Codeless testing has emerged as a game-changer, enabling teams to automate tests without requiring deep programming knowledge.
Overview
What is Codeless Testing?
Codeless testing automates test creation and execution without code, using visual interfaces, drag-and-drop, and AI. It enables non-technical teams to contribute, speeding up testing and improving coverage.
How it Works
- Visual Interfaces: Design tests through graphical interfaces instead of coding.
- Drag-and-Drop: Build test flows by dragging pre-built actions or components.
- Record and Playback: Capture user interactions and convert them into automated steps.
- AI and Machine Learning: Generate test data, auto-update tests, and improve accuracy.
Key Benefits
- Increased Accessibility: Enables non-technical users to create and manage tests.
- Faster Test Creation: Reduces test design time from days to hours or minutes.
- Faster Feedback: Provides rapid insights to developers for quicker issue resolution.
- Better Collaboration: Promotes shared responsibility for quality across teams.
- Reduced Maintenance: AI-driven updates simplify test upkeep as applications evolve.
- Comprehensive Coverage: Achieve higher automation coverage more efficiently.
This article gives you a complete overview of codeless testing, its benefits, best practices, and popular tools.
Understanding Codeless Testing
Codeless testing refers to the process of automating test case creation and execution without writing any code. Instead, users can design tests using visual interfaces, drag-and-drop functionality, or record-and-playback tools.
This approach makes test automation easier, faster, and more accessible, especially for those without programming expertise.
Codeless testing typically focuses on ensuring software behaves as expected across different devices, browsers, and environments.
How Codeless Testing Differs from Traditional Automated Testing
Codeless testing and traditional automated testing differ significantly in their approach and execution. While both aim to automate the testing process, the key distinction lies in the skill requirements, flexibility, and ease of implementation.
| Aspect | Codeless Testing | Traditional Automated Testing |
|---|---|---|
| Skill Requirement | No coding skills required; designed for non-technical users. | Requires coding knowledge and scripting skills (e.g., Java, Python). |
| Test Creation | Visual interfaces or drag-and-drop tools for easy test design. | Test cases are written through code, which can be complex and time-consuming. |
| Flexibility | Limited to predefined actions and configurations. | Highly customizable and flexible for complex test scenarios. |
| Maintenance | Easier to maintain, as test updates don’t require code changes. | Requires manual updates to code when the application changes. |
| Integration | Typically integrates easily with CI/CD tools. | Integrating with CI/CD requires additional configurations and scripting. |
| Speed of Implementation | Faster test creation and implementation. | Slower due to code writing and debugging processes. |
| Scalability | Less scalable for complex test scenarios. | More scalable for large, complex test suites. |
Learn More: How to Create Test Cases for Automated tests?
Importance of Codeless Testing
Codeless testing has become an essential part of modern software development for several reasons:
- Faster Test Creation: With no need to write code, tests can be created much faster, reducing development cycles and speeding up time-to-market.
- Increased Accessibility: It allows non-technical users, such as QA testers or business analysts, to actively participate in automation, broadening team involvement in testing.
- Cost-Effective: By reducing the need for specialized developers to write and maintain test scripts, organizations can lower testing costs.
- Improved Collaboration: Codeless tools foster better communication between developers, testers, and other stakeholders by providing a shared, visual representation of the test cases.
- Higher Test Coverage: Automated tests can be run across various environments and devices, ensuring more comprehensive testing and fewer manual errors.
- Quick Adaptability: Test cases are easier to update when the application changes, reducing maintenance effort and allowing quicker adjustments to new features.
Core Principles of Codeless Testing
Codeless testing focuses on automating software tests without the need for coding skills, making it accessible to both technical and non-technical users. The core principles include:
- Visual Test Design: Tests are created using drag-and-drop, record-and-playback, or other visual interfaces.
- Reusable Test Steps: Common actions or workflows can be saved and reused across multiple test cases.
- AI-Powered Automation: AI can detect UI changes and auto-heal tests to reduce maintenance.
- Cross-Platform Support: Execute tests across browsers, devices, and operating systems without complex setup.
- Integration with CI/CD: Seamlessly integrates into development pipelines to enable continuous testing.
- Ease of Maintenance: Updates to tests can be done visually without rewriting scripts.
Top Codeless Testing Tools in 2025
Here are some of the leading codeless testing tools shaping automation in 2025. Each tool offers unique features for different use cases.
Popular Codeless Testing Tools
- BrowserStack Low Code Automation
- TestSigma
- Perfecto
- Bugbug
- TestRigor
- Functionize
- CloudQA
Here is a detailed description of each of these tools.
