Businesses rely heavily on Customer Relationship Management (CRM) platforms like Salesforce to manage sales, customer support, marketing, and more. With its complex architecture and customizable nature, thorough testing is essential to ensure any implementation, upgrade, or new feature works as intended.
This is where Salesforce User Acceptance Testing (UAT) plays a crucial role. It acts as the final validation layer before a solution goes live, ensuring that the platform meets business requirements and user expectations.
Overview
What is a Salesforce UAT Testing Template?
Salesforce UAT Testing Template is a structured document that helps track and validate end-user testing of Salesforce features before go-live.
Types of Salesforce UAT Testing Templates:
- Feature-based Templates
- Business Process Templates
- Regression Testing Templates
- Integration Templates
Types of User Acceptance Testing in Salesforce:
- Alpha Testing
- Beta Testing
- Black Box Testing
This article offers a deep dive into Salesforce UAT and provides comprehensive guidance on using Salesforce UAT testing templates.
What is Salesforce User Acceptance Testing (UAT)?
User Acceptance Testing (UAT) in Salesforce is a critical phase where end-users validate whether the developed solution meets their requirements. It is typically performed after system testing and before moving the solution to production. The main goal is to verify that the Salesforce environment functions correctly in real-world scenarios.
Objectives of Salesforce UAT:
- Ensure business requirements are met
- Identify gaps or bugs from a user’s perspective
- Minimize post-deployment issues
- Improve user confidence in the system
- Validate integrations, automations, and custom features
- Check for performance and usability issues
UAT helps businesses avoid costly rework by capturing user feedback before go-live. It ensures the delivered solution reflects real user needs and business operations.
Read More: What is UAT Environment in Software Testing
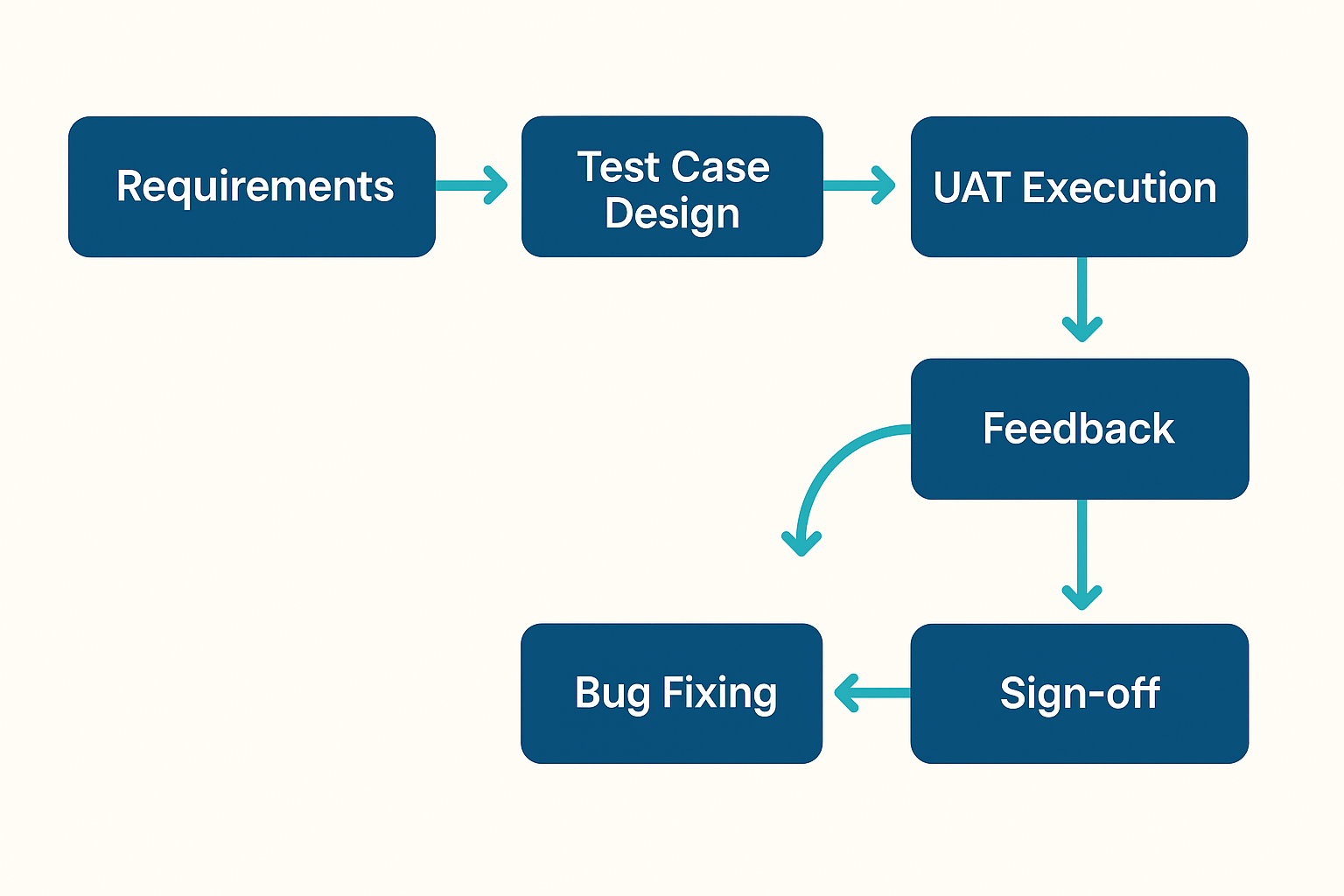
UAT Workflow Diagram
Key Aspects of Salesforce UAT
Conducting effective UAT in Salesforce involves multiple factors:
- Involvement of actual users: Business users who understand the processes and use cases should perform testing.
- Clear definition of test cases: Well-documented scenarios aligned with business requirements.
- Data readiness: Use of realistic data sets for accurate validation.
- Defined entry and exit criteria: Know when UAT should start and when it can be signed off.
- Test environment: A sandbox that mirrors the production environment.
- Feedback loop: A clear mechanism to log, prioritize, and address issues during the UAT phase.
