Your test suite is only as reliable as the browser it runs on.
I have spent years scaling automated tests, and the choice between headless browser testing vs real browser testing still stands as one of the biggest questions. The choice affects speed, stability, coverage, and the number of bugs that slip through.
This matters for teams that ship fast and cannot afford flaky tests or slow feedback loops.
Overview
What is Headless Testing?
The browser executes automated test scripts silently in the background without a visible GUI.
What is Real Browser (Headed) Testing?
The browser executes automated test scripts on a full, visible instance with the UI displayed.
Key Differences Between Headless and Real Browser Testing
- Speed: Headless tests run faster since there is no UI rendering, while real browser tests take longer due to full rendering.
- Resource usage: Headless testing consumes fewer CPU and memory resources, whereas real browsers are more resource intensive.
- Debugging: Real browser testing allows visual debugging and UX validation, which headless testing cannot provide.
- Accuracy: Real browsers deliver pixel-perfect rendering and true user behavior, while headless testing may miss visual issues.
If you are an SDET, QA lead, engineering manager, or developer in a growing engineering org, this guide is for you. It breaks down what truly works at scale and how to choose the right approach. Let’s start with the fundamentals.
Headless vs Real Browser Testing- Comparison Table
| Feature | Headless Approach (Self-Managed) | Real Browser Testing with BrowserStack Automate (Managed Cloud) |
| Testing Realism | Low. Fails to catch visual bugs, layout shifts, or rendering issues that only appear with a full Graphical User Interface (GUI). | High. Tests run on real, headed browsers and real devices, replicating the actual end-user experience. |
| Mobile Coverage | Limited to simulators/emulators; no true real device conditions. | 3,500+ Real Devices (Android, iOS) and OS combinations, with guaranteed Day 0 access to new devices. |
| Maintenance/Setup | High Overhead. Requires constant manual setup, patching, and scaling of Docker containers, browser binaries, and OS libraries. | Zero Infrastructure Maintenance. BrowserStack manages the entire cloud fleet; you just run your tests. |
| Debugging | Difficult. Relies only on logs and screenshots. No live visual debugging for complex UI issues. | Easy & Fast. Provides test videos, logs, and screenshots instantly. Seamlessly integrates with debugging tools. |
| Parallel Scaling | Limited by the resources (CPU/RAM) of your local machine or self-managed grid. | Massive, instant parallel execution across a secure, global cloud fleet for rapid CI/CD feedback. |
| Best Use Case | Quick, early-stage functional checks and unit testing. | Comprehensive cross-browser, cross-device QA and critical pre-release validation. |
What is Headless Browser Testing?
Headless browser testing means running a browser without showing the UI (User Interface). The browser still loads pages, executes JavaScript, applies CSS, and interacts with the DOM, but everything happens in the background. This gives teams a fast way to validate flows without rendering the visual layer.
How do Headless Browsers Work?
A headless browser:
- Launches the browser engine without opening a visible window
- Executes each test step programmatically
- Renders pages internally and returns logs, errors, and screenshots
- Runs efficiently inside CI pipelines because it requires fewer system resources
In short, you get the same underlying engine as Chrome or Firefox, just without the visible interface.
When to Use Headless Testing?
Headless mode is most effective in situations where speed, efficiency, and automation outweigh the need for full visual rendering:
- Rapid development feedback: Run tests instantly while coding to validate interactions and logic without waiting for a full browser window to load.
- High-throughput CI pipelines: Execute large test suites in parallel with lower resource consumption, cutting down overall pipeline time.
- Lean smoke and sanity checks: Quickly verify that core user journeys work before investing time in more comprehensive, visually accurate tests.
- Automated, non-visual UI validations: Trigger UI tests through APIs or workflows where confirming behavior matters more than pixel-perfect rendering.
It speeds up pipelines but does not fully represent how users interact with your product.
What are the Popular Tools and Frameworks that support Headless testing?
Headless execution is widely supported across modern testing ecosystems. Below are the most prominent tools along with what makes them effective for headless workflows:
- Playwright: A next-gen automation framework from Microsoft with built-in headless support across Chromium, Firefox, and WebKit. It excels at fast parallel execution, auto-wait mechanisms, and stable cross-browser testing-making it one of the strongest choices for CI-heavy teams.
- Puppeteer: Google’s Node.js library that provides direct control over Chrome and Chromium. Its API is tightly aligned with the Chrome DevTools Protocol, offering highly reliable, fast headless execution for tasks like scraping, PDF generation, and UI validation.
