In QA, manual testing is slow and error-prone. Test recorders automate script creation by capturing interactions, reducing effort, and improving coverage.
Overview
What is a Test Recorder?
A test recorder is a tool that captures user actions like clicks, inputs, and navigation to automatically generate test scripts. It simplifies test creation, reduces manual effort, and enables both technical and non-technical teams to automate testing quickly.
Popular Test Recorders:
- BrowserStack Test Recorder: Low-code recorder that captures user actions, adds visual checks, and creates resilient automated tests.
- Ghost Inspector: Browser extension for recording and scheduling web tests with CI/CD integration and cross-browser support.
- BugBug: Simple no-code recorder for Chromium browsers with flexible editing and CI/CD pipeline integration.
- testRigor: Recorder that turns plain-English test steps into automated scripts with support for logic and branching.
- MUnit Test Recorder: MuleSoft tool that records execution flows to generate automated unit and integration tests.
- Espresso Test Recorder: Android Studio feature to record UI interactions and auto-generate Espresso test code.
This guide explores what a test recorder is, why it matters, how it works, its features, popular options, step by step usage, common limitations, effective best practices, and most importantly, why BrowserStack Test Recorder is the leading solution for modern QA teams.
What is a Test Recorder?
A test recorder, also known as a record-and-playback tool, is software that records user actions such as clicks, typing, navigation, and form fills on a user interface (UI). After capturing these steps, it generates an automated test script that replays the same actions. The script often contains assertions or verifications to confirm whether the UI or application behaves correctly.
Why Test Recorders are Important for QA Teams
Test recorders are important for QA teams for several reasons, including faster test creation, accurate results, and easier automation. Here are some key benefits that make them essential for quality assurance.
- Speed and efficiency: Automatically captures flows into scripts, enabling faster execution without coding.
- Lower barrier to entry: Lets non-developers create automated tests, boosting team-wide adoption.
- Consistency and repeatability: Ensures error-free, repeatable results across all test cycles.
- Regression testing: Detects bugs from updates by re-running saved scripts reliably.
- Better collaboration: Generates clear test steps for easier communication and review.
- Cost savings: Cuts repetitive effort, delivering long-term time and resource savings.
Benefits of Using a Test Recorder
Test recorders offer more than one advantage for QA teams, from faster test creation to higher reliability and cross-platform coverage.
Here are some key benefits that improve software quality.
- Faster test creation: A test recorder captures user interactions and converts them into automated scripts, which allows QA teams to execute test scenarios quickly. This reduces time spent on manual scripting while increasing coverage.
- Reduced maintenance effort:Test scripts generated by a test recorder handle repetitive tasks consistently. Updates to the application require fewer modifications to tests, which lowers the effort needed for long-term maintenance and error resolution.
- Visual verification support: Many test recorders include screenshot comparison and visual checkpoints. This ensures the interface appears correctly across environments, identifies layout changes, and prevents UI inconsistencies from reaching production.
- Accurate user-flow representation: A test recorder captures actual user paths in the application, which preserves real-world interaction logic. This provides QA teams with tests that mirror authentic usage and uncover hidden defects effectively.
- Cross-browser and cross-device validation: Test recorders often integrate with multiple browsers and devices. Scripts execute across different platforms, which ensures consistent behavior and appearance for web and mobile applications under various conditions.
- Higher test coverage: Automated scripts created by a test recorder allow QA teams to cover a larger set of scenarios, including edge cases. This strengthens quality assurance, identifies defects earlier, and improves overall product reliability.
- Clear documentation for teams: Scripts produced by a test recorder provide detailed records of each step performed. This documentation enhances collaboration, enables knowledge sharing, and allows developers and stakeholders to understand tested actions.
- Long-term cost efficiency: While the initial setup may require resources, automated test execution reduces repeated manual effort. Over multiple releases, a test recorder generates significant savings in time, labor, and operational costs.
How Test Recorders Work
Test recorders work by capturing user interactions and converting them into executable test scripts. Here are the key stages that define how a test recorder operates effectively in QA workflows.
1. Event capture and element identification: The recorder monitors user actions such as clicks, typing, navigation, or gestures. Each element is identified using ID, CSS selector, XPath, or visual locators to ensure precise mapping of interactions.
