Performance testing requires simulating realistic user behavior to understand how applications handle load. JMeter Thread Groups allow testers to generate controlled traffic and observe system responses under varying conditions.
Overview
What is a JMeter Thread Group?
A JMeter Thread Group defines a set of virtual users (threads) and controls their execution, including the number of users, ramp-up period, and iteration count. It serves as the foundation for creating performance and load tests in JMeter.
Purpose of a JMeter Thread Group
- Simulate Concurrent Users: Represent multiple users accessing the application simultaneously.
- Control Load Patterns: Adjust ramp-up and loop counts to mimic real-world usage.
- Test System Behavior: Evaluate performance, stability, and scalability under varying loads.
- Integrate with Test Elements: Serve as a container for samplers, controllers, and listeners.
Key Aspects and Configurations of a JMeter Thread Group
- Number of Threads (Users): Defines how many virtual users will execute the test simultaneously.
- Ramp-up Period: The time over which all threads are started, controlling how quickly the load is applied.
- Loop Count: Determines how many times each thread will execute the test scenario.
- Scheduler Configuration: Allows tests to run for a specific duration or schedule start and end times.
- Actions on Sample Error: Defines what happens if a request fails, such as continue, stop thread, or stop test.
Example of a JMeter Thread Group
A Thread Group with 50 threads, a ramp-up period of 100 seconds, and a loop count of 10 will gradually start 50 virtual users over 100 seconds, each executing the test scenario 10 times.
This article explains what a JMeter Thread Group is, how to configure it, and how it affects test execution and results.
What is a JMeter Thread Group?
A JMeter Thread Group is the basic building block of a test plan. It defines the number of virtual users (called threads), how frequently they send requests, and how long the test runs. Each thread simulates one user performing a series of actions against your application.
In essence, the Thread Group defines the load pattern and execution flow of your performance test, making it a critical component for accurate and meaningful test results.
Components of a JMeter Thread Group
Each component in the Thread Group controls how virtual users behave during the test. Below is what each component does:
1. Action to be taken after a Sampling Error
Specifies how JMeter should behave when a sampler (like an HTTP Request) fails. Options include:
- Continue
- Start Next Thread Loop
- Stop Thread
- Stop Test
- Stop Test Now
Choosing the right option helps control test flow in case of failures.
2. Thread Properties
This includes several critical settings that define the behavior and load pattern of your test:
- Number of Threads (Users): Sets how many virtual users JMeter will simulate. Each thread runs independently to mimic real user activity throughout the test.
- Ramp-Up Period (seconds): Specifies the time JMeter takes to launch all threads. For example, if you set 10 threads with a 20-second ramp-up, one thread starts every 2 seconds, gradually allowing the load to build.
- Loop Count: Controls how many times each thread repeats the test. You can enter a fixed number or select “Forever” to keep it running until the test is stopped.
3. Same User on Each Iteration
When enabled, it ensures each thread (user) maintains the same session (like cookies and cache) across iterations. This is useful when testing session-based applications.
Read More: Understanding Cookies in Software Testing
4. Delay Thread Creation Until Needed
If checked, JMeter creates each thread only when it’s about to start running, instead of creating all threads at once during ramp-up. This can reduce memory consumption during the test’s initial phase.
5. Specify Thread Lifetime
The Thread Lifetime settings in JMeter allow you to define how long your threads (virtual users) should run and when they should start.
- Duration: Total time (in seconds) to run the test after the start.
- Startup Delay: Delay (in seconds) before the test begins after hitting “Start”.
These configurable components allow precise control over your test execution, enabling you to accurately replicate real-world traffic and user behavior.
Types of Thread Groups in JMeter
JMeter supports multiple types of thread groups to model various test scenarios. Here’s a breakdown of the most commonly used ones:
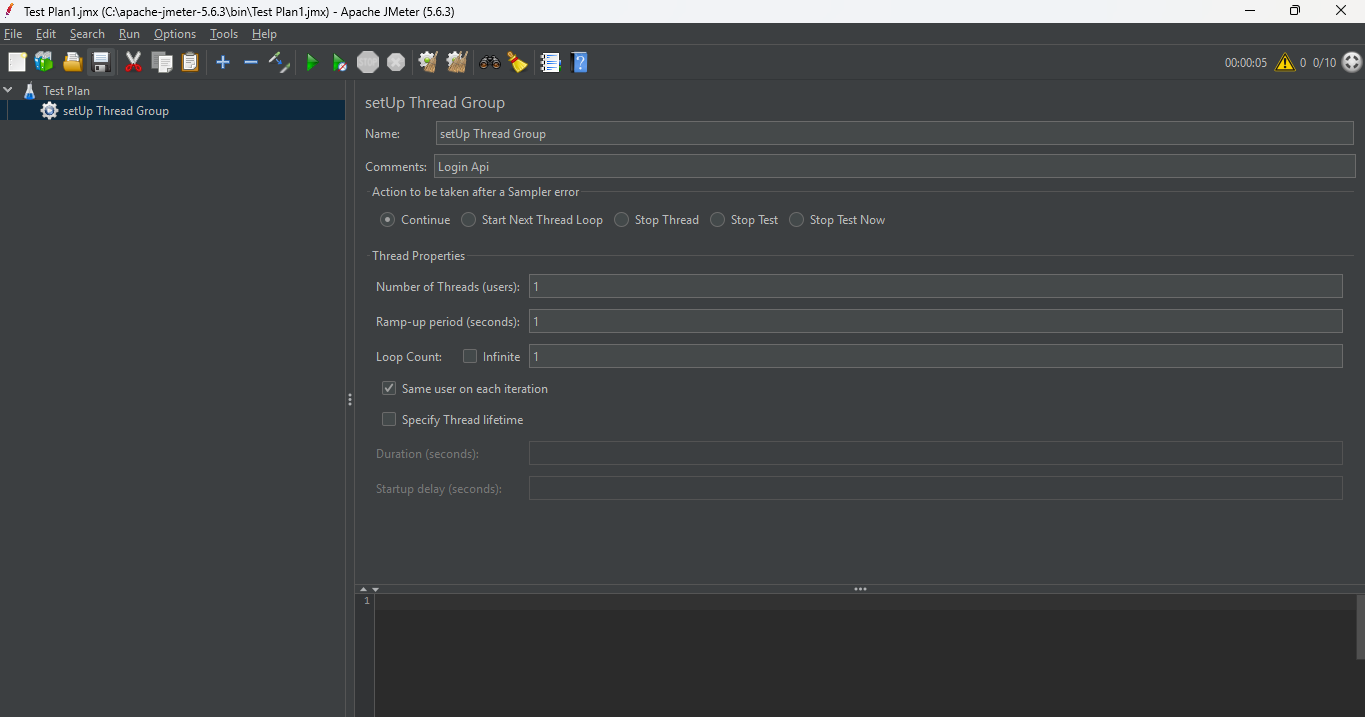
1. setUp Thread Group
The setUp Thread Group in JMeter is a special thread group that runs before the main test execution. It is used to perform pre-test setup tasks like logging in, initializing data, or preparing the environment for the actual test.
