
Security principles define how access should be granted, how data should be protected, and how the system should respond to various access scenarios. Follow these principles during the design phase to reduce risk.
1. Least Privilege
The Principle of Least Privilege (PoLP) is a security concept where users, applications, and systems are granted only the minimum level of access needed to perform specific tasks.
This reduces the chances of accidental misuse, limits insider threats, and contains the damage if an account is compromised. Even if attackers gain access to a low-privilege account, they can only reach a limited part of the system.
To implement the Least Privilege Principle effectively:
- Define roles based on specific job responsibilities and assign only the minimum permissions required for each role.
- Use role-based access control (RBAC) to apply access rules consistently across users and systems.
- Regularly audit permissions to identify unused or excessive access and remove anything unnecessary.
- Enforce time-bound or just-in-time access so elevated privileges are granted only when needed and automatically revoked afterward.
2. Explicit Permissions
Explicit permissions mean access must be intentionally granted before it can be used, and that no user or system should have access to any resource by default. This helps prevent accidental exposure or misuse caused by overly broad or automatic access.
To enforce explicit permissions:
- Set all access to “deny” by default and require explicit approval or configuration to enable it.
- Define and document access policies clearly before granting any permissions or deploying new components.
- Use centralized permission management to avoid inconsistencies across different APIs or services.
- Review the default settings in your API platform or gateway to ensure they prevent unintended access or data exposure.
3. Access Validation at Every Request
Every API request should be independently verified on the server, even if it comes from the same user or session. To prevent misuse, the server must validate the authentication token, confirm the user’s access rights, and ensure the token is still active and within scope.
To apply access validation:
- Always include a valid authentication token (such as OAuth2 or JWT) with each API request.
- Verify the token’s integrity, expiration time, and access scope on the server before allowing any operation.
- Avoid storing or enforcing permissions on the front end, as client-side checks can be bypassed.
- Reject requests if the token is missing, malformed, expired, or outside the allowed scope.
Read More: How to Test Two-Factor Authentication
4. Segregation of Data Privileges
Data privileges segregation ensures that users can only access the information relevant to their role or clearance level. This reduces unnecessary internal exposure and limits the impact of account compromise by keeping sensitive data isolated from general access.
To implement data privilege segregation:
- Tag and classify data based on sensitivity, then apply access controls according to those classifications.
- Design APIs to return different data views based on user roles, limiting what each role can see or retrieve.
- Enforce data access rules at the backend to prevent bypassing restrictions through direct API calls.
- Combine role-based access control (RBAC) with attribute-based access control (ABAC) for more fine-grained control.
Best Practices to Secure Your REST API
Apply these practical methods to reduce risk, protect sensitive data, and build secure systems.
1. Use HTTPS for All API Traffic
REST APIs often transmit sensitive data like login credentials, access tokens, or personal user information. If this data is sent over an unencrypted connection (HTTP), attackers can easily intercept it using tools like packet sniffers or man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks. HTTPS encrypts this data during transit, making it unreadable to anyone who intercepts it.
To enforce HTTPS properly across all API calls:
- Set up an SSL/TLS certificate for your domain using a trusted certificate authority (CA) like Let’s Encrypt or DigiCert.
- Redirect all HTTP traffic to HTTPS using web server rules or gateway policies.
- Use HSTS headers to ensure clients never downgrade to HTTP after the first secure connection.
- Block requests that come over HTTP instead of silently accepting them.
2. Sanitize and Validate All Inputs
REST APIs often accept input through query parameters, request bodies, or headers. If this input is not validated correctly or checked for malicious content, attackers can exploit it using techniques like SQL injection, command injection, or cross-site scripting (XSS). These attacks can compromise backend systems, expose sensitive data, or impact other users.
To prevent injection or malformed input attacks:
- Define strict input schemas using tools like Joi or JSON Schema to enforce expected structure and data types.
- Use whitelisting to allow only valid characters or formats, especially for fields like email addresses, IDs, or dates.
- Escape or encode special characters before using user input in SQL queries, log files, or API responses to avoid injection and XSS.
- Reject any unexpected fields or incorrect data types early in the request lifecycle to stop invalid input from reaching your backend.
3. Secure Authentication Mechanisms
Authentication is the first layer of defense for your API. If it’s poorly implemented, attackers can impersonate users, access sensitive data, or perform actions they’re not authorized to. REST APIs should use token-based authentication instead of traditional session-based methods to support stateless and secure communication.
To implement secure authentication:
- Use established standards like OAuth 2.0 or JWT to issue and validate access tokens.
- Store passwords using strong hashing algorithms such as bcrypt or Argon2 and never store them in plain text.
- Limit login attempts to prevent brute-force attacks, and consider using CAPTCHA after repeated failures.
