Creating an ADA-compliant mobile app ensures your digital product is accessible to everyone, including users with disabilities. It protects your business from potential legal risks and promotes inclusivity.
Overview
Why is an ADA-compliant app important?
It is important as it helps make digital experiences accessible and inclusive for all users.
- Ensure Legal Compliance: Avoid lawsuits and penalties by adhering to accessibility laws.
- Improve SEO: Accessible apps tend to rank better in search results.
- Expand User Base: Reach a wider audience, including users with disabilities.
How to Make an ADA-Compliant App?
Follow these tips to make your app ADA-compliant.
- Ensure compatibility with screen readers.
- Provide alternative texts for all images and icons.
- Enable keyboard and switch navigation.
- Maintain at least a 4.5:1 contrast ratio between text and background to keep content readable for users with visual challenges.
- Support text scaling so users can enlarge fonts without disrupting the layout or design flow.
- Add accurate captions and transcripts to all audio and video elements to make media content accessible.
This article covers the benefits, guidelines, and steps to make your app ADA-compliant.
Why Should Businesses Invest in ADA-Compliant App Development?
Accessibility is a legal requirement in almost every country. It also improves user experience, strengthens brand reputation, and expands market reach. Here are the key reasons to ADA compliance is important.
1. Ensure Legal Compliance
The ADA Act provides equal access to digital content, and failure to do so can lead to lawsuits, penalties, and reputational damage. The penalty for a single ADA violation is $75,000, which can increase to $150,000 for multiple violations.
2. Improve SEO
ADA-compliant apps align with key SEO best practices, like using semantic HTML and adding alt text for images. These elements improve how search engines index content. Additionally, better accessibility enhances the user experience, increasing engagement and retention, both of which are key factors for search ranking.
3. Expand User Base
ADA compliance increases your app’s accessibility by allowing people of all abilities to engage with your product. As a result, inclusive apps reach a wider audience and enhance your brand reputation by promoting equality and providing a user-friendly experience.
Read More: Accessibility Training for Designers
Common Accessibility Issues When Using Mobile Apps
Here are some of the frequent issues users face while using mobile apps:
- Small touch points: When buttons or links are too tiny or placed too close, users with limited dexterity struggle to tap accurately.
- Poor color contrast: Users with visual impairments struggle to read text that doesn’t stand out clearly from the background.
- Lack of screen reader support: Without proper support for screen readers, visually impaired users struggle to navigate the app.
- Missing or non-descriptive alt text: Images without descriptive alt text exclude users who rely on screen readers to understand visual content.
- Complex navigation: App navigation that is not keyboard or switch-friendly can be difficult for users with mobility impairments.
- No captions or transcripts: Multimedia content without captions or transcripts limits accessibility for users with hearing impairments.
Understanding Mobile App ADA Compliance
Developers must follow various guidelines and legal requirements to make mobile apps accessible.
1. Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA)
The Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) ensures individuals with disabilities have equal access to all public spaces, including digital platforms like mobile apps. ADA compliance requires that apps be accessible to people with various disabilities, such as those affecting vision, hearing, or mobility. Here are some key ADA requirements.
- Apps must be usable with assistive technologies like screen readers or voice commands.
- Navigation should be clear and not dependent solely on touch gestures or visual cues.
- Text must be adjustable and meet sufficient contrast standards for readability.
- All multimedia content, including videos, must provide captions or transcripts.
- Forms and error messages must be clearly labeled with instructions for correction.
- Interactive elements should be accessible via keyboard or alternative input methods.
2. Section 508
Section 508 is a U.S. federal law that mandates accessibility for all electronic and information technology developed, procured, maintained, or used by federal agencies. It applies to digital platforms such as websites, software, and mobile apps to ensure they are accessible to individuals with disabilities. Section 508 requires the following:
- Federal agencies must ensure their apps and websites are accessible.
- Section 508 influences private sector apps by setting accessibility benchmarks.
