Mobile apps enhance engagement, improve operational efficiency, and connect businesses with customers in real time. However, developing separate iOS and Android apps can be costly and time-intensive. Hybrid apps provide a more efficient solution, allowing you to develop once and deploy across multiple platforms.
Overview
What is a Hybrid App?
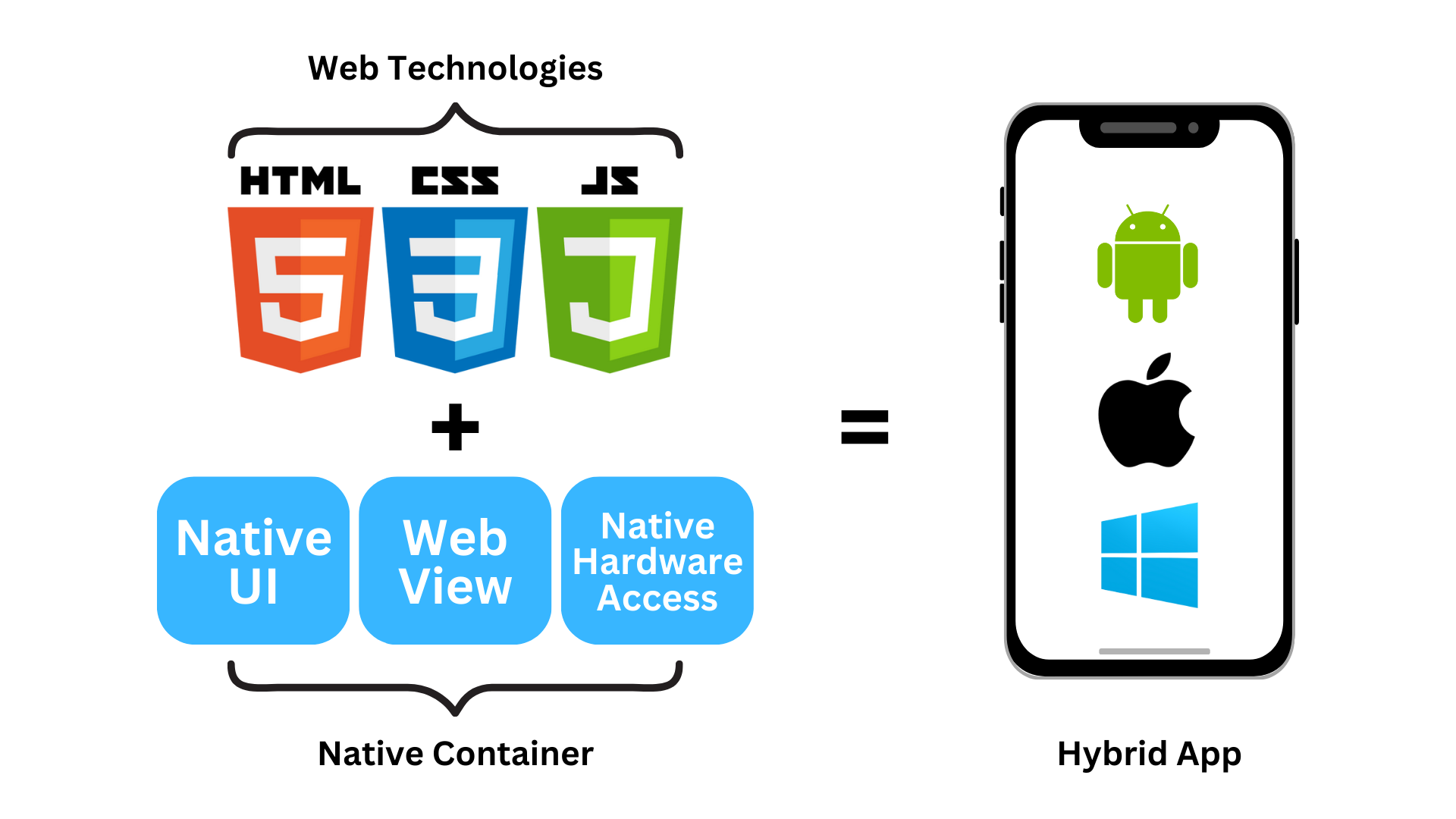
A hybrid application is a mobile app built using web technologies (HTML, CSS, JavaScript) and wrapped in a native container. It runs on multiple platforms using a single codebase.