For example, if you’re testing APIs that require login plus two-factor authentication, you can use the setUp Thread Group to handle both steps. This ensures your main test runs only after the user is fully authenticated.
How to Use setUp Thread Group?
1. Add setUp Thread Group under the test Plan
Right-click on Test Plan > Add > Threads (Users) > setUp Thread Group
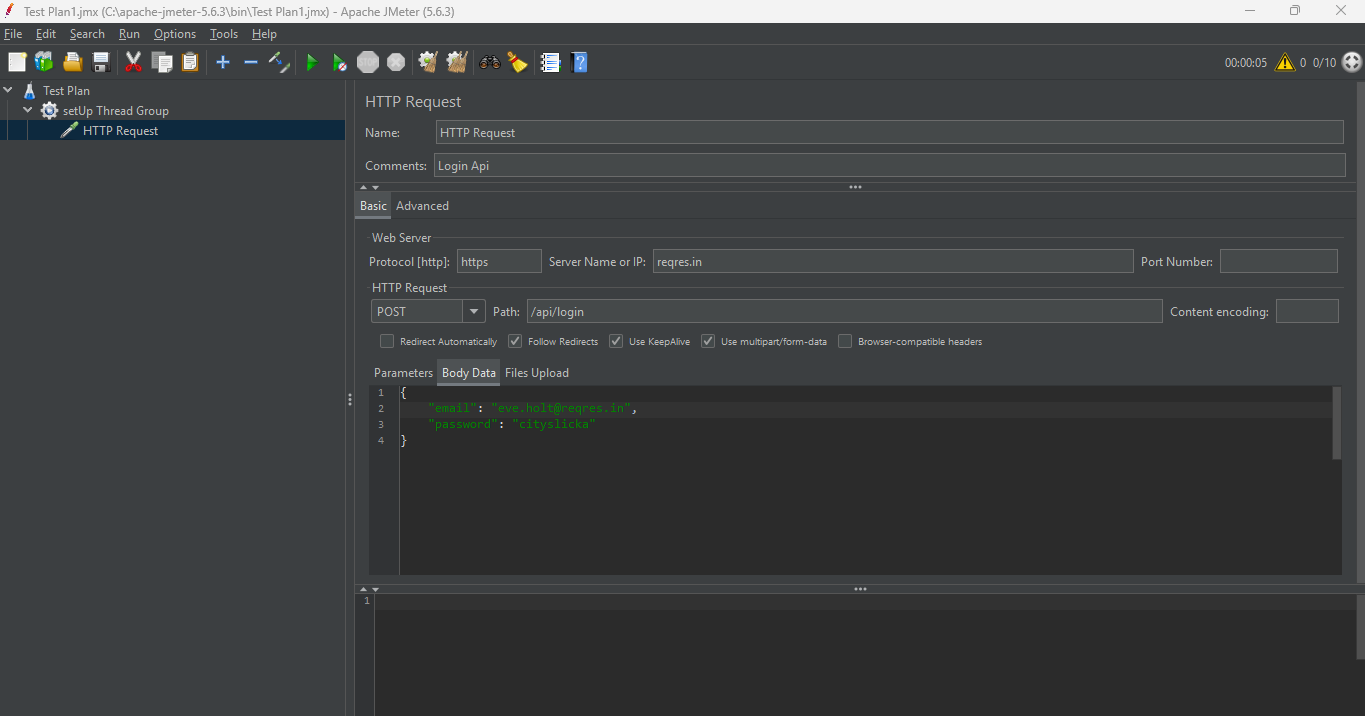
2. Add HTTP Request to Login API
setUp Thread Group > Add > Sampler > HTTP Request
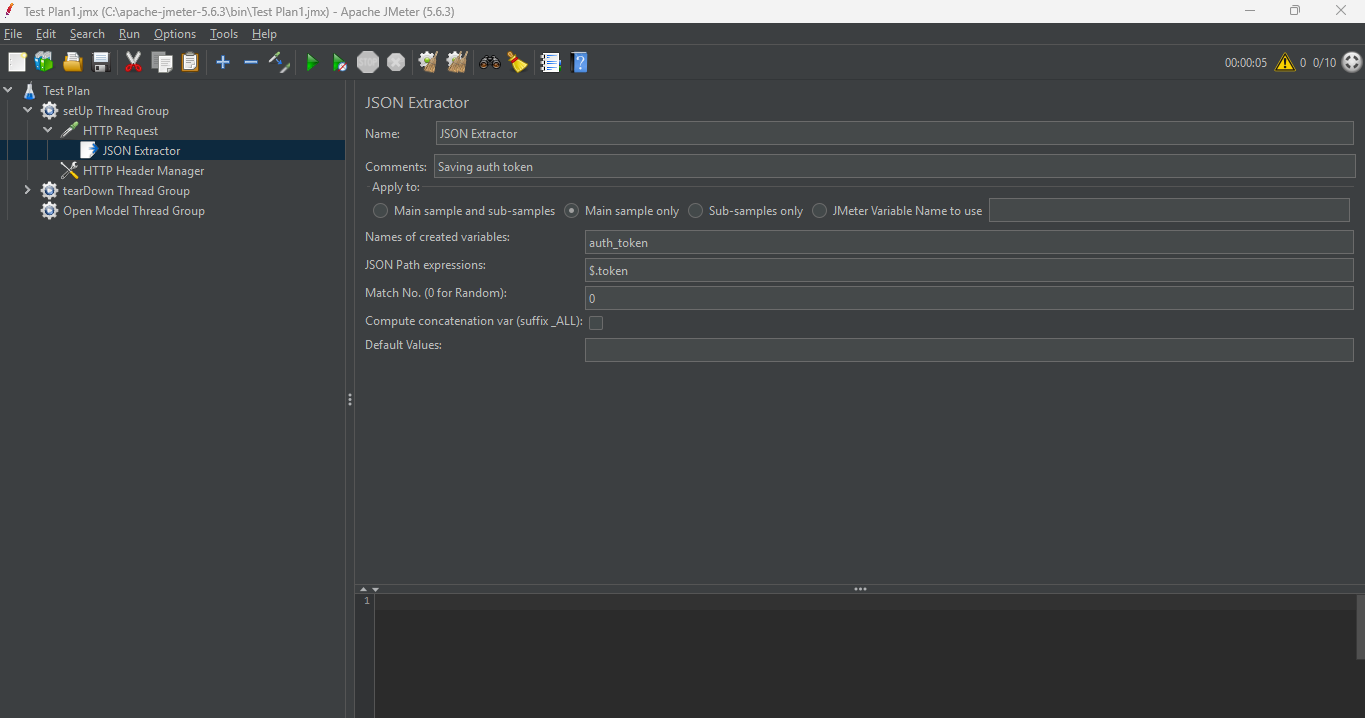
3. Add a JSON Extractor
HTTP Request > Add > Post Processors > JSON Extractor
This extracts the token from the login response and stores it in ${auth_token}.