- Developers must follow specific guidelines to ensure usability for users with disabilities
Read More: 508 Compliance Testing Tools
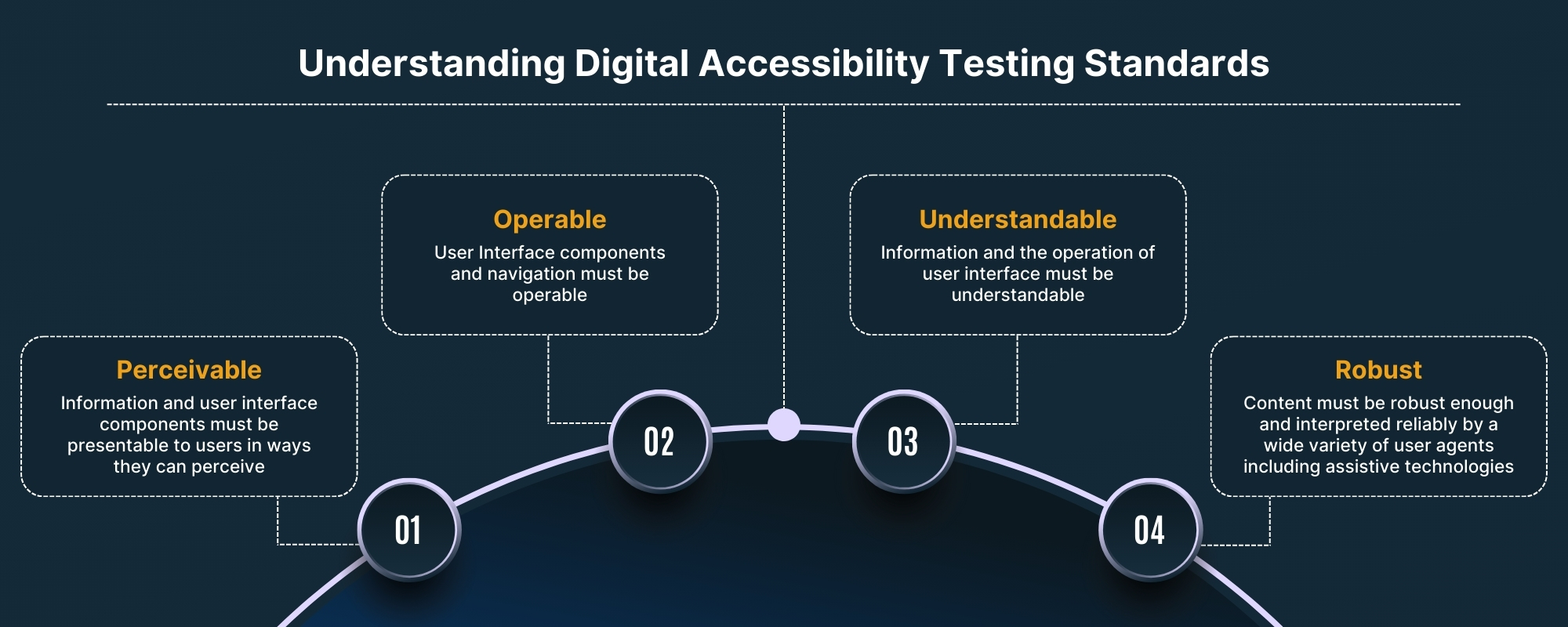
3. WCAG Guidelines for Apps
The Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG) focus on making web and mobile content more accessible. These guidelines follow four key principles: Perceivable, Operable, Understandable, and Robust (POUR).
To comply with WCAG, your
- Content must be presented in ways that users can perceive, such as providing alternative text for images.
- Users must be able to interact with the app, such as offering keyboard navigation options.
- Information should be clear and understandable, with easy-to-follow instructions.
Read More: Must-have Chrome extensions for WCAG Testing
4. Twenty-First Century Communications and Video Accessibility Act (CVAA)
The CVAA ensures that modern communication technologies, like video and messaging, are accessible to individuals with disabilities. It applies to mobile apps with video or voice features.
- Users with hearing or vision impairments must have access to video and audio content.
- Apps must provide alternatives, like captions or transcripts, for video and audio content.
How Accessible Design Benefits All Users?
Here’s a detailed breakdown of how various accessibility features benefit different groups of users:
| Accessibility Feature | Helps Users with Disabilities | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| High color contrast | Users with low vision or color blindness | Enhances readability in various lighting conditions for users with visual impairments |
| Large touchpoints | Users with motor impairments or tremors | Makes it easier for users with limited dexterity or large fingers to interact with the app |
| VoiceOver/TalkBack support | Blind or visually impaired users | Assists blind users by reading aloud the content on the screen |
| Text resizing | Users with low vision or aging eyes | Provides flexibility for users to adjust text size for better readability |
| Clear and simple navigation | Users with cognitive or learning disabilities | Simplifies navigation for users with cognitive challenges |
| Multimedia captions | Users with hearing impairments | Makes content accessible for users who are deaf or hard of hearing |
| Keyboard/switch navigation | Users with severe motor disabilities | Enables navigation through external keyboards or assistive tech like switches |
| Consistent layouts | Users with cognitive or memory challenges | Helps users quickly adapt and navigate, and improves overall user experience. |
| Error suggestions | Users struggling with forms or task flows | Provides clear error guidance, reduces frustration, and ensures successful task completion. |
How to Make Your Mobile Apps ADA-Compliant?