Key Features of Hybrid Apps
- Cross-platform compatibility
- Faster development cycles
- Lower development and maintenance costs
- Access to native device features via plugins
- Easier updates and scalability
Popular Frameworks for Hybrid App Development
- Ionic: Web-first framework with a rich UI library and strong community support.
- React Native: Uses JavaScript and React to build near-native performance apps.
- Flutter: Google’s UI toolkit using Dart, known for fast rendering and expressive UIs.
- Cordova: Lightweight wrapper that enables access to native APIs with web code.
- Xamarin: It allows developers to build cross-platform apps using C# and .NET.
This article explores a hybrid app, how it works, and why it’s essential to test it properly before going live.
Understanding Hybrid Apps
Hybrid apps combine elements of both native and web applications. They are designed to work across multiple platforms, such as iOS, Android, and sometimes even Windows, using a single codebase.
Hybrid apps are often used when businesses want to provide a seamless experience across different devices without building separate apps for each platform. They balance the performance and speed of native apps with the flexibility and efficiency of web applications.
Read More: Native vs hybrid app: Which one to choose?
Features of a Hybrid App
Hybrid apps offer valuable features that make them easy to build, maintain, and run on multiple platforms. The primary features include:
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: These apps are built to function on different platforms, such as iOS and Android, using a single codebase. It helps save time and resources during development and maintenance.
- Access to Device Features: These apps can access device-specific features such as the camera, GPS, contacts, and more through native plugins, allowing them to offer functionality similar to native apps.
- Faster Development: Since developers write one set of code for all platforms, the overall development time is reduced. This is especially useful for businesses that want to launch their app quickly.
- Easier Maintenance: In these apps, the updates and bug fixes need to be applied to just one codebase, making the maintenance process simpler and more efficient. It also ensures consistency across different platforms.
- Offline support: Many hybrid apps can store data locally, allowing users to access certain features without an internet connection. This enhances the user experience in low-connectivity environments.
Popular Examples of Hybrid Apps
Many leading companies use hybrid apps to deliver consistent user experiences across different platforms. Here are some well-known examples of successful hybrid applications:
- Instagram uses a hybrid approach to deliver a consistent experience across platforms. It combines native elements for performance with web technologies for features like image rendering and real-time updates.
- X (formerly Twitter) leverages hybrid architecture to provide quick content updates and a smooth user interface. This enables the app to function reliably across various mobile devices.
- Gmail is built using hybrid technology to support web and mobile users with the same interface and functionality. This helps maintain performance and user experience across devices.
- Uber uses a hybrid framework to support its global operations efficiently. Their app delivers fast performance while simplifying updates across Android and iOS platforms.
- Evernote uses hybrid technology to offer a consistent note-taking experience across devices. It combines native performance with web-based features for syncing and accessibility.
Read More: How to Make an App Responsive
How do Hybrid Apps Work?
Hybrid apps blend features of web and native applications into a single solution. These apps are developed using standard web technologies like HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, and are enclosed within a native shell that enables them to operate on multiple platforms, including iOS and Android.
When a hybrid app is launched on a device, the native shell opens a WebView, a browser-like component within the app where the web code runs. This WebView renders the user interface and manages the app’s logic and interactions, similar to how a website functions inside a mobile app shell.
The app uses native plugins that serve as bridges between the web code and the device’s operating system to access native device features like the camera, GPS, or push notifications.
This architecture allows developers to build cross-platform apps that resemble native apps in look and feel, all while maintaining a single codebase.