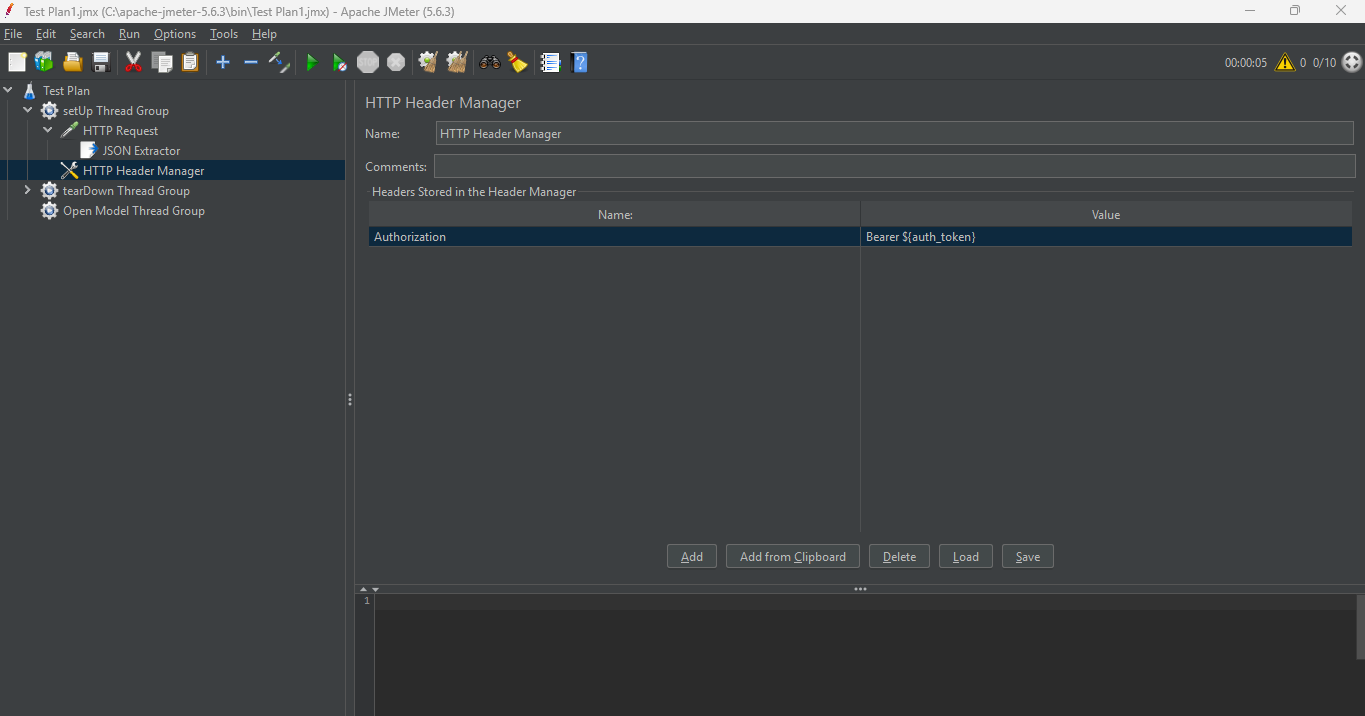
4. Use the Token in the Main Thread Group
Now, in the main Thread Group, when sending an authenticated request:
setUp Thread Group > Add > Config Element> HTTP Header Manager
5. In the HTTP Header Manager, add:
Name: Authorization
Value: Bearer ${auth_token}
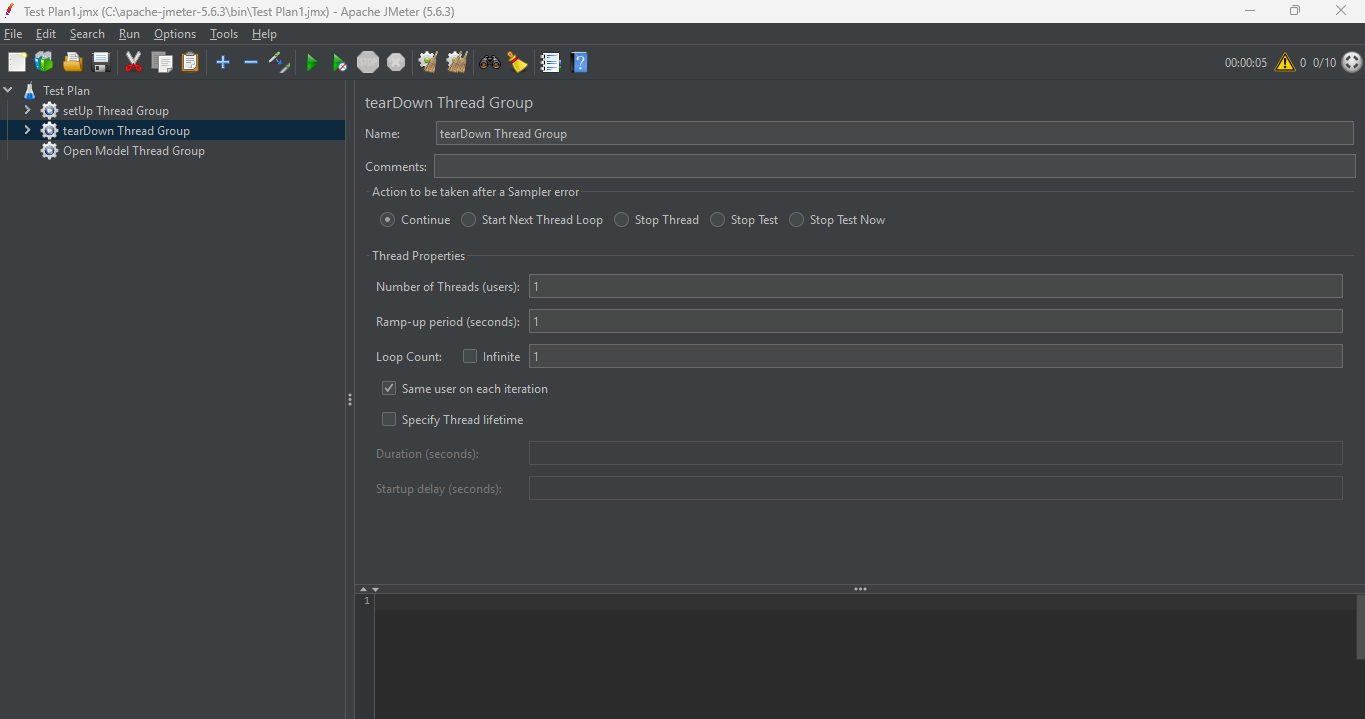
2. tearDown Thread Group
The tearDown Thread Group in JMeter is a special thread group that runs after the main test execution is complete. It performs post-test cleanup tasks like logging out, deleting test data, closing sessions, or resetting environments to their original state.
For example, imagine you’ve created multiple test users during your main test run. You can use the tearDown Thread Group to send requests that clean up those users, release resources, or log out sessions to leave your environment clean for the next test run.