What is a Salesforce UAT Testing Template?
A Salesforce UAT testing template is a structured document or tool that outlines the test cases, expected results, and actual outcomes during user acceptance testing. It acts as a guide for testers to validate each feature or process systematically.
These templates help:
- Standardize test execution
- Track test results efficiently
- Reduce errors and duplication
- Facilitate faster approvals and sign-offs
- Improve collaboration across QA, business, and technical teams
Templates are usually created in Excel, Google Sheets, or integrated into test management tools like TestRail, Jira, or Zephyr.
Example Salesforce UAT Testing Template
Here is an example of a Salesforce UAT testing template:
| Test Case ID | Test Scenario | Pre-conditions | Steps to Execute | Expected Result | Actual Result | Pass/Fail | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| UAT-001 | Create a new Lead | Logged in as Sales Rep | 1. Go to Leads tab 2. Click ‘New’ 3. Fill form and save | Lead is created and visible in list view | Lead created successfully | Pass | |
| UAT-002 | Convert Lead to Opportunity | Existing Lead record | 1. Open lead 2. Click ‘Convert’ 3. Complete conversion | Lead converted to account, contact, and opportunity. | Contact not created | Fail | Issue with contact creation |
Read More: Test Case Templates with Example
Types of Salesforce UAT Testing Templates
Salesforce testing templates can vary depending on project complexity and the phase of the implementation. Some common types include:
- Feature-based templates: Focused on validating specific Salesforce modules like Sales Cloud, Service Cloud, or Marketing Cloud.
- Business process templates: Centered around end-to-end workflows, e.g., Lead to Opportunity, Case Management.
- Regression testing templates: Used for validating existing features during enhancements or upgrades.
- Integration templates: Focused on testing data flow and triggers between Salesforce and external systems.
Types of User Acceptance Testing in Salesforce
User Acceptance Testing (UAT) in Salesforce involves several types of approaches, each tailored to test the system from a unique perspective and address different user needs and project goals.
There are different types of UAT that can be implemented in Salesforce projects:
1. Alpha Testing
- Conducted internally by a limited group of employees, such as QA engineers, business analysts, or Salesforce power users.
- Typically performed in a sandbox environment using scrubbed or mock data.
- Focuses on core functionality, UI validation, and early identification of critical bugs.
- Helps filter out major issues before engaging external or broader internal audiences.