The Importance of Testing Hybrid Apps
Testing hybrid apps is essential to ensure they function smoothly, look consistent, and perform well across all platforms and devices. Here are some key points why testing hybrid apps is essential:
- Cross-Platform Consistency: Testing ensures that the app behaves consistently on iOS and Android devices, helping maintain a uniform user experience across platforms.
Read More: How to approach Cross Platform Testing
- UI and UX validation: A consistent look and feel are crucial for user satisfaction. UI/UX testing verifies that the interface displays correctly on different screen sizes and resolutions.
- Performance optimization: Hybrid apps can experience performance issues if not properly optimized. Performance testing helps identify slow load times, unresponsive elements, and other performance-related concerns, ensuring smooth and responsive interactions.
- Device Feature Compatibility: Hybrid apps rely on native plugins to access various device features like the camera, GPS, and push notifications. Testing verifies that these integrations work reliably across different devices and operating systems.
- Bug detection: Functional and visual bugs can negatively impact user experience and lead to app store rejections. Testing allows for the early detection and resolution of issues, minimizing the chances of negative reviews and complications after the app is released.
- Security checks: Like any app, hybrid apps must protect user data and prevent unauthorized access. Security testing uncovers potential vulnerabilities and ensures compliance with data protection standards.
- Network behavior testing: Many hybrid apps rely on internet connectivity, and testing helps ensure the app adequately handles poor or no-network conditions.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Testing Hybrid Apps
Testing hybrid applications comes with its own set of benefits and limitations. Understanding these can help teams plan their test strategies more effectively.
Advantages
- Cross-platform Testing Efficiency: Hybrid apps are built to run on multiple platforms with a single codebase. This allows QA teams to reuse most test cases across Android and iOS, reducing effort and time.
- Faster Development-Test Cycles: With fewer platform-specific changes, hybrid apps can be built and tested more quickly, making it easier to push updates frequently.
- Cost-Effective Testing: Since the same team can test the app across platforms, businesses save on resources and testing infrastructure.
- Easier Integration with Web Automation Tools: Hybrid apps rely heavily on web technologies (HTML, CSS, JavaScript), making them compatible with many existing web testing frameworks.
Disadvantages
- Device-Level Limitations: Hybrid apps often struggle with accessing platform-specific hardware features. This can create edge cases that are harder to test or simulate.
- Inconsistent Performance Across Devices: Since hybrid apps rely on web views, performance may vary significantly depending on the device, OS version, and network conditions, requiring extensive real-device testing.
- UI/UX Testing Challenges: Ensuring a native-like user experience is tough. Minor inconsistencies in animations, gestures, or layouts may go unnoticed unless testing is done on real devices or a real device cloud.
Read More: UI Testing: A Detailed Guide
- Debugging Complexities: Debugging hybrid apps can be tricky because issues might stem from the web layer, native shell, or how they interact, demanding deeper knowledge and tools.
To address these challenges, especially those related to real device testing and debugging, teams can use platforms like BrowserStack Automate. With access to real iOS and Android devices, the platform ensures comprehensive test coverage across various environments and real user conditions.
Why Choose BrowserStack for Testing Hybrid Apps?
When it comes to testing hybrid apps, ensuring seamless performance across multiple devices and platforms is essential. BrowserStack offers a reliable, efficient, and scalable solution to simplify this process. Here’s why it is an ideal choice:
- Real Device Testing: Test hybrid apps on real devices to ensure accurate, real-world performance.
- Parallel Testing: Run tests on multiple devices simultaneously, reducing testing time and speeding up the feedback process.
- Automation Testing: Execute automated test scripts across different devices for consistent and efficient results.
- CI/CD Integration: Seamlessly integrate BrowserStack into your CI/CD pipelines to automatically test every new build.
- Real-Time Debugging: Use live logs, screenshots, and videos to identify and fix issues during testing quickly.
- No Device Maintenance: Avoid the hassle of managing, upgrading, or maintaining physical devices and emulators.