How to Use tearDown Thread Group?
1. Add tearDown Thread Group under the Test Plan
Right-click on Test Plan > Add > Threads (Users) > tearDown Thread Group
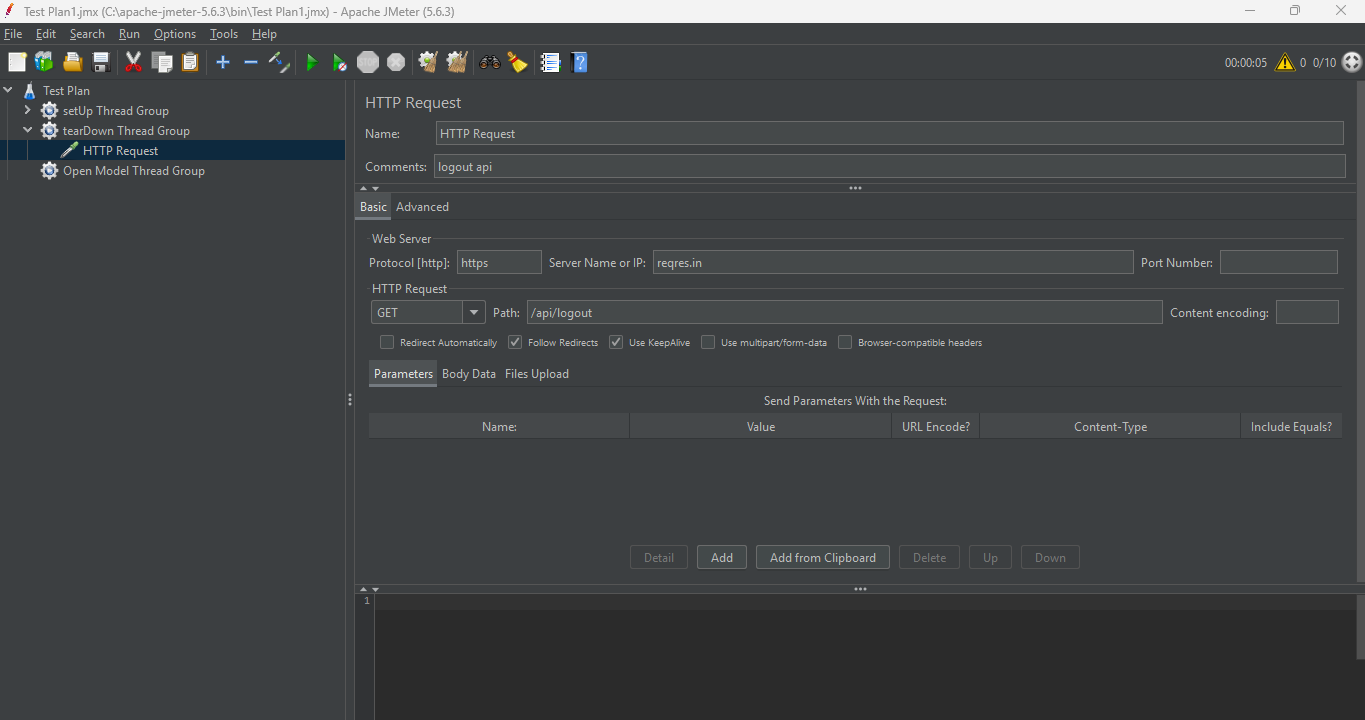
2. Add HTTP Request for Cleanup Tasks
Inside the tearDown Thread Group:
tearDown Thread Group > Add > Sampler > HTTP Request
3. Open Model Thread Group
The Open Model Thread Group is an advanced thread group in JMeter, designed for realistic and flexible load modeling. Unlike the classic Thread Group, it allows you to simulate more dynamic traffic patterns, such as ramp-up/down, arrivals over time, and more, which better reflect real-world usage.
For example, suppose you want to simulate 100 users arriving at a rate of 10 users per minute, followed by a spike, then a cooldown. The Open Model Thread Group allows you to model such scenarios using its custom schedule builder.