- Selenium (Chrome & Firefox Headless): The long-standing industry standard for browser automation. Through browser-specific flags, Selenium lets you run existing test suites headlessly with minimal changes, making it ideal for teams modernizing large legacy frameworks or scaling parallel runs.
- Cypress (Headless Run Modes): While Cypress is known for its visual test runner, it offers headless execution via the cypress run command, commonly used in CI. It’s particularly useful for running fast regression suites without the overhead of the interactive UI.
- Chrome Headless & Firefox Headless: These native headless browser modes let developers execute scripts, crawl pages, or run lightweight UI checks without any external framework. They’re a strong fit for custom tooling, performance profiling, or infrastructure-level automation.
Teams often start with headless testing to ensure speed, then move to browser automation with actual browsers to validate real-world behavior. Platforms like BrowserStack Automate let you run both headless tests and full real-browser tests at scale, using official browser engines and regularly updated environments that match real user conditions.
Limitations of Headless Testing
Headless testing is fast, but several gaps become clear as teams scale.
- Missing Real-World Rendering: Visual issues, layout differences, and GPU-dependent behaviors often do not appear in headless mode.
- Flaky Behavior for Complex UI: Dynamic components and animations can behave inconsistently, causing hard-to-reproduce failures.
- Limited Browser-Specific Coverage: Headless runs miss vendor-specific quirks and device-level differences seen in actual browsers.
- Not Suitable for Visual or UX Validation: Pixel accuracy, responsiveness, and interactive visual states cannot be reliably tested headlessly.
- Harder Debugging and Failure Analysis: Screenshots, logs, and error states may not match what users experience in real browsers.
These limitations highlight why teams rely on browser automation using actual browsers when quality and user experience matter. Let’s look at what real browser testing is and how it solves these challenges.
What is Real Browser Testing?
Real browser testing runs your automation suite in the same browsers, versions, and environments your users rely on. The browser launches with a full UI, loads pages exactly as a user would, and renders every visual and interactive element end to end.
How Real Browsers Work in Automation Testing?
Real browsers behave exactly like the browsers your users interact with-loading, rendering, and executing every part of the application stack. When used in automation, a real browser:
- Loads and renders the complete UI: It opens a full graphical window and processes HTML, CSS, JavaScript, network requests, layout calculations, animations, and GPU-driven rendering exactly as it would for an actual user.
- Performs actions through automation drivers or frameworks: Tools like Selenium, Playwright, and Cypress send commands to the browser engine, triggering real clicks, typing, navigation, and DOM interactions.
- Captures high-fidelity diagnostics: Real browsers can generate accurate screenshots, DOM snapshots, console logs, performance metrics, and network traces, enabling deep debugging of complex UI issues.
- Reflect true cross-browser behavior: Because tests run within actual browser engines (Chromium, WebKit, Firefox), they expose differences in rendering, layout, event handling, and performance across devices and configurations
This gives teams the closest possible match to real-world usage.
When to Use Real Browser Testing?
Real browsers are essential when you need full accuracy and user-level fidelity. They reproduce the complete rendering and interaction layer, making them critical for:
- Accurate end-to-end validation of user flows: Complex journeys such as checkout, onboarding, payments, or authentication require full rendering and real event handling to ensure the experience matches what users actually see.
- Cross-browser and cross-version coverage: Only real browsers reveal differences in rendering, DOM behavior, CSS handling, and performance across Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge, and their various versions.
- Visual, layout, and responsive checks: Real browsers allow you to verify pixel accuracy, breakpoints, animations, fonts, color behavior, and visual regressions. These visual aspects are often incomplete or inaccurate in headless environments.
- Reliable debugging and root-cause analysis: When a test fails in a real browser, the failure mirrors actual user behavior. This results in clearer logs, meaningful screenshots, and issues that are easier to reproduce.
- High confidence before major releases: For high-risk features, high-traffic pages, or mission-critical flows, real browsers provide the closest representation of real-world usage. This significantly reduces the chance of unexpected failures after deployment.
Any scenario where correctness matters more than raw speed benefits from real browser execution.
Why Browser Automation with Actual Browsers Matters?
Your users experience your product through real browsers on real devices, not through simplified headless engines. They rely on Chrome, Safari, Firefox, Edge, and countless mobile browsers across many devices. Testing in these real environments is the only way to see how your application truly behaves in production. This approach:
- Uncovers browser-specific quirks and rendering differences: Each browser engine interprets CSS, layout, and events in slightly different ways, and real-browser testing exposes these variations.