Step-by-Step Guide to Testing Hybrid Apps on BrowserStack:
Follow these steps to test your app:
1. Sign Up or Log In: Create a new account or access your existing BrowserStack account.
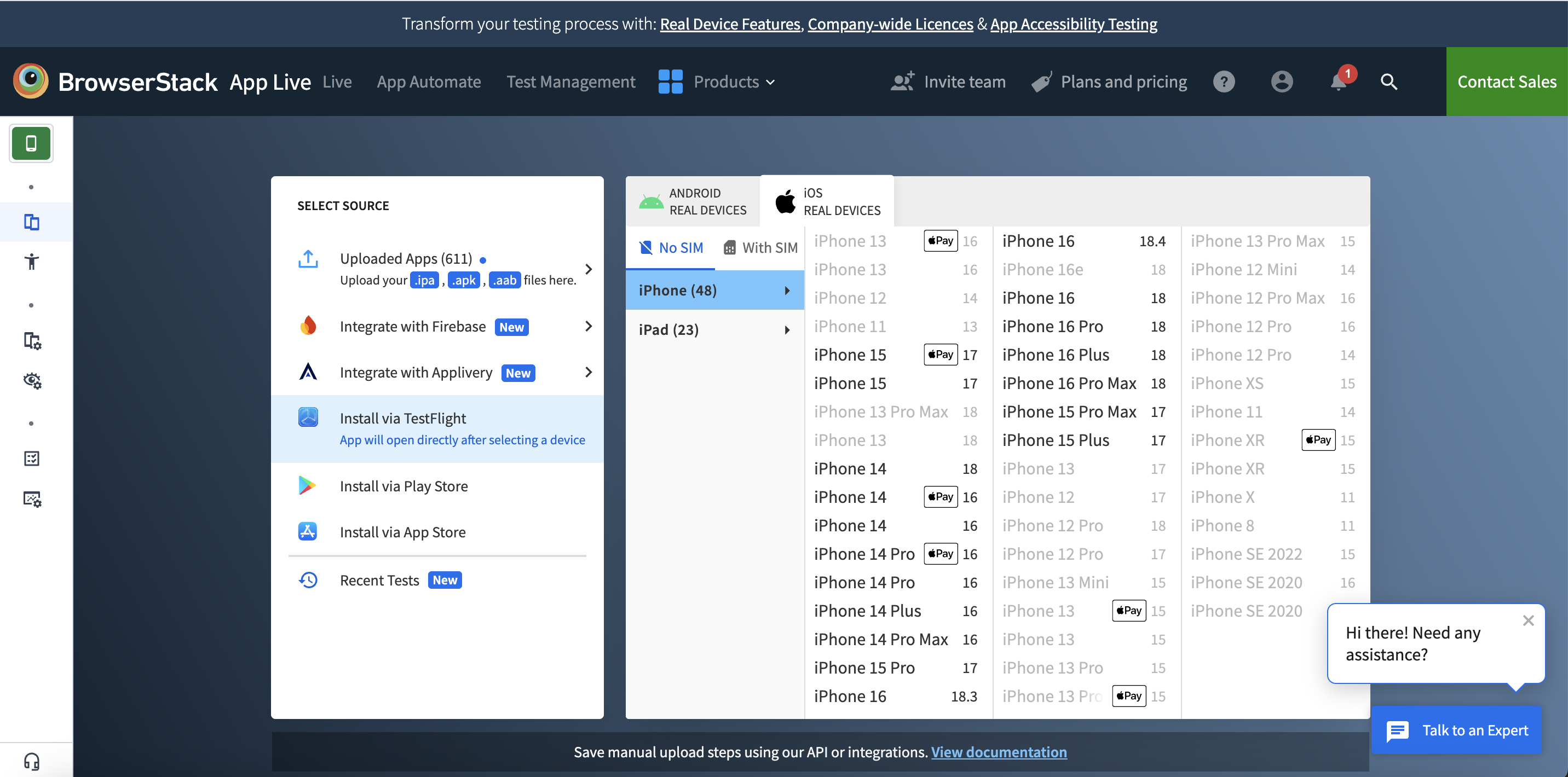
2. Select App Live or App Automate: After creating your account, you’ll be redirected to the dashboard. Navigate to ‘App Live‘ for manual testing or ‘App Automate’ for automated testing. Select either an Android or iOS device according to your app’s support.