How to Use Open Model Thread Group?
1. Add Open Model Thread Group under the Test Plan
Test Plan > Add > Threads (Users) > Open Model Thread Group
2. Configure Load Pattern
Use the following expressions to define the test schedule:
- rate (1/min)
- random_arrivals (10 min)
- pause (1 min)
- /* comment */
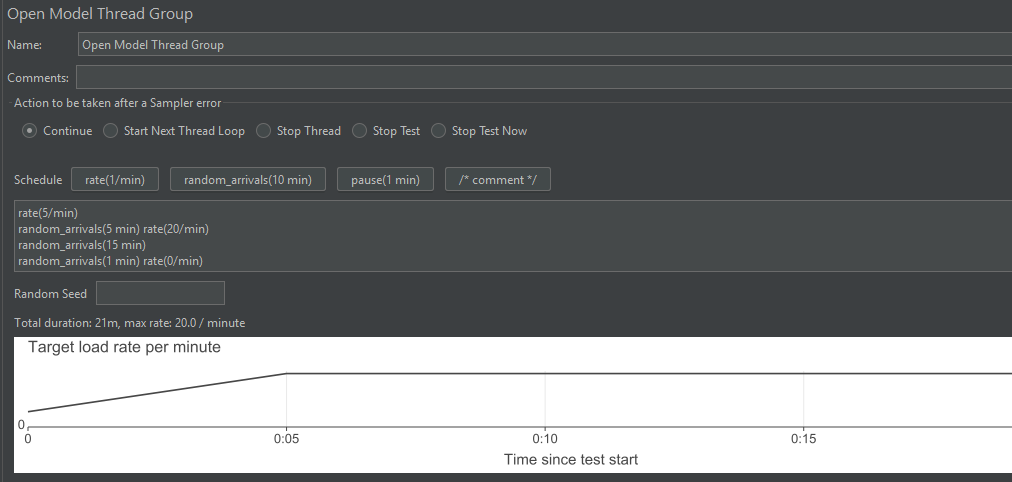
For example, to start the test at a rate of 5 requests per minute, then increase to 20 requests per minute after 5 minutes, the setup would be:
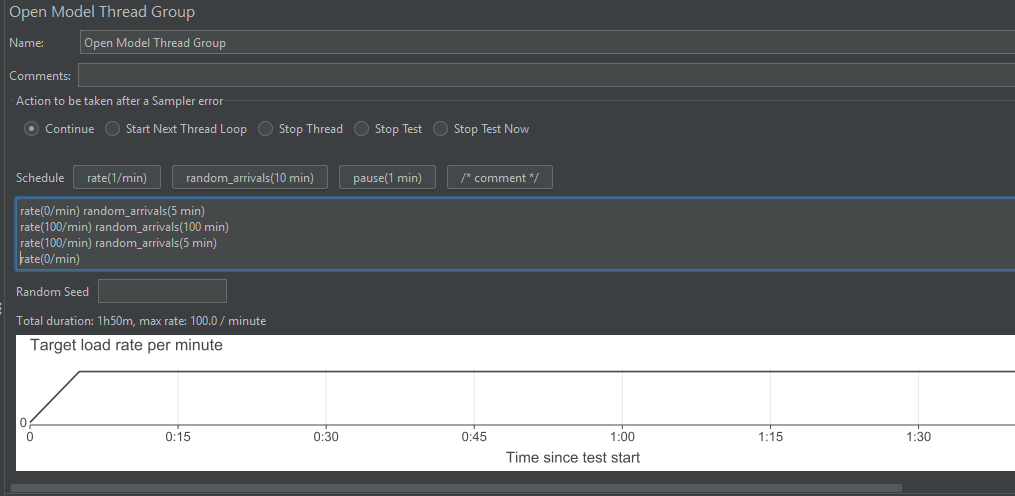
rate(5/min) random_arrivals(5 min) rate(20/min) random_arrivals(15 min) random_arrivals(1 min) rate(0/min)
To define a steady state, use the following expression:
rate(0/min) random_arrivals(5 min) rate(100/min) random_arrivals(100 min) rate(100/min) random_arrivals(5 min) rate(0/min)
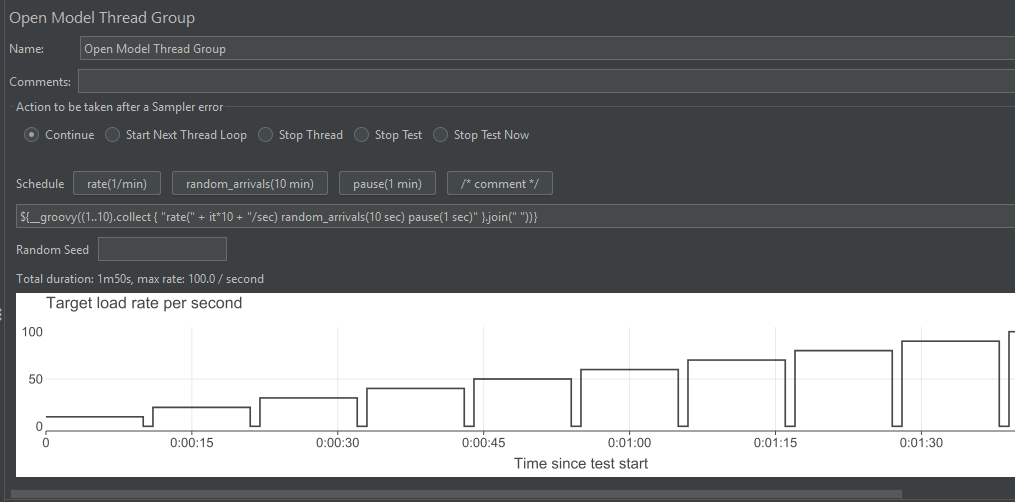
For a step-by-step pattern, use:
${__groovy((1..10).collect { "rate(" + it*10 + "/sec) random_arrivals(10 sec) pause(1 sec)" }.join(" "))}4. Custom Thread Groups in JMeter Plugins
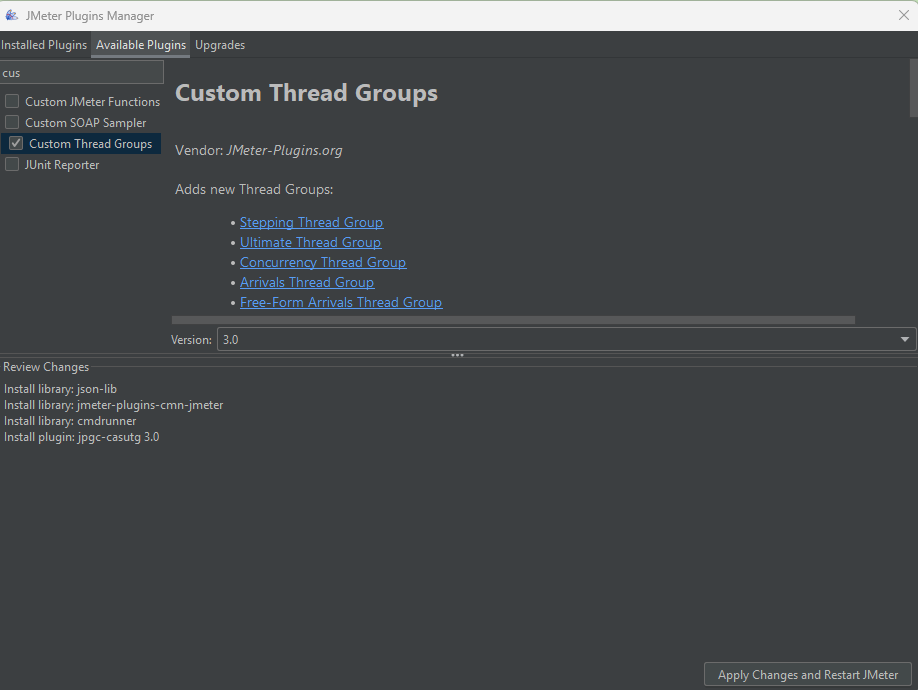
The Custom Thread Groups plugin in JMeter offers advanced options for simulating user load patterns beyond what the default Thread Group provides. These are useful for performance testing scenarios that need more flexible and realistic traffic models.