2. Step logging and assertion creation: Every action is recorded with the target element and input data. Assertions define expected results, such as text visibility, button state, or UI changes, providing robust validation for each step.
3. Script generation: Captured steps and assertions are converted into executable scripts compatible with automation frameworks or internal formats. These scripts can run across multiple platforms and environments.
4. Playback and verification: Recorded scripts execute on different browsers or devices. Each step replays, assertions are evaluated, waits and retries are handled, and detailed pass/fail reports are generated for analysis.
Top 10 Features of Test Recorders
To select the best test recorder tool, it is important to evaluate its capabilities. While the requirements may vary across organisations, the following are the most critical functionalities for QA automation.
1. Record and Playback: Captures user actions such as clicks, typing, and navigation, then generates scripts that can run automatically on the application for accurate test execution.
2. Step Editing and Modification: Recorded test steps can be inserted, deleted, or reordered, providing flexibility to refine tests without repeating the entire recording process.
3. Assertion and Validation: Supports checking text, element presence, or visual differences to ensure expected results match actual application behavior at every step.
4. Dynamic Element Support: Handles changes in UI elements, waits for content, and manages AJAX or DOM updates, which reduces failures caused by page or content updates.
5. Self-Healing Selectors: Automatically adapts to minor UI changes to maintain test reliability, preventing failures when element IDs or attributes change across releases.
6. Visual Validation: Captures screenshots and performs pixel or layout comparisons to detect UI anomalies, ensuring visual consistency across devices and environments.
7. Cross-Browser and Cross-Device Execution: Runs tests on multiple browsers, operating systems, and devices to confirm consistent application behavior and appearance.
8. CI/CD Integration: Connects automated tests with continuous integration and delivery pipelines to provide fast feedback on application quality during development cycles.
9. Test Code Export: Generates scripts compatible with popular frameworks like Selenium, Espresso, or Appium, enabling advanced customization or integration into existing automation suites.
10. Collaboration and Reporting: Allows teams to share tests, manage versions, review logs, and access debugging aids such as screenshots or video recordings of test runs.
Popular Test Recorder Tools
Our experts have picked some of the top test recorder tools. Explore their key features, advantages, limitations, and essential technical details.
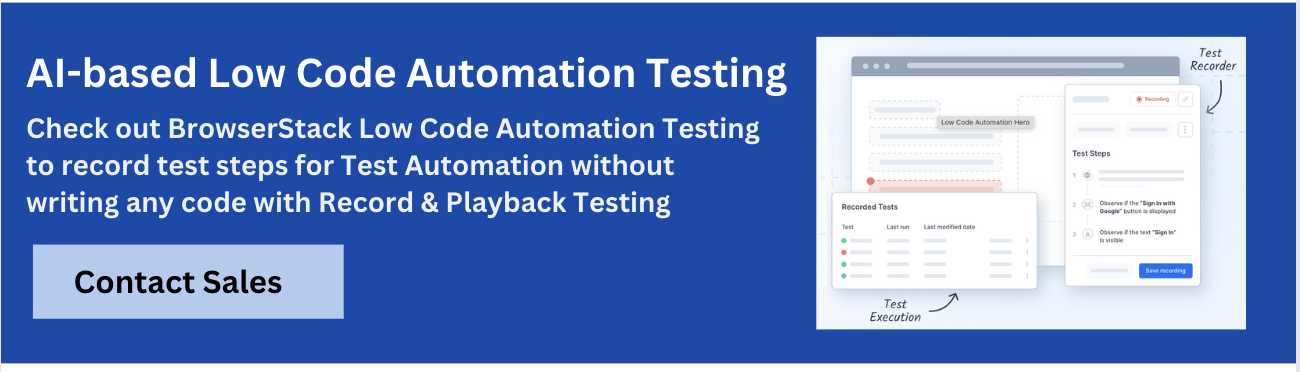
1. BrowserStack Test Recorder
BrowserStack’s Test Recorder empowers teams to perform low-code test automation without writing code. By recording interactions on the application, testers and non-technical team members can quickly create automated UI tests, edit them with ease, and visually validate results. This makes automation more collaborative, resilient, and faster to adopt across teams.
With its intuitive recorder interface, BrowserStack removes the complexity of scripting, reduces test maintenance, and ensures reliable execution across environments.