Also Read: Captcha Test Case
- Never expose access tokens, API keys, or secrets in client-side code, URLs, or browser storage.
4. Validate and Sanitize All Inputs
REST APIs often receive input from external sources through query parameters, request bodies, or headers. If these inputs aren’t properly validated or cleaned, attackers can use them to inject malicious commands, bypass logic, or alter system behavior. This can lead to severe vulnerabilities like SQL injection, remote code execution, or data leaks.
To protect your API from unsafe inputs:
- Validate all inputs by enforcing strict data types, formats, and value ranges.
- Use allowlists to define precisely what input is permitted, rather than relying on denylists to block known bad values.
- Sanitize inputs by escaping or removing special characters before using them in SQL queries, logs, or HTML responses.
Read More: A Detailed Guide on HTML Semantics
- Reject any requests containing malformed, unexpected, or extra fields that don’t match your schema.
5. Rate Limit and Throttle Requests
APIs are often targeted by automated traffic that can slow down or crash systems. This includes brute-force login attempts, data scraping, enumeration attacks, or repeated access to resource-intensive endpoints. Without proper limits in place, a single client or bot can overwhelm your backend.
To implement effective request control:
- Set per-user and per-IP rate limits using API gateway tools such as Kong, AWS API Gateway, or Azure API Management.
- Return appropriate error responses like HTTP 429 (Too Many Requests) when limits are exceeded.
- Include headers like Retry-After to inform clients when they can safely retry a request.
- Monitor traffic to detect sudden spikes, abnormal request patterns, or signs of abuse, and block or throttle as needed.
6. Avoid Sensitive Data Exposure
APIs often return data pulled directly from internal systems. If not carefully controlled, these responses may include sensitive fields such as credentials, tokens, internal IDs, or configuration details. Attackers can use this information to map your system, escalate access, or exploit weaknesses.
To prevent overexposing sensitive data:
- Return only the necessary fields by applying response filtering or field-level access rules.
- Mask, redact, or omit sensitive information such as passwords, tokens, internal flags, and debug messages.
- Log data securely by removing or obfuscating sensitive fields before storing or sharing it.
- Review API responses regularly during development and testing to identify and eliminate unintentional data leaks.
7. Implement Authorization Checks on Every Endpoint
Authentication confirms who the user is, but it doesn’t determine what they’re allowed to do. Every API endpoint must enforce authorization to ensure users can only access the data and actions their role permits.
To enforce strict authorization:
- Apply role-based or scope-based access control at the endpoint or method level.
- Perform all permission checks on the server to ensure users cannot bypass restrictions using tools like browser dev tools or direct API calls.
- Use middleware or access control libraries to apply consistent and centralized permission checks.
- Log failed authorization attempts to detect suspicious activity, abuse, or access probing.
Also Read: Top 20 API Testing Tools
8. Throttle Requests to Prevent Abuse
Bots can flood your API endpoints with login attempts, scrape large volumes of data, or exhaust server resources in denial-of-service (DoS) attacks. Throttling limits how often clients can make requests, helping you block abuse and maintain system stability.
To implement request throttling effectively:
- Set rate limits based on IP address, user identity, or access token using an API gateway or server-side middleware.
- Respond with HTTP 429 (Too Many Requests) when the client exceeds the allowed limit.
- Include the Retry-After header in the response to let clients know when they can try again.
- Use both burst and sustained rate models to handle sudden spikes while controlling total usage.
9. Configure Programmatic Data Access with API Keys
While browser-based API requests can use session tokens or SSO, programmatic clients like scripts, backend services, or third-party integrations often need a different authentication method. API keys provide a simple and secure way to authenticate non-interactive systems without relying on browser sessions or user login flows.
To securely configure programmatic access:
- Generate a unique API key for each user, system, or integration that needs direct access.
- Store the API key securely in your backend, linked to access rules or roles.
- Validate incoming API keys on the server and reject any request with a missing, expired, or mismatched key.
- Avoid displaying or logging API keys, and support key rotation when needed.
How to Secure Your REST API in the Development Stage
To build secure APIs, you must embed security across your entire development workflow, not just at runtime. This includes your code, configuration, pipelines, and testing practices.
Here’s how to secure your REST API in the development process.
1. Add Security Checks to CI/CD Pipelines
CI/CD pipelines automate the build and deployment process, making them ideal for early API security enforcement. If security checks are skipped here, issues like vulnerable dependencies, leaked secrets, or insecure configs can reach production.
Here’s how to secure your CI/CD process:
- Scan third-party libraries and dependencies for known vulnerabilities during each build.
- Add automated secret detection to flag hardcoded tokens, passwords, and keys in source code or configuration files.
- Set rules to block builds automatically if high-risk security issues are found, so they can be fixed before release.