These are some of the important steps to be followed for making your mobile apps ADA-compliant:
- Design for various screen sizes and orientations: Use adaptable layouts that work on all screen sizes and orientations. Make sure users can navigate smoothly across devices without losing usability.
- Make buttons easy to tap: Maintain a minimum button size of 44 x 44 pixels. Provide enough spacing between interactive elements to avoid accidental taps.
- Provide text alternatives for images and icons: Include descriptive alt text for all images and icons. This helps users who rely on screen readers to understand content.
- Ensure keyboard and switch navigation: Make your app fully navigable using a keyboard or switch controls. Ensure all interactive elements are accessible using keyboard shortcuts or assistive technologies.
- Allow text resizing without breaking the layout: Enable users to resize text without causing layout issues. This is essential for users with low vision or those who prefer larger text.
Read More: How to resize an image using CSS
- Use sufficient color contrast: For readability, keep at least a 4.5:1 ratio between text and background. Use additional cues beyond color to highlight important content.
- Provide captions and transcripts for multimedia: Offer captions and transcripts for video and audio content. This ensures accessibility for users who are deaf or hard of hearing.
- Provide clear and simple navigation: Design a straightforward navigation system. Label buttons and links clearly and avoid overcomplicating the interface.
Read More: Web Accessibility Best Practices
How BrowserStack Can Help Achieve Mobile App ADA Compliance?
BrowserStack App Accessibility is a cloud-based platform for testing and monitoring the accessibility of mobile apps. It supports screen reader testing on over 3,500 real Android and iOS devices and ensures your app is inclusive and follows all the accessibility compliance, like ADA, WCAG, and Section 508.
The key features of BrowserStack App Accessibility include,
- Real-Device Testing: Conduct tests on a 3,500+ real iOS and Android devices without any setup or maintenance overhead.
- Workflow Analyzer: Monitor your app for common accessibility issues like insufficient accessibility labels, improper touch target sizes, color contrast, screen orientation, and text resizing.
- Screen Reader Compatibility: Test your app with screen readers like TalkBack on Android and VoiceOver on iOS to ensure all content is accessible and navigable.
- Automated Accessibility Tests: BrowserStack offers plug-and-play accessibility automation
- Detailed Issue Reports: Get actionable insights with reports like annotated screenshots that highlight issues and provide feasible solutions.
Why Choose BrowserStack for App Accessibility Testing?
An inaccessible app can exclude millions of users and expose your brand to legal and reputational risk. With global standards like WCAG 2.2, ADA, EAA, and more than 10 regional regulations, mobile accessibility is no longer optional—it’s essential.
BrowserStack App Accessibility Testing is designed to help teams meet global accessibility standards efficiently. The advanced Spectra™ Rule Engine identifies up to 66% more accessibility issues compared to traditional tools. It also performs end-to-end workflow scans up to 8× faster, allowing teams to build accessible apps without impacting development speed.
What sets BrowserStack apart?
- Real Device Coverage: Test on 1,000+ real iOS and Android devices, spanning native, hybrid, and web apps, for unmatched accuracy and reliability.
- Spectra™ Rule Engine: Catch more issues, including complex edge cases often missed by open-source tools.
- Automated App Accessibility Scans: Quickly analyze UI components, content labels, touch areas, and color contrast with precision.
- Screen Reader Testing: Validate accessibility using real screen readers like TalkBack (Android) and VoiceOver (iOS) on physical devices—not emulators.
- Centralized Reporting & Logs: Get annotated issue logs, video recordings, and collaborative dashboards.
- Seamless CI/CD Integration: Supports automation frameworks like Appium, Espresso, and XCUITest for continuous accessibility checks during development.
- Cross-Functional Collaboration: Enable product, QA, and dev teams to work off a single source of accessibility truth.
- Part of the Trusted BrowserStack Platform: Trusted by over 50,000 teams worldwide for enterprise-grade quality assurance.
Conclusion
An ADA-compliant app helps widen the user base, prevent legal issues, and improve SEO. To create an inclusive and accessible app, follow the ADA, Section 508, WCAG, and CVAA guidelines thoroughly.
Then, test on real devices with BrowserStack to ensure your app works properly with screen readers, has the right contrast, and follows all the accessibility requirements. You can also set up automated tests to ensure every update or feature release is thoroughly tested for accessibility on real devices.