QA in low-code development plays a vital role in maintaining robust, scalable, and error-free software, bridging the gap between speed and quality in modern development workflows.
Overview
Why QA is Still Crucial in Low-Code Development
- Prebuilt Modules Aren’t Bug-Free: Pre-built components can still have bugs.
- Data Security Risks: Complex low-code apps increase security vulnerabilities.
- Non-Professional Developers: QA ensures reliability when apps are built by less experienced users.
- External Integrations: Robust integration testing is essential for low-code apps.
Key Practices for Low-Code QA
- Early Collaboration: Encourage teamwork from the start.
- Requirements Validation: Ensure clear, validated requirements.
- Test Planning & Setup: Plan tests and set up environments.
- Automated & Exploratory Testing: Combine automation and exploratory testing.
- Continuous Improvement: Regularly refine the QA process.
This article will give a detailed overview of QA’s role in low code development, popular tools, and best practices.
What is QA in Low-Code Development
QA in low-code development refers to the process of testing applications created on low-code platforms to ensure they function correctly, meet business requirements, and deliver a smooth user experience.
While low-code tools simplify development through drag-and-drop interfaces and prebuilt components, QA ensures that the accelerated development process does not compromise software quality.
QA teams validate workflows, business logic, integrations, and cross-platform compatibility, helping identify defects early and prevent costly errors post-deployment.
Importance of QA in Low-Code Development
QA is crucial in low-code development for several reasons:
- Ensures Application Reliability: Even with prebuilt components, low-code apps can have configuration errors or integration issues that QA helps identify.
- Maintains Performance Standards: QA tests app performance under different loads, ensuring smooth operation for all users.
- Validates Business Logic: Ensures workflows and business rules are implemented correctly, meeting organizational requirements.
- Enhances Security and Compliance: QA evaluates security controls and regulatory compliance, reducing risks in production.
- Supports Faster Delivery: By integrating QA early in the low-code development lifecycle, teams can accelerate release cycles without sacrificing quality.
- Improves User Experience: QA ensures interfaces, navigation, and functionality provide a seamless experience across devices and platforms.
QA Challenges in Low-Code Development
While low-code platforms accelerate application development, QA teams face unique challenges:
- Limited Visibility into Code: Prebuilt components may obscure underlying logic, making it difficult to identify potential defects.
- Integration Complexity: Ensuring seamless integration with external systems, APIs, and databases can be challenging.
- Platform-Specific Limitations: Some low-code platforms may have constraints that impact custom test coverage.
- Rapid Changes: Frequent updates to low-code apps can outpace traditional QA processes.
- Test Maintenance: Automated tests may require frequent updates as workflows or configurations evolve.
- Performance and Scalability Issues: Ensuring apps remain responsive under varying loads requires careful validation.
Benefits of Low-Code Test Automation for QA Teams
Low-code test automation simplifies QA workflows and improves efficiency for teams managing rapid application development:
- Faster Test Creation: Record-and-playback, visual scripting, and low-code tools reduce the time needed to design and execute tests.
- Reduced Manual Effort: Automates repetitive test cases, freeing QA teams to focus on critical workflows and exploratory testing.
- Higher Test Coverage: Enables cross-browser, cross-device, and multi-environment validation quickly.
- Improved Accuracy: Minimizes human errors in test execution and ensures consistent results.
- Seamless CI/CD Integration: Automated tests can be integrated into development pipelines for continuous validation.
- Better Collaboration: Non-technical team members can contribute to test creation, enhancing shared ownership of quality.