2. Run Regular Security Audits and Pen Tests
While automated tools help catch common vulnerabilities, they often miss issues that require a deeper understanding of application logic or system behavior. Regular security audits and penetration tests help uncover flaws in access control, misconfigurations, or integration points that automated scans cannot detect.
To strengthen your API security:
- Schedule penetration tests before major releases, architectural changes, or after onboarding third-party services.
- Review access logs, audit trails, and error reports regularly to spot unusual behavior or unauthorized activity.
- Check headers, TLS settings, and rate-limiting rules to ensure they are correctly configured and up to date.
- Test authentication and authorization flows to confirm users can only access data and actions allowed by their roles.
Read More: What is Black-Box Penetration Testing?
3. Use Threat Modeling in Early Development
Threat modeling helps teams anticipate attacks by mapping out risks before any code is written. It identifies critical assets, entry points, and potential abuse cases. This proactive approach reduces rework and tightens design-level security from day one.
To apply threat modeling during development:
- Identify all API entry points, data flows, and integration touchpoints during the design phase.
- Document attacker goals and potential ways each part of the API could be misused or exploited.
- Involve developers, testers, and security engineers to review and refine the model collaboratively.
- Revisit and update the model whenever features, access rules, or external integrations change.
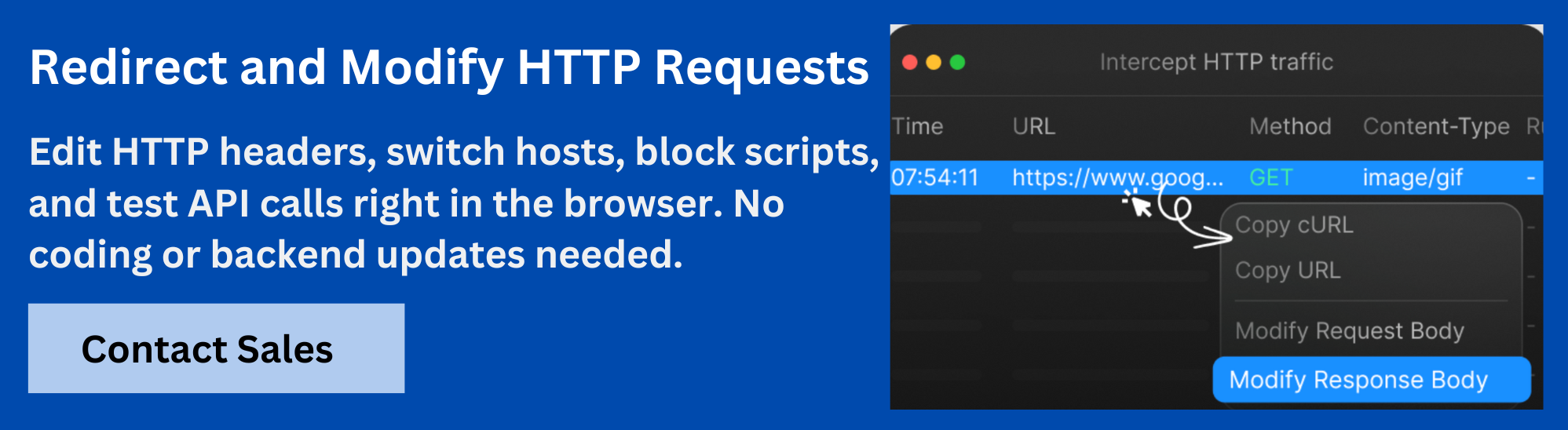
How Requestly Helps Test REST API Security
Requestly by BrowserStack is a cloud-based tool that lets you intercept, inspect, and modify HTTP requests and responses directly in your browser. It helps developers and testers simulate different scenarios to check how an API behaves under various conditions, without changing backend code or setting up complex testing environments.
Requestly’s HTTP Interceptor supports API security testing by allowing you to:
- Modify authorization headers to verify that unauthorized requests are blocked properly.
- Change input parameters in the request body or query string to test how the API handles incorrect or unexpected data.
- Alter API responses to simulate error conditions and verify that sensitive data is not exposed.
- Simulate network delays and blocked requests to test rate limiting and error handling.
- Redirect URLs or switch domains to validate CORS policies and cross-origin access controls.
Conclusion
Securing your REST API is essential to protecting sensitive data, maintaining user trust, and preventing unauthorized access or attacks. Apply strong authentication, input validation, rate limiting, and proper authorization throughout your API to build a robust defense against common threats.
Use Requestly by BrowserStack to verify these security measures and intercept and modify HTTP requests and responses in real time. Requestly lets you simulate attack scenarios, manipulate inputs and headers, and inspect responses, which helps you uncover weaknesses and improve your API security.