- Surfaces visual and UI defects early: Pixel shifts, broken layouts, missing assets, and animation issues only become visible in a fully rendered environment.
- Reduces flaky or hard-to-reproduce failures: Real browsers remove many of the timing and rendering inconsistencies that appear in headless environments.
- Increases confidence in every release: You can validate that real-world interactions match expectations, especially for high-impact features.
- Helps teams ship features that behave exactly as intended: Production behavior aligns with test results because the tests run in the same environment your users rely on.
Real browser execution becomes even more practical when teams can run these tests on reliable, always-updated environments. A cloud based infrastructure such as BrowserStack Automate provides this at scale, giving teams access to real browsers and devices without the cost of maintaining infrastructure.
Advantages of Real Browser Automation
Real browser automation gives teams the accuracy and reliability needed to ship high-quality releases with confidence.
- Full Rendering and Visual Accuracy: You see the exact layouts, styles, animations, and GPU effects that real users experience.
- Reliable Behavior for Complex UI: Dynamic components, transitions, and client-heavy interfaces behave consistently with production.
- True Cross-Browser and Cross-Device Coverage: You can validate differences across engines, versions, operating systems, and device types.
- Accurate Visual and UX Validation: Responsive layouts, pixel accuracy, and interactive UI states can be tested as intended.
- Easier Debugging and Failure Analysis: Screenshots, logs, and errors align with real user behavior, making triage faster and more precise.
Teams get the most value when real browsers are always available and kept up to date.
Why Choose BrowserStack Automate for Real Browser Testing?
Headless testing helps with speed, but it cannot deliver the accuracy and reliability modern engineering teams need. BrowserStack Automate brings both speed and real-world correctness, making it the stronger choice for teams shipping high-quality releases at scale.
Developers and testers know that nothing replaces testing on a real device. Why? Because, teams get the most value when real browsers are always available and kept up to date.
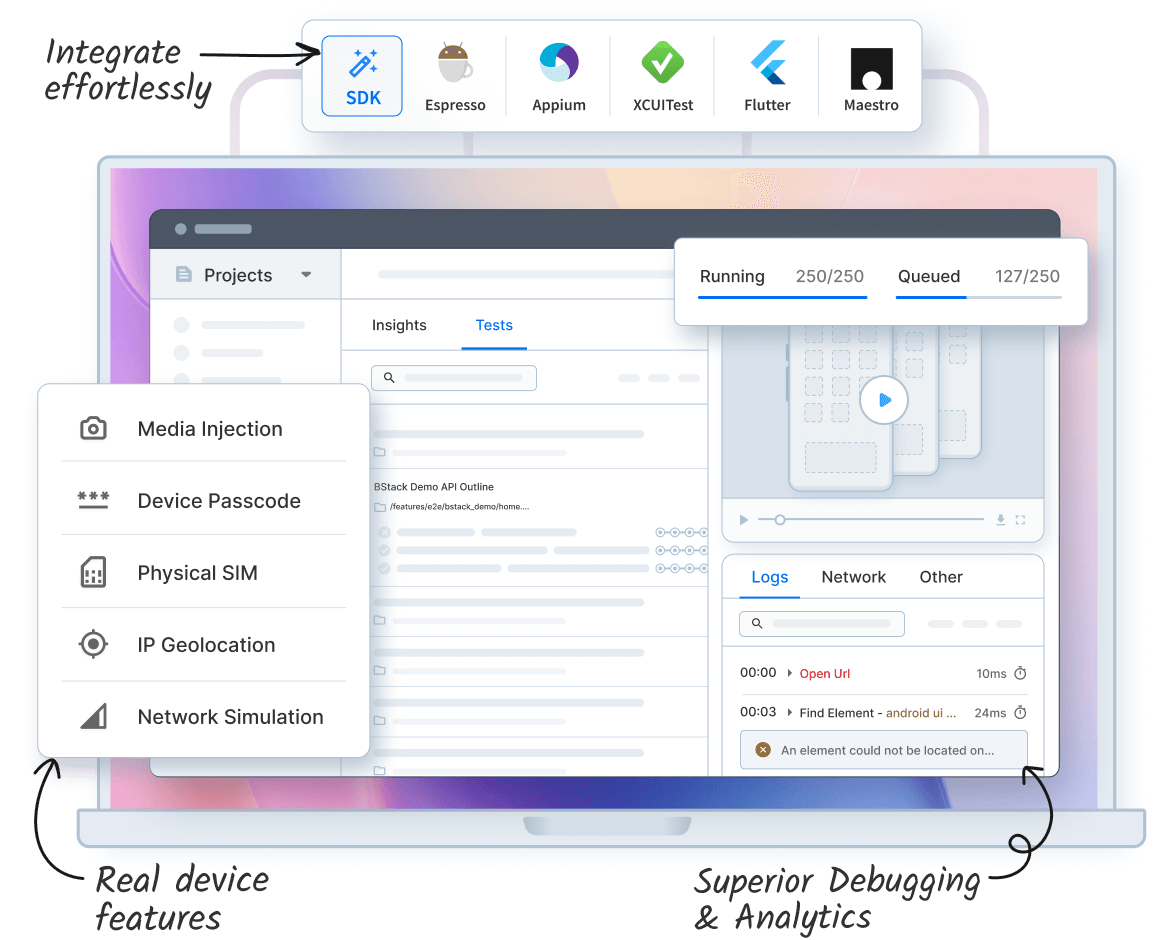
BrowserStack Automate solves this by providing a fully managed cloud of 3,500 plus real desktop and mobile browser OS combinations, allowing you to run tests at scale with no setup complexity.