3. Upload Your App: Upload your hybrid app’s APK (for Android) or IPA (for iOS) file.
4. Select a Real Device: Choose from different real Android and iOS devices available on the platform.
5. Initiate Testing: Launch the app on the selected device to begin testing. The platform provides an easy-to-use interface with different tools to test your app in various scenarios, helping you identify and resolve bugs.
Use Cases of Hybrid Apps
Hybrid apps are used in various scenarios where cross-platform support, faster development, and cost efficiency are essential. Here are some use cases of hybrid apps:
- Content-Based Apps: Apps like news portals, blogs, and magazines use hybrid development to deliver content efficiently across platforms.
- eCommerce Apps: Online shopping apps benefit from hybrid frameworks to ensure a consistent user experience and faster updates.
- Enterprise and Internal Tools: Companies use hybrid apps for internal communication, reporting, and productivity tools that need to work on different devices.
- Social Media Platforms: Social networking apps can use hybrid technology to reach a wider audience with reduced development time
- Customer Support Apps: Helpdesk or service apps use hybrid models to provide quick access to FAQs, live chat, and support across devices.
- MVPs (Minimum Viable Products): Startups often build MVPs as hybrid apps to test their ideas quickly and gather user feedback before full-scale development.
Top Frameworks for Hybrid App Development
Here are some of the most popular frameworks for building hybrid apps:
- Ionic: Used to build cross-platform apps with Angular and React, Ionic offers a rich UI component library that mimics native interfaces. These apps run inside a WebView, delivering a near-native experience, making them ideal for content-heavy and interactive applications.
- React Native: Developed by Meta (formerly Facebook), it enables developers to build apps using React and JavaScript. Unlike traditional hybrid frameworks, it renders UI components using native APIs, which improves performance and user experience.
- Flutter: It is Google’s open-source UI toolkit for building natively compiled applications using a single codebase written in Dart. Flutter offers a fast development cycle with features like hot reload and provides its own rich set of customizable widgets.
- Cordova: Apache Cordova (formerly PhoneGap) enables teams to build mobile apps using CSS, HTML, and JavaScript, wrapping them in a native container. It relies on plugins to access device features like camera and GPS.
- Xamarin: A Microsoft-backed framework, Xamarin allows developers to build cross-platform apps using C# and .NET. It provides a shared codebase for Android, iOS, and Windows with full access to native APIs, offering performance close to native apps, making it ideal for complex enterprise solutions.
Read More: Understanding the Differences Between Mobile Application Testing and Web Application Testing
How are Hybrid Apps different from Native and Web Apps
Here’s a table comparing Hybrid Apps, Native Apps, and Web Apps, highlighting their key differences:
| Aspect | Hybrid Apps | Native Apps | Web Apps |
|---|---|---|---|
| Platform | Single codebase for multiple platforms (Android, iOS) | Developed for a specific platform (Android, iOS) | Accessible via browsers across all platforms |
| Performance | Moderate performance, relies on WebView | High performance, optimized for the platform’s hardware | Dependent on internet and browser performance |
| Access to Device Features | Limited access to device features via plugins | Full access to all device hardware features | Limited access to device features (via browser) |
| Development Time | Faster development with one codebase for both platforms | Longer development time for separate platforms | Fastest, as no separate development for each platform |
| User Experience | Close to native, but can have slight limitations | Best user experience, fully optimized for the platform | Basic experience depends on browser capabilities |
Conclusion
Hybrid apps provide practical solution for businesses aiming to reach users across different platforms with a single codebase. They offer a balance between development efficiency and user experience, which makes them suitable for various applications.
However, to offer optimal performance and user satisfaction, thorough testing on real devices is important. Utilizing platforms like BrowserStack can help detect and address issues, ensuring the app functions reliably across different operating systems and devices.