Also Read: Performance Testing Vs Load testing
Download the plugin to enable Custom Thread Groups and place the JAR file in the bin/ext directory inside the JMeter installation folder. Then open the Plugins Manager and install Custom Thread Groups from the Available Plugins tab.
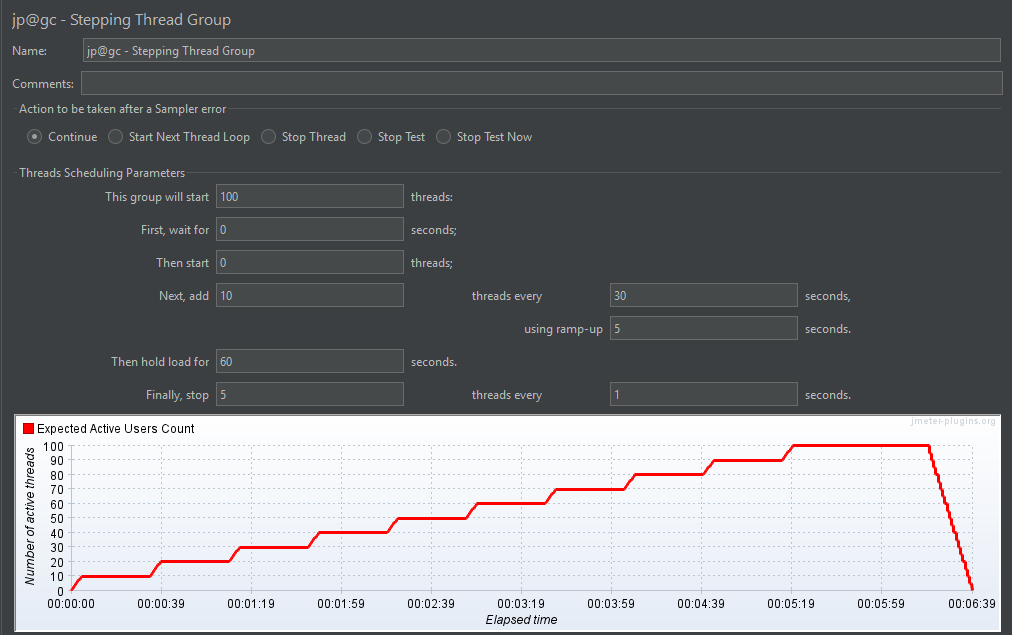
1. Stepping Thread Group
The Stepping Thread Group lets you increase user load step by step. It helps detect when the system starts to show signs of stress as the load rises.
Key Features:
- Start Users Count: Sets the number of users to start immediately
- Add Users Every (sec): Interval between each step increase
- Users to Add: Number of users added at each step
- Hold Load For (sec): Duration to maintain the full user load
- Ramp-Down Time (sec): Time to gradually stop all users after the test
Use case: Ideal for identifying the point where a system starts to degrade.
Also Read: JMeter Stress Testing: A Tutorial
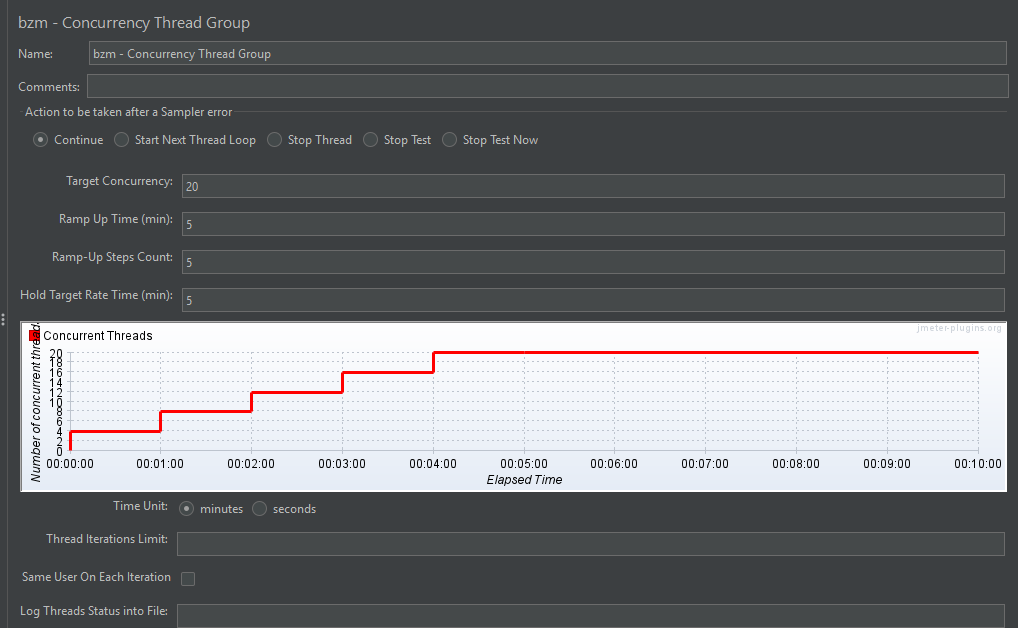
2. Concurrency Thread Group
The Concurrency Thread Group maintains a steady number of active users by launching new threads as soon as others complete.