Read More: Difference between Alpha and Beta Testing
2. Beta Testing
- It involves actual end-users, usually stakeholders, customers, or a select group of employees.
- Executed in a near-production environment.
- Captures usability feedback, performance issues, and alignment with business workflows.
- Helps in finalizing user experience improvements and validating readiness for release.
3. Black Box Testing
- Focuses on validating that outputs match expectations based on specific user inputs.
- Testers do not need access to source code or internal logic.
- Effective in verifying that Salesforce customizations and automations meet user requirements.
- Suitable for business users who are testing from a functional perspective.
4. Operational Acceptance Testing (OAT)
- Ensures the Salesforce system is operationally ready for production.
- Includes validation of backup processes, monitoring, maintenance tasks, and performance tuning.
- Typically conducted by DevOps or IT teams.
Contract Acceptance Testing:
- Validates that all contractual or statement of work (SOW) deliverables have been met.
- Involves client stakeholders or project sponsors.
- Provides legal and business assurance that the system is compliant with agreements.
5. Regulation Acceptance Testing:
- Focuses on compliance with industry regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, or financial governance standards.
- May involve legal, compliance, or audit teams.
- Verifies that the system securely handles sensitive data and adheres to policies.
Top Tools for Salesforce UAT Testing
To streamline UAT, several tools are available that integrate well with Salesforce. While many popular platforms are commercial and open source, there are also robust open-source alternatives that offer flexibility, community support, and cost-efficiency for teams with development expertise.
- Selenium: One of the most widely used open-source frameworks for automating web applications. It supports testing Salesforce UI through custom scripts and integrates with CI/CD pipelines.
- BrowserStack Salesforce Test Automation: It is an AI-powered, cloud-based solution for seamless, no-setup testing of Salesforce apps across real browsers and devices. It simplifies test creation, execution, and debugging, ensuring consistent performance. With AI-driven test creation, smart authoring for dynamic elements, and reliable execution on real devices, it enhances stability and reduces flakiness.
- Cypress: A modern testing tool with growing popularity for UI testing, also available with paid dashboard features.
- Opkey: Codeless automation with support for UAT and regression testing. Allows business users to write and manage tests.
- TestRail: A comprehensive test case management tool that helps organize, execute, and track UAT scenarios with detailed reporting.
- Leapwork: A no-code automation platform that empowers business users to design and run Salesforce tests using visual flowcharts, making it ideal for UAT and regression testing.
- Provar: A test automation solution built specifically for Salesforce. It supports end-to-end testing across Salesforce Classic, Lightning, and custom apps, with deep metadata integration and minimal maintenance.
- Copoda: A DevOps and test automation platform for Salesforce that includes UAT management, version control, and release automation. It aligns testing with CI/CD workflows and governance.
- Avosure: An AI-powered test automation and validation platform that supports UAT and change impact analysis for Salesforce. It enables non-technical users to validate functionality with minimal scripting.
- ACCELQ: A cloud-based, codeless testing platform with native Salesforce support. ACCELQ enables fast creation of business process tests and integrates well with CI/CD tools for scalable UAT.