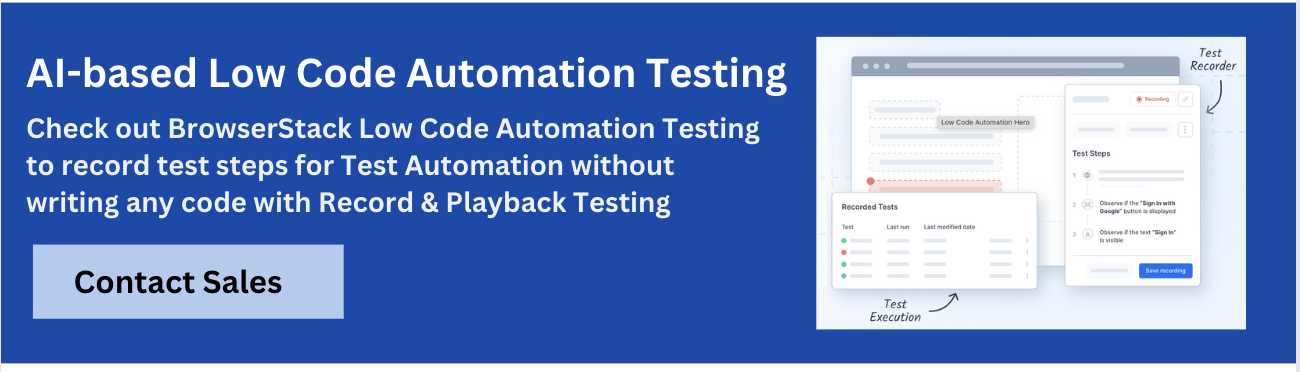
1. BrowserStack Low-Code Automation
BrowserStack Low-Code Automation empowers teams to create, run, and maintain automated tests without writing code.
It combines an interactive test recorder, AI-powered self-healing, and real device cloud testing so teams can begin testing and start automation in minutes and scale across browsers and devices.
With AI-powered self-healing and low-code authoring agents, it speeds up test creation by up to 10x and reduces build failures by up to 40%, delivering faster, more stable automation for both technical and non-technical users.
Key Features of BrowserStack Low-Code Automation:
- Test Recorder: Easily capture user actions like clicks and form inputs and transform them into automated tests. This recorder supports complex functional validations including visual and text validations.
- Readable Test Steps: Actions recorded are converted into simple, human-readable English instructions, making it easy for anyone to understand and modify tests.
- Visual Validation: Enables testers to add checkpoints during recording that verify the correct display of UI components or screens, ensuring that visual elements render as expected.
- AI-Powered Self-Healing: Uses AI to detect when UI elements change and automatically updates the test to prevent failures. This minimizes the need for manual test maintenance.
- Low-Code Authoring Agent: Uses AI to turn natural language prompts into executable test steps, automating tasks from simple instructions.
- Cross-Browser & Mobile Testing: Runs tests on real desktop browsers and mobile devices in the BrowserStack cloud, covering a wide range of operating systems and devices.
- Data-Driven Testing: Allows the same test to be executed with different input values, enabling broader coverage of scenarios without creating separate tests.
- Reusable Modules:Lets teams save common sequences of steps as reusable modules that can be inserted into multiple test cases, reducing duplication and simplifying maintenance.
- API Step Integration: Adds flexibility by letting testers call APIs from within the test for tasks such as generating data, setting up test conditions, or cleaning up databases.
- Test Scheduling and CI/CD Integration: Enables automated tests to run on a set schedule or trigger directly from build pipelines via REST APIs or popular CI tools, ensuring continuous validation without manual intervention.
- Test Editing Without Re-Recording: Allows testers to open an existing test and modify, insert, or delete steps without having to re-record the whole test, saving time during maintenance.
- Private Environment Testing & Email Notifications: Teams can test websites behind firewalls or on internal and staging environments with zero setup. BrowserStack Low-Code Automation also sends detailed email reports with build pass/fail status and logs, giving stakeholders timely insights while validating applications securely.
BrowserStack Low-Code Automation delivers faster, smarter, and more reliable test automation with zero coding required.
It combines AI-driven stability, intuitive design, and the power of the BrowserStack real-device cloud to help teams test better, ship faster, and maintain quality at scale.
Pricing:
- Free Plan: Offers unlimited test creation along with AI-generated test data, intelligent wait handling, API steps, secure private environment testing, video debugging, and 24×7 support.
- Paid Plan: Unlocks AI agents, advanced self-healing, parallel execution, and enterprise-grade features, with custom pricing based on organizational needs.
Try BrowserStack Low Code Automation
2. TestSigma
TestSigma is a codeless automation platform for web, mobile, and API testing, focusing on simplicity and AI-driven test management.
Key Features:
- Visual test creation and execution
- AI-powered step suggestions and test optimization
- Integrates with CI/CD and popular project management tools
Pros: Easy for non-technical users, scalable for enterprise projects
Cons: Some advanced customizations may require technical input
Read more: TestSigma Alternatives
3. Perfecto
Perfecto provides codeless and low-code automation for web and mobile apps with cloud-based device access.
Key Features:
- Scriptless test creation via record-and-playback
- Real device cloud for cross-browser testing
- AI-based visual validation and reporting
Pros: Supports real devices, integrates with CI/CD pipelines
Cons: Higher cost for enterprise plans
4. Bugbug
Bugbug offers codeless browser test automation using an intuitive visual interface for QA and business users.