Key Features:
- Target Concurrency: Sets the number of concurrent users to maintain during the test
- Ramp-Up Time: Time taken to reach the target concurrency
- Hold Target Rate Time: Duration to maintain the target concurrency
- Time Unit: Defines the unit for ramp-up and hold duration, like seconds or minutes
- Iterations Limit: Optional cap on how many iterations each thread can run
Use Case: Test how your application handles a consistent, real-world user load over a period of time.
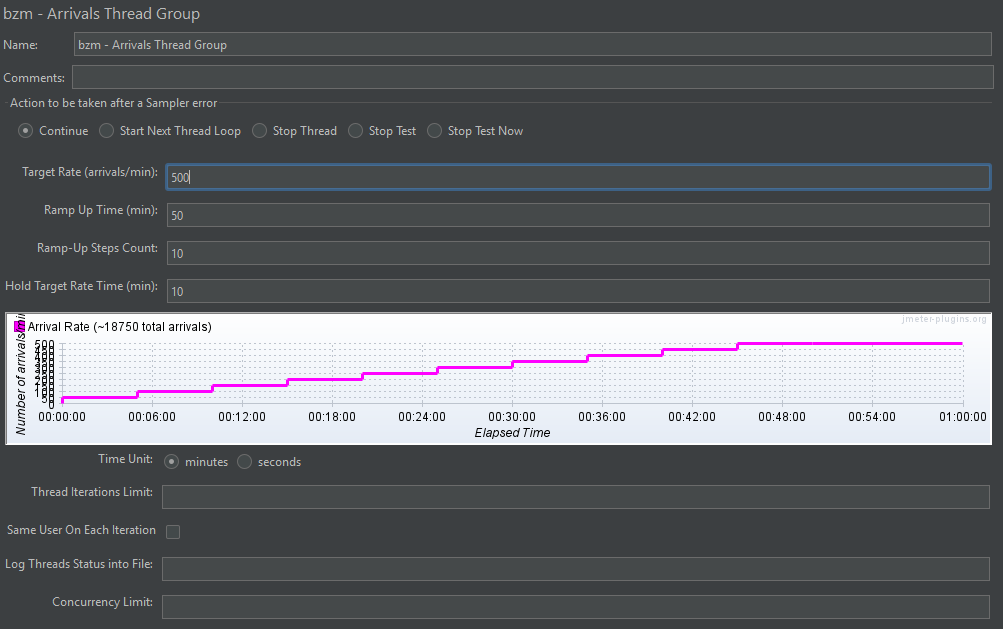
3. Arrivals Thread Group
The Arrivals Thread Group simulates user load based on arrival rate instead of total thread count. It focuses on how frequently users arrive rather than how many are active at once.
Key Features:
- Target Rate (users/sec): Sets the desired arrival rate of virtual users
- Ramp-Up Time: Time to gradually reach the target arrival rate
- Duration: Total time to maintain the arrival rate
- Thread Limit: Maximum number of threads allowed during the test
Use Case: It is perfect for simulating systems where user requests arrive at a steady rate, such as login attempts or API calls from multiple clients.
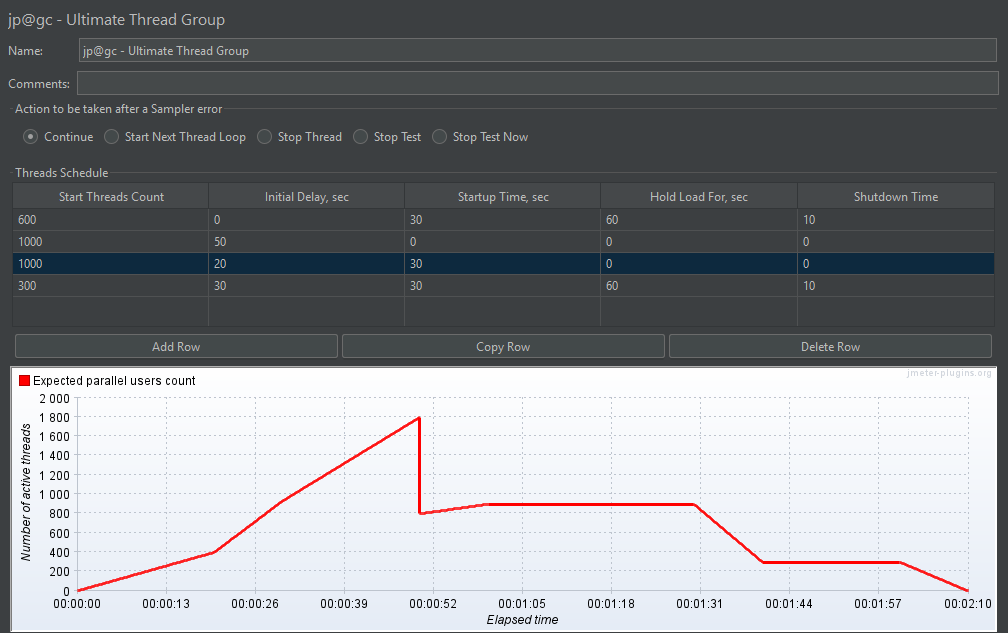
4. Ultimate Thread Group
The Ultimate Thread Group allows complete control over how and when users are introduced into the test. It lets you define multiple user segments, each with its own ramp-up, hold, and shutdown schedule.