Key Features of BrowserStack Test Recorder:
- Record and Playback Testing: Capture interactions on the application UI by performing user actions. Replay them anytime to validate functionality without manual effort.
- Easy Test Authoring: Create tests with no coding required. User actions are instantly converted into automated test steps.
- Visual Validation: Check critical UI elements with snapshot-based visual checks, removing the need for complex assertions.
- Easy Test Editing: Edit steps in a recorded test without starting from scratch. Modify actions or validations with a few clicks.
- Readable Test Steps: Automatically generated, human-readable descriptions make tests easy for any team member to understand.
- Smart Auto-Waiting: Boost reliability with adaptive wait times that respond to network conditions and UI performance.
- Self-Healing Tests: Cut down flakiness with AI-powered smart selectors that adapt to UI changes, reducing maintenance and failures.
Try BrowserStack Low Code Automation
2. Ghost Inspector Test Recorder
Ghost Inspector is a browser extension that allows users to record and automate web application tests. It supports cross-browser testing, scheduling, and CI/CD integration, making it suitable for both developers and non-technical testers.
Key Features of Ghost Inspector:
- Browser Extension-Based Recording
- Visual Regression & Comparators
- Scheduling and CI/CD Integration
- Drag-and-Drop Test Editing
- Cross-Browser Testing
Pros of Ghost Inspector:
- User-friendly interface for non-technical users.
- Provides detailed logs and video recordings for debugging.
Cons of Ghost Inspector:
- Limited support for backend or API testing.
- May lack advanced AI-driven features found in newer tools.
Read More:Ghost Inspector Alternatives
3. BugBug Web Test Recorder
BugBug is a no-code test recorder focusing on simplicity and stability. It captures user interactions in Chromium-based browsers, offers flexible test editing, and integrates with CI/CD pipelines for efficient testing workflows.
Key Features BugBug Web:
- Automatic Selectors
- Built-In Inbox Testing
- Flexible Test Editing
- CI/CD Integration
- Cloud and Local Execution
Pros BugBug Web:
- Easy for non-technical testers with a low learning curve.
- Offers a freemium model, useful for small teams or evaluation.
Cons BugBug Web:
- Limited to Chromium-based browsers.
- Does not support mobile applications or non-web contexts in many cases.
4. testRigor Test Recorder
testRigor allows writing tests in plain English, combining recording capabilities with logic and branching. It supports multi-browser execution and is suitable for complex test scenarios requiring natural language descriptions.
Key Features of testRigor:
- Plain-English Test Scripting
- Multi-Browser Support
- Conditional Logic and Loops
- Test Case Import from TestRail
- Native Desktop Testing
Pros of testRigor:
- Enables non-programmers to create automated tests easily.
- Supports complex test scenarios with conditional logic.
Cons of testRigor:
- May require initial setup and learning for optimal use.
- Higher cost for scaling across many test scenarios and environments.
Read More:testRigor Alternatives
5. MUnit Test Recorder
MUnit Test Recorder, part of MuleSoft’s testing framework, records execution flows in Anypoint Studio. It captures real data and generates unit tests, aiding in testing APIs and integration flows within Mule applications.
Key Features of MUnit:
- Flow Recording
- Mocking and Spying Processors
- Automatic Test Generation
- Test Configuration
- Error Handling
Pros of MUnit:
- Saves time in writing unit or integration tests for Mule flows.
- Increases test coverage for complex data transformations.
Cons of MUnit:
- Cannot record flows with certain error handling configurations.
- Limited support for time-based or parallel processing data.
Also Read: Top 18 Test Data Management Tools
6. Android Espresso Test Recorder
Espresso Test Recorder, integrated into Android Studio, allows recording UI interactions on Android devices or emulators. It generates Espresso test code, facilitating automated UI testing for Android applications.
Key Features of Android Espresso:
- Record User Interactions
- Code Generation
- Integration into Android Project
- View Assertions
- Synchronization with UI Thread
Pros of Android Espresso:
- Part of the official Android testing framework, ensuring reliability.
- Reduces test flakiness by synchronizing with the UI thread.
Cons of Android Espresso:
- Limited to Android applications; not usable for web or other platforms.
- May require manual coding for complex UI interactions or deep integrations.
How to Use a Test Recorder: Step-by-Step Guide
To get the most from a test recorder, follow these seven steps to capture actions, add validations, and create accurate automated tests.