Popular Low-Code Automation Tools
Here are some of the leading low-code automation tools for efficient test creation and execution:
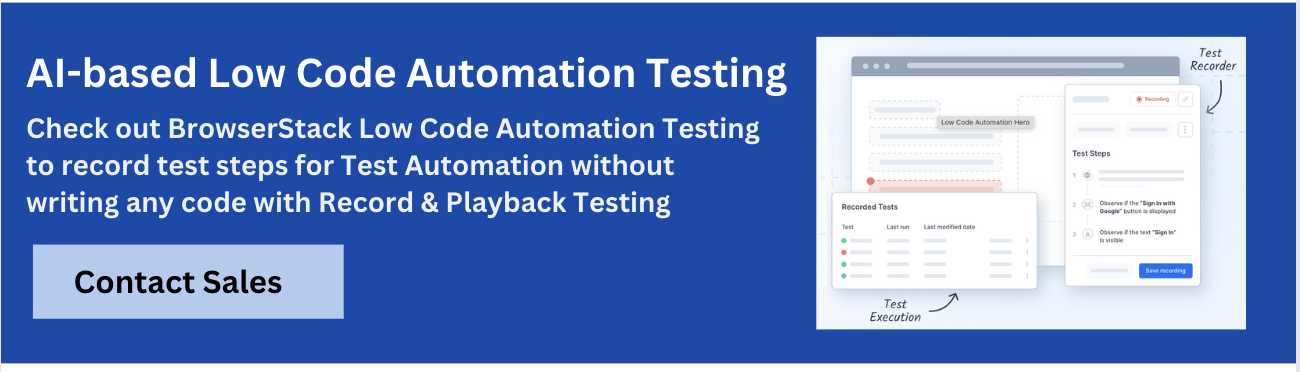
1. BrowserStack Low Code Automation
BrowserStack Low-Code Automation lets teams create, run, and maintain automated tests without coding.
With a test recorder, AI-powered self-healing, and real-device cloud testing, it accelerates test creation by up to 10x, reduces failures by 40%, and scales across browsers and devices for both technical and non-technical users.
Key Features:
- Test Recorder: Capture user actions like clicks and form inputs and transform them into automated tests with functional and visual validations.
- Readable Test Steps: Converts recorded actions into plain English instructions for easy review and modification.
- Visual Validation: Add checkpoints to verify correct display of UI components and screens.
- AI-Powered Self-Healing: Detects UI changes and automatically updates tests to prevent failures.
- Low-Code Authoring Agent: Converts natural language prompts into executable test steps.
- Cross-Browser & Mobile Testing: Run tests on real desktop browsers and mobile devices in the cloud.
- Data-Driven Testing: Execute the same test with multiple input values for broader coverage.
- Reusable Modules: Save frequently used steps as modules to reduce duplication and simplify maintenance.
- API Step Integration: Call APIs from within tests for setup, teardown, or data generation.
- Test Scheduling & CI/CD Integration: Automate test runs on schedules or trigger from build pipelines.
- Test Editing Without Re-Recording: Modify existing tests without re-recording the entire workflow.
- Private Environment Testing & Email Notifications: Test internal or staging environments securely with detailed email reports.
Pricing:
- Free Plan: Unlimited test creation, AI-generated test data, intelligent wait handling, API steps, private environment testing, video debugging, and 24×7 support.
- Paid Plan: Unlocks AI agents, advanced self-healing, parallel execution, and enterprise-grade features with custom pricing based on organizational needs.
Try BrowserStack Low Code Automation
2. Katalon Platform
A unified low-code automation platform for web, API, desktop, and mobile testing with AI-driven guidance.
Key Features:
- Visual test creation and execution.
- AI-based step suggestions and test optimization.
- Jira integration for test management.
Pros:
- Encourages collaboration between technical and non-technical users.
- Strong integration with CI/CD pipelines.
Cons:
- Some AI features are in beta.
- Complex test logic may require scripting.
3. Perfecto
Cloud-based low-code and no-code platform for web and mobile apps with real-device testing.
Key Features:
- Scriptless test creation with record-and-playback.
- AI-based visual validation and reporting.
- Real-device cloud for cross-browser testing.
Pros:
- Supports real devices for accurate validation.
- Integrates easily with CI/CD workflows.
Cons:
- Higher pricing for enterprise plans.
- Limited offline testing support.
Must Read: testRigor Alternatives
4. TestRigor
Codeless platform using natural language to automate web and mobile tests.
Key Features:
- NLP-based test creation in plain English.
- Mobile, web, and API testing support.
- CI/CD pipeline integration.
Pros:
- Quick adoption by non-technical QA team members.
- Accelerates regression testing cycles.
Cons:
- Advanced customizations may require paid tiers.
- Limited reporting for very complex workflows.
Read More: Functionize Alternatives
5. Functionize
AI-powered codeless testing platform for web applications with automated test generation and self-healing.