Key Features:
- Start Threads Count: Sets how many users to start in each row
- Initial Delay (sec): Time to wait before starting any users in the row
- Start Every (sec): Interval between each thread launch
- Hold Load For (sec): Duration to keep the users active
- Shutdown Time (sec): Time to ramp down users after the hold period
Use Case: Useful for simulating traffic spikes, regional user rollouts, or multi-phase tests.
Also Read: JMeter Distributed Testing: Tutorial
5. Free-Form Arrivals Thread Group
The Free-Form Arrivals Thread Group provides full control over arrival patterns using a table-driven configuration. It allows defining detailed traffic curves that change over time.
Key Features:
- Start Time: Sets when each arrival phase begins
- Duration: Length of time to maintain the specified arrival rate
- Target Rate (users/sec): Defines the arrival rate for each phase
- Ramp-Up Time: Time to reach the target rate from the previous phase
- Thread Limit: Maximum number of users allowed during execution
Use Case: Ideal for mimicking complex traffic patterns like those seen on e-commerce websites during sales or flash events.
How to Choose the Right Thread Group for Your Test Plan
Choosing the right thread group in JMeter depends on your test objectives, load patterns, and complexity of scenarios. Here’s how you can decide:
- For simple load tests with a fixed number of users and iterations, the Default Thread Group is sufficient.
- If your test requires pre-test or post-test actions like authentication or cleanup, use setUp and tearDown Thread Groups respectively.
- To simulate real-world traffic patterns with varying user arrival rates or ramp-up behaviors, prefer advanced thread groups like:
- Stepping Thread Group: for gradually increasing user load.
- Concurrency Thread Group: to maintain a steady number of concurrent users.
- Arrivals Thread Group: when testing based on requests per second (RPS).
- Ultimate Thread Group: for full control over stages, timings, and thread behavior.
- Consider the Open Model Thread Group if you want to define flexible load curves similar to modern load-testing tools.
How to Add Thread Groups to the Test Plan
Creating and configuring thread groups in JMeter is the first step toward building an effective test plan. Below is a step-by-step guide to help you set up a basic test plan with multiple thread groups, HTTP requests, and reporting.
1. Create a Basic Test Plan
Start JMeter and create a new test plan:
- Right-click on Test Plan > Add > Threads (Users) > Thread Group
- Give it a descriptive name (e.g., “Login Test Users”)
- Set the number of threads, ramp-up period, and loop count.
Read More: What to Include in a Regression Test Plan?
2. Add Multiple Thread Groups
To simulate different user flows or environments, add more thread groups:
- Right-click on Test Plan > Add > Threads (Users) > Choose another thread group type (e.g., setUp, tearDown, or any custom plugin-based group).
- Configure each one independently.
3. Add HTTP Request
To simulate real actions like logging in or viewing products:
- Right-click on the Thread Group > Add > Sampler > HTTP Request
- Configure the URL, method, and parameters.
Read More: Life Cycle of an HTTP Request
4. View Summary Report
To monitor test execution results:
- Right-click on Test Plan > Add > Listener > Summary Report
- This shows key metrics like sample count, average time, min/max time, and errors.
Also Read: How to write a good Test Summary Report?
5. Run Tests in Sequence or Parallel
To run thread groups sequentially or in parallel:
- By default, thread groups run in parallel.
- To run them in sequence, check “Run Thread Groups consecutively” under Test Plan properties.
Read More: Parallel Testing: The Essential Guide
How to Create Multiple Thread Groups
In JMeter, adding multiple thread groups allows you to simulate different types of user behavior or separate test stages, such as login, browsing, and checkout, within a single test plan.
To create multiple thread groups:
- Open JMeter and create a new test plan.
- Right-click on the Test Plan > Add > Threads (Users) > Thread Group.
- Repeat the same steps to add as many thread groups as needed.
- Configure each thread group with its own:
- Number of threads (virtual users)
- Ramp-up time
- Loop count
- Samplers (HTTP Requests, etc.)
- Logic controllers and listeners
Each thread group runs independently unless you enable “Run Thread Groups consecutively” in the Test Plan settings. This allows you to run them all in parallel (default) or in a defined order (sequential).
This setup is beneficial when you want to:
- Separate performance testing scenarios by module.
- Use a setUp Thread Group for authentication before load testing.
- Add a tearDown Thread Group to clean up data post-test.
How to Run JMeter Load Tests From the Cloud With Minimal Setup
Configuring JMeter thread groups for cloud-based distributed testing requires setting up remote servers, establishing secure connections between master and worker nodes, and synchronizing test plans across multiple machines. This infrastructure complexity delays test execution and demands ongoing maintenance.
BrowserStack Load Testing eliminates setup complexity by providing managed infrastructure for running load tests at scale. Teams can simulate concurrent users without configuring JMeter’s distributed architecture or managing remote thread group execution.
Key advantages of cloud-based load testing with BrowserStack:
- No distributed JMeter setup: Run load tests on managed cloud infrastructure without configuring master-slave architecture, remote thread groups, or cross-server communication that JMeter cloud testing requires.
- Immediate execution: Start testing within minutes without provisioning cloud servers, installing JMeter on remote machines, or troubleshooting distributed thread group synchronization issues.
- Simulate up to 1,000 concurrent users: Generate realistic traffic from multiple geographic locations without manually distributing JMeter thread groups across cloud instances or calculating thread allocation per node.
- Use existing test scripts: Execute load tests from current functional test code instead of creating JMeter thread group configurations or managing XML test plan distribution to remote servers.
- Unified performance metrics: Access frontend and backend performance data in one dashboard without aggregating results from multiple JMeter instances running distributed thread groups across cloud nodes.
- Automatic scaling: The platform handles load distribution and scaling automatically, eliminating manual thread group calculations and resource allocation across distributed JMeter workers.
Conclusion
JMeter thread groups control how virtual users interact with your application during a test. Each thread group offers different ways to shape traffic, whether you want to gradually increase load, maintain constant concurrency, or simulate complex usage patterns. Picking the right one helps match your test design to real-world scenarios.
For accurate results, it’s essential to test under real conditions. BrowserStack lets you run JMeter tests on real devices and networks without managing infrastructure. With over 3,500+ real devices, browsers, and OS combinations, it gives teams a complete and scalable solution for modern testing needs.