Read More: Salesforce Test Automation (Tools included)
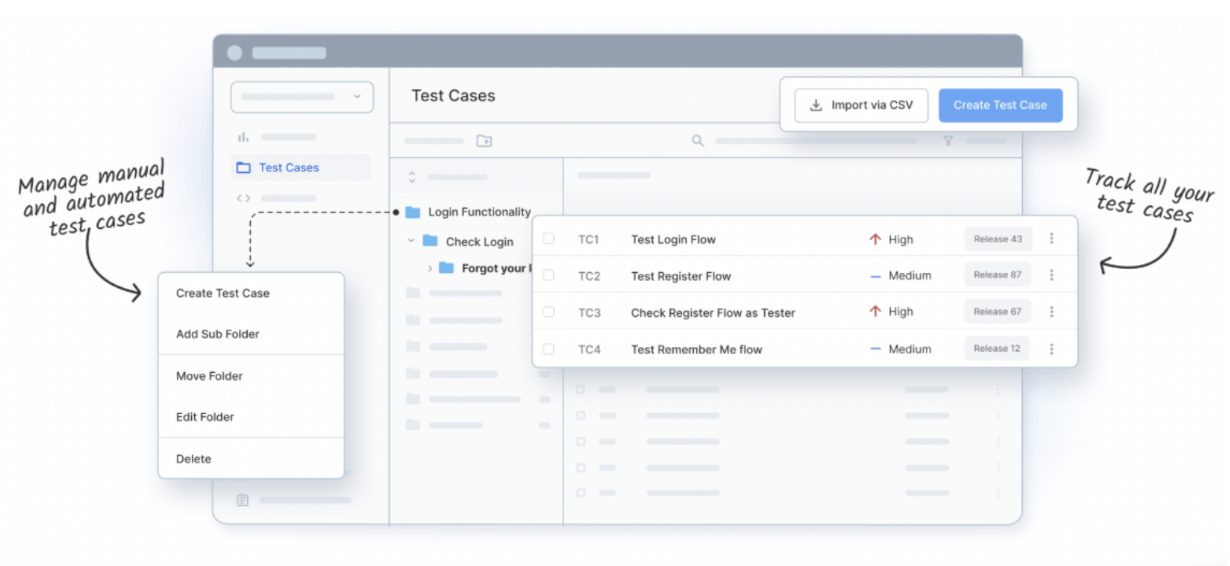
How to Create and Manage Test Cases for Salesforce UAT Testing?
BrowserStack Test Management offers a streamlined approach to creating, organizing, and executing test cases efficiently for Salesforce UAT Testing. Here’s how to get started:
Creating Test Cases
- Log In to BrowserStack Test Management: Sign in to your account and navigate to your desired project.
- Go to the Test Cases Section: From the project dashboard, select the “Test Cases” tab.
- Create a New Test Case: Click on “New Test Case” to start creating one.
- Fill in Test Case Details: Add a clear title, description, and relevant tags.
- Define Test Steps: Outline actionable steps for testers to follow during execution.
- Set Priority Level: Assign a priority (High, Medium, Low) to help manage testing focus.
- Save and Review: Review your inputs, then save the test case to finalize it.
Managing Test Cases
- Access Existing Test Cases: Navigate back to the Test Cases section of your project.
- View and Organize: Filter or sort test cases by priority, tags, or status for better clarity.
- Edit Test Cases: Click on any test case to update its steps, details, or priority.
- Add or Remove Cases: Use “New Test Case” to add, or delete outdated ones to keep things current.
- Execute Test Cases: Run test cases and track their execution status within the tool
- Review Results: Analyze execution outcomes, note any bugs or issues, and document them.
- Update as Needed: Refine test cases based on test outcomes or changes in app functionality.
Differences Between Salesforce UAT and Functional Testing
Functional testing ensures that individual components of Salesforce work correctly. UAT confirms those components work as expected from a business perspective.
| Feature | UAT | Functional Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Goal | Verify business requirements | Validate system functions |
| Testers | Business users | QA/Testers |
| Focus | End-to-end flows | Specific functionalities |
| Environment | Pre-production/Sandbox | QA/Test Environment |
| Output | Go/No-Go decision | Bug reports |
| Language | Business-oriented | Technical oriented |
Best Practices for choosing Salesforce UAT Test Case Templates
Here are the best practices for choosing Salesforce UAT Test Case Templates:
- Align with business processes: Ensure your template reflects actual workflows (e.g., Lead Conversion, Quote to Cash).
- Use simple language: Non-technical users should easily understand test steps.
- Include expected outcomes: Define what success looks like for each case.
- Integrate with tools: Templates compatible with tools like BrowserStack, Jira, or Excel enhance tracking.
- Prioritize reusable templates: Focus on templates that can be adapted for future projects.
- Incorporate traceability: Link each test case to a business requirement or user story.
- Plan for documentation: Templates should have space for tester comments, screenshots, and issues logged.
Conclusion
Effective Salesforce UAT ensures your CRM system is aligned with real business needs and ready for deployment. A structured approach, supported by well-designed testing templates and modern tools, can save time, reduce risks, and enhance user satisfaction.
BrowserStack Salesforce Test Automation, combined with integration with Test Management, provides a powerful platform for running Salesforce UAT at scale. It supports real-device testing, cross-browser compatibility checks, and smooth collaboration between QA and business teams.