Key Features:
- Record and replay browser interactions
- Supports testing across multiple browsers
- Easy maintenance and step reusability
Pros: Beginner-friendly, fast test creation
Cons: Web-only focus, limited advanced features
5. TestRigor
TestRigor is a no-code automation platform using natural language to write and execute test cases for web and mobile apps.
Key Features:
- NLP-based test creation in plain English
- Supports mobile, web, and API testing
- Integrates with CI/CD pipelines and cloud execution
Pros: Easy for non-technical teams, accelerates regression testing
Cons: Advanced customization requires paid tiers
Must Read: testRigor Alternatives
6. Functionize
Functionize is an AI-driven codeless automation tool for web applications, designed for high-scale test creation and maintenance.
Key Features:
- AI-based test generation and self-healing
- Cloud-based parallel execution
- Chrome plugin for quick test recording
Pros: Low barrier to entry, stable and scalable tests
Cons: Best suited for large enterprises, primarily web-focused
Also Read: Functionize Alternatives
7. CloudQA
CloudQA offers codeless automation for web apps, focusing on record-and-playback tests with cloud execution.
Key Features:
- Visual test recorder and editor
- Cloud-based execution and scheduling
- Integration with CI/CD and project management tools
Pros: Quick setup, no coding required
Cons: Limited mobile app support
How Codeless Testing Works
Codeless testing works by allowing testers to create, execute, and manage automated tests without writing code. Instead of coding each test scenario, users interact with an intuitive interface, using drag-and-drop features, record-and-playback tools, or visual scripting.
The process generally involves:
- Test Creation: Testers capture user interactions or define test cases through graphical interfaces or natural language descriptions.
- Test Execution: These tests are then executed across different environments, browsers, or devices.
- AI Support: AI-driven tools enhance the testing process by automatically identifying UI changes, adapting tests, and ensuring stability.
By simplifying the process, codeless testing reduces time, minimizes human error, and enables a broader team (including non-technical members) to participate in test automation.
Best Practices for Codeless Test Implementation
To maximize the effectiveness of codeless testing, follow these best practices:
- Start with a Clear Testing Strategy: Define your goals, objectives, and the test scenarios you want to automate before creating test cases.
- Use Modular Test Cases: Create reusable test steps and modules to avoid duplication and enhance test maintenance.
- Leverage AI Features: Take full advantage of AI-powered self-healing and intelligent test suggestions to minimize manual effort.
- Incorporate Cross-Platform Testing: Ensure your tests cover multiple browsers, devices, and OS environments to ensure comprehensive validation.
- Collaborate Across Teams: Enable non-technical users to contribute by providing easy-to-use tools, while maintaining communication with developers to cover complex use cases.
- Regularly Review and Update Tests: Continuously refine your tests based on feedback and test results to ensure they remain effective as the application evolves.
Limitations and Challenges of Codeless Testing
While codeless testing offers many advantages, there are some challenges to consider:
- Limited Flexibility: For complex test scenarios, codeless tools might not offer the same flexibility as traditional coding-based testing.
- Scalability Issues: As test cases grow, managing large test suites or scaling across different platforms can become difficult with some codeless tools.
- Integration Complexity: Certain codeless testing tools may face difficulties integrating with legacy systems or specific third-party applications.
- Less Control Over Test Logic: Users may have less control over the underlying test execution logic compared to manually scripted tests.
- Performance Constraints: Some tools may not handle performance testing well, limiting their use in large-scale or high-traffic environments.
Future Trends in Codeless Testing
As software development continues to evolve, so does codeless testing. Here are some key trends to watch for:
- AI Integration: Expect more advanced AI features, such as smart test creation, automated defect detection, and enhanced self-healing capabilities.
- Increased Cross-Platform Compatibility: Tools will support more devices, browsers, and OS versions for comprehensive coverage across environments.
- Enhanced Usability for Non-Developers: Expect improvements in ease of use, making it even more accessible to non-technical team members.
- Integration with DevOps: Codeless testing tools will be more seamlessly integrated with CI/CD pipelines, enabling continuous testing and faster release cycles.
- Real-Time Analytics: Enhanced reporting and real-time data analysis will become integral, providing deeper insights into test performance and application quality.
- Cloud-Based Solutions: As cloud testing grows, codeless testing will become more scalable, offering instant access to different devices and browsers without needing local infrastructure.
Conclusion
Codeless testing is revolutionizing test automation by making it faster and more accessible. It allows both technical and non-technical team members to contribute to the testing process, speeding up test creation, execution, and maintenance.
Despite some limitations, the growing capabilities of codeless testing tools, especially with AI and cloud-based solutions, promise a more streamlined and efficient testing process.
As the industry embraces these innovations, codeless testing will continue to drive better quality, faster releases, and enhanced collaboration across teams.