Here is why you should choose BrowserStack Automate, as it offers:
1. Massive Scale and Coverage, Instantly
You need to test your application on every combination a user might have, so, BrowserStack gives you instant access to this coverage without the physical headaches.
- 3,500+ Real Devices and Browsers: Access thousands of real desktop and mobile browser-OS combinations (like the latest versions of Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and specific Android/iOS devices). This ensures you test in real-user conditions.
- Instant Scalability: Easily run hundreds or even thousands of tests in parallel. This is key for CI/CD pipelines and dramatically speeds up your build and release cycles.
- Zero Infrastructure Maintenance: You can finally say goodbye to managing, updating, and maintaining your own in-house device labs. BrowserStack handles all the heavy lifting.
- Day 0 Access: Get testing-ready on the newest devices globally on the day they launch, so your QA stays ahead of the market.
2.Seamless Integration and Zero Code Changes
BrowserStack is designed to integrate easily into your existing workflow, not replace it.
- No Code Changes Needed: You can run your existing test suites (using frameworks like Selenium, Playwright, Cypress, and Puppeteer) in the cloud platform with minimal effort. Integration is done in minutes using simple SDKs.
- Local Environment Testing: Need to test a website hosted on your staging server or behind a firewall? BrowserStack allows you to test these local environments without complex infrastructure changes.
- 150+ Tool Integrations: Automate connects seamlessly with the tools you already use, including: CI/CD systems (e.g., Jenkins, Travis CI), Project management (e.g., Jira), and Bug trackers (e.g., GitHub)
3. Accelerated Debugging with AI Insights
Testing is only half the battle; fixing bugs fast is what truly matters. Therefore, BrowserStack uses AI to streamline failure analysis and reporting.
- AI-Powered Smart Insights: Get proactive test reporting and automatic failure analysis to quickly identify flaky tests.
- Fast Test Failure Analysis: Provides AI-driven root cause analysis and automatically categorizes failures, highlighting remediation steps for faster debugging.
- Advanced Reporting: Access crucial debugging information instantly, including test videos, screenshots and logs.
- Self-Healing Agent: This feature helps stabilize your pipeline by automatically remediating broken scripts during execution, which can reduce build failures by up to 40%.
- AI Test Selection: Only run the tests impacted by recent code changes. This intelligent selection makes test cycles up to 50% faster.
In short, BrowserStack Automate is a fully managed, secure, and scalable cloud platform that allows you to deliver a flawless user experience faster and with higher confidence.
Pricing for Automate:
- BrowserStack Automate offers a free trial so teams can evaluate the platform quickly.
- Paid plans start at $99 per month, giving you access to real browsers without managing any infrastructure.
Conclusion
Headless testing is great for speed, but it can’t match the accuracy teams need for reliable releases. Real browser testing reveals visual issues, browser quirks, and interaction bugs that headless mode often misses.
BrowserStack Automate brings this to life by giving teams instant access to thousands of real broheadwsers and devices, strong parallelization, and AI-powered insights without any infrastructure work. This lets QA teams move faster, debug smarter, and ship with confidence. Real browsers catch real issues, and BrowserStack makes it effortless to test them at scale.