Step 1: Choose a Test Recorder: Select a test recorder based on your project needs, platform, and supported browsers or devices. Consider tools like BrowserStack, testRigor, or Ghost Inspector that match your application type and testing requirements.
Step 2: Install the Recorder: Download and install the recorder. For browser-based tools, add the extension to Chrome, Firefox, or Edge. For desktop or mobile tools, follow setup instructions and ensure proper permissions to capture UI actions.
Step 3: Prepare the Test Environment: Open the application, website, or software module to be tested. Clear caches, log in, and navigate to the relevant starting point. Ensure the environment is stable and free from interruptions that may affect recording.
Step 4: Start Recording User Actions: Activate the recorder and perform the actions to be tested, such as clicks, typing, navigation, and form submissions. The recorder captures every interaction and maps it to corresponding UI elements accurately.
Step 5: Stop Recording and Review Steps: Once all actions are performed, stop the recording. Review the captured steps carefully, check that each action is correctly mapped, and remove or adjust unnecessary or redundant steps.
Step 6: Add Assertions and Validations: Insert assertions to verify expected results, such as text presence, button states, or visual changes. These validations help the test catch errors if the application behaves differently in future runs.
Step 7: Save, Execute, and Integrate: Save the test script and run it to verify proper execution. Integrate it into CI/CD pipelines or schedule periodic runs to automate regression testing across browsers and environments consistently.
Limitations and Challenges of Test Recorders
While test recorders offer many advantages as discussed above, they are not without challenges. Here are some of its major limitations:
- UI changes break scripts: Test scripts often fail when IDs, classes, or layouts shift. Without strong locators or self-healing, maintenance becomes complex.
- Limited logic and branching: Many recorders lack support for conditions, loops, or complex workflows, requiring manual coding for full coverage.
- Hard-coded data issues: Scripts with fixed values or dynamic inputs can become flaky and inconsistent, reducing reusability across runs.
- Scaling challenges: Running large suites across browsers, devices, or environments needs strong infrastructure and can slow CI/CD cycles.
- Restricted platform support: Some tools only cover web or mobile-web, missing native app and backend workflows, limiting overall automation.
Best Practices for Using a Test Recorder
To get the most from a test recorder as well as to overcome the challenges listed above, QA teams should follow these practices while using a test recorder:
- Choose the right tool: Select a recorder that fits the application type, platform, and complexity of tests.
- Plan test flows: Outline steps and scenarios before recording to reduce unnecessary actions.
- Use stable locators: Prefer IDs, names, or unique attributes to avoid brittle tests.
- Add assertions: Verify text, elements, or visual changes to ensure meaningful validation.
- Keep scripts concise: Remove extra steps like hover or scroll actions that do not affect outcomes.
- Parameterize data: Replace hard-coded values with variables for reusability across environments.
- Review steps: Check recorded steps for accuracy before saving the test script.
- Use version control: Track changes to test scripts for better collaboration.
- Schedule regular runs: Integrate with CI/CD pipelines for automated regression testing.
- Monitor results: Analyze failures and adjust scripts to maintain stability over time.
Why Choose BrowserStack Test Recorder?
BrowserStack Test Recorder combines AI-powered low-code automation with cross-browser and cross-device coverage, making it a strong choice for modern QA.
- Intuitive Recording: Capture clicks, inputs, and navigation to auto-generate scripts without coding.
- AI Test Generation: Convert written cases into automated steps, reducing effort and speeding up creation.
- Visual Validation: Add checkpoints to catch UI regressions and ensure consistent experiences.
- Self-Healing Tests: AI adapts scripts to minor UI changes, reducing maintenance needs.
- Smart Auto-Waiting: Adjusts to network responses, cutting flakiness and boosting reliability.
Seamless integration with real-device cloud testing, wide browser coverage, and detailed analytics further strengthen its value for QA teams.
Conclusion
Test recorders simplify automation by capturing user interactions and generating reliable scripts, reducing manual effort and improving test coverage. They help teams maintain consistency, detect regressions, and verify visual elements across multiple devices and browsers.
To reap these benefits, it is also important to choose top test recorders such as BrowserStack. It stands out with superior features, including AI-powered step generation and self-healing tests. Contact our experts to learn more and see how BrowserStack can improve your QA processes.