Key Features:
- AI-based test creation and automatic healing.
- Cloud-hosted parallel test execution.
- Chrome plugin for quick test recording.
Pros:
- Low barrier to entry; product experts can create tests.
- Scalable and stable for large projects.
Cons:
- Primarily focused on web apps.
- Some features require premium pricing.
Must Read: 12 Open source Low Code Testing Tools
6. CloudQA
Cloud-based codeless automation tool for web apps with record-and-playback functionality.
Key Features:
- Visual test recorder and editor.
- Cloud execution with scheduling.
- Integration with CI/CD and project management tools.
Pros:
- Fast setup; no coding required.
- Supports continuous test execution on the cloud.
Cons:
- Limited mobile app support.
- May require additional tools for complex workflows.
Read More: Mabl Alternatives
7. Mabl
Low-code platform for web and mobile testing with AI-driven self-healing and modular test flows.
Key Features:
- Intuitive point-and-click test recorder.
- AI-based self-healing for UI changes.
- Modular flows with JavaScript and Appium snippets.
Pros:
- Accessible to users without coding expertise.
- Reduces test maintenance with AI-driven adaptation.
Cons:
- Best suited for record-and-playback flows.
- Proprietary platform with limited integrations in some cases.
Why Choose BrowserStack Low-Code Automation?
BrowserStack Low-Code Automation offers a powerful solution for teams seeking to automate tests without writing code. It combines real-device testing, AI-powered self-healing, and low-code authoring agents to provide fast, reliable, and scalable test automation.
Key reasons to choose BrowserStack include:
- Instant Test Creation: Record user actions and create automated tests in minutes, without coding expertise.
- AI-Powered Self-Healing: Automatically detects UI changes and updates tests, reducing manual maintenance.
- Cross-Browser & Mobile Testing: Test on 3500+ real devices and browsers, ensuring broad coverage and accuracy.
- Low-Code Authoring: Convert natural language prompts into executable test steps, making automation accessible for non-technical users.
- Seamless Integration with CI/CD: Automate test execution directly within your development pipeline for continuous validation.
- Real-Time Reporting: Get instant insights into test progress and issues with detailed logs, screenshots, and videos.
Best Practices for QA in Low-Code Development
Incorporating quality assurance (QA) in low-code development requires a blend of speed and thoroughness. These best practices can help ensure a high-quality product:
- Integrate QA Early: Start testing from the early stages of low-code development, ensuring that errors are identified and fixed early.
- Collaborate Across Teams: Encourage close collaboration between business analysts, developers, and QA testers for comprehensive test coverage.
- Focus on User Experience: Validate that UI elements, interactions, and workflows are intuitive and meet user expectations.
- Leverage Automation: Use low-code automation tools like BrowserStack to speed up repetitive test scenarios and free up QA teams for more complex tests.
- Test Across Devices and Browsers: Ensure consistency by testing on real devices and browsers to check for cross-platform compatibility.
- Prioritize Critical Paths: Identify and prioritize key functionalities that directly impact user experience, such as login, registration, and payment systems.
- Maintain Continuous Testing: Integrate tests into the CI/CD pipeline to continuously validate each release and minimize disruptions in the development cycle.
- Document and Track Defects: Implement a clear system for documenting defects and tracking their resolution to improve future testing efforts.
Read More: Why No Code is the Future of Testing
Why Low-Code and No-Code is the Future of QA
Low-code and no-code platforms are transforming how QA teams build and manage tests. They make testing faster, more collaborative, and less dependent on coding expertise.
Key reasons driving adoption:
- Faster test creation: Drag-and-drop interfaces and reusable components reduce setup time.
- Broader participation: Non-technical team members can design and execute tests.
- Improved collaboration: Cross-functional teams share responsibility for quality.
- Agility with complex apps: Scales easily to keep pace with rapid product changes.
- Focus on high-value work: Frees testers to prioritize exploratory and user-focused testing.
Conclusion
QA is shifting from traditional scripting to more accessible and collaborative approaches. Low-code and no-code testing, supported by real-device cloud platforms, enable faster releases, stronger test coverage, and better user experiences.
The future of QA is about speed, simplicity, and inclusivity, where testing becomes an enabler of innovation rather than a barrier.