As software becomes more complex and deployment cycles faster, quality assurance must keep up.
Overview
What is Data Driven Testing?
Data-Driven Testing is a methodology that separates test logic from test data, allowing the same test script to be executed with multiple input sets from external sources.
Key Aspects of Data-Driven Testing:
- Separation of Concerns: Test scripts focus on logic, while test data is stored externally, improving reusability and maintainability.
- External Data Sources: Test data can come from spreadsheets (Excel, CSV), databases (MySQL, SQL Server), XML, and JSON files.
- Enhanced Test Coverage: Uses diverse data sets (positive, negative, edge cases) for comprehensive application validation without duplicating test scripts.
- Automation and Efficiency: Executes the same script with varying inputs, automating repetitive tests and speeding up the process.
- Process: Data is captured from external sources, used as input in automated scripts, and the output is compared to expected results for each data set.
This article explains what data-driven testing is, why teams use it, how it works, its challenges, best practices, tools and how it ties in with low code automation.
What is Data Driven Testing?
Data-driven testing (also called parameterized testing or table-driven testing) is a methodology in software testing where test logic (test scripts) is separated from test data.
Instead of hardcoding input values and expected results inside test scripts, data is stored externally (in tables, spreadsheets, CSV/XML files, databases, etc.).
The same test logic is executed multiple times with different data sets, each time picking different inputs and verifying accordingly.
Importance of Data Driven Testing
Data-driven testing offers several advantages:
- Improved test coverage by enabling the same test to run with many data combinations.
- Reusability of test logic, since the same test script can be used with changing data only.
- Maintainability, because when a data case changes (e.g. new input values or expected outputs), you often only need to update external data files rather than the test logic.
- Scalability, especially in automated testing, since many scenarios can be tested quickly with different data sets.
- Consistency and accuracy, reducing manual errors.
Also Read: Data Driven Framework in Selenium
Why Perform Data Driven Testing
Teams choose data-driven testing for several practical reasons:
- To validate the system under many more scenarios (positive, negative, edge cases) without duplicating code.
- To support regression testing where new data sets are introduced over time.
- To make tests easier to maintain when requirements or input specifications change.
- To allow non-technical stakeholders to review or even supply test data (e.g., business rules) without having to edit scripts.
- To integrate into CI/CD pipelines where automated tests need to adapt to many environments or input parameter variations.
How Does Data Driven Testing Work
Here is a high-level view of how Data Driven Testing is structured:
- Test logic / script: A test that defines the flow, steps, verification but uses placeholders/parameters instead of fixed inputs.
- Data source(s): External file(s) or database(s) holding multiple sets of inputs and expected outputs. Types include CSV, Excel, XML, JSON, database tables.
- Driver or framework: The mechanism that reads data from the data source, feeds each data set into the test logic, runs the test, captures results.
- Iteration/looping: The test is looped for each data set (or row) in the data source.
- Result collection & reporting: Each iteration’s pass/fail result is recorded, often reporting which data sets failed, to help pinpoint issues.
Steps to Implement Data-Driven Testing
Here is a step-by-step process a team might follow:
- Define Your Test Cases: Identify which test cases will benefit most – those where the same logic must be applied to multiple input datasets.
- Prepare Test Data: Collect and structure your test data in formats like Excel, CSV, JSON or databases.
- Select an Automation Framework: Choose a testing framework or tool that supports parameterization and external data sources.
- Write Test Scripts: Develop scripts designed to read input dynamically from external sources using data providers or parameterization.
- Link to Test Data: Connect your test scripts with the chosen data source using libraries, drivers or APIs.
- Iterate Over Data: Add loops so your script runs once for each dataset. Each iteration should pull new input and expected output.
- Run the Tests: Execute your test suite across all the datasets to ensure full coverage of scenarios.
- Record Results: Log pass/fail outcomes, error details and execution times for every iteration.
- Analyze and Troubleshoot: Investigate failed cases to distinguish between genuine bugs and test data/script issues.
- Maintain Test Data: Keep your datasets up-to-date as the application evolves, reflecting new rules and features.
- Integrate with CI/CD: Embed the framework into CI/CD pipelines for automated, consistent execution with every build.
Top Tools for Data-Driven Testing
Data-driven testing tools allow teams to validate applications against multiple input sets without duplicating tests.
By separating test logic from test data, these tools increase coverage, reduce redundancy, and make automation more scalable and efficient.
1. Selenium with TestNG/JUnit
Selenium is one of the most popular open-source test automation frameworks for web applications. When combined with TestNG or JUnit, it supports parameterized tests and external data handling making it a strong choice for data-driven testing.
Key Features:
- Supports multiple programming languages (Java, Python, C#, etc.).
- TestNG DataProvider and JUnit Parameterized Tests for Data Driven Testing.
- Integration with Excel, CSV or databases via libraries.
- Cross-browser and cross-platform support.
Pros:
- Highly flexible and customizable.
- Large community and ecosystem.
Cons:
- Requires strong coding knowledge.
- Maintenance can become complex for large test suites.
2. Katalon Platform
Katalon is a low code/no-code test automation platform that provides built-in support for data-driven testing. It is suitable for both technical and non-technical users.
Key Features:
- Built-in data-driven test execution.
- Supports Excel, CSV and database inputs.
- Record-and-playback plus script customization.
- Seamless CI/CD integration.
Pros:
- Easy setup for teams without deep coding skills.
- Provides detailed reports and dashboards.
Cons:
- Limited flexibility compared to full-code frameworks.
- Some advanced features require paid plans.
3. TestComplete (by SmartBear)
TestComplete is a commercial test automation tool that supports desktop, web and mobile apps. It has built-in features for creating and executing data-driven tests.
Key Features:
- Keyword-driven + scripting-based test creation.
- Supports Excel, CSV, XML and databases.
- Works across multiple platforms (web, desktop, mobile).
- Data generation utilities for testing at scale.
Pros:
- Easy to use with strong data source support.
- Reduces coding effort with keyword tests.
Cons:
- License cost can be high.
- Complex advanced use cases may need scripting.
4. Robot Framework
Robot Framework is an open-source, keyword-driven test automation framework widely used for functional testing. It supports parameterized tests via templates and integrates well with external data sources.
Key Features:
- Keyword-driven and table-based test syntax.
- Test templates for easy parameterization.
- External data integration (CSV, Excel, DB).
- Large library ecosystem (Selenium, Appium, APIs).
Pros:
- Human-readable test cases (good for collaboration).
- Extensible with Python/Java libraries.
Cons:
- Execution can be slower than code-based frameworks.
- Some advanced customization requires scripting.
5. Functionize
Functionize is a modern AI-powered testing platform that provides strong data-driven testing capabilities. It focuses on intelligent automation and scalability.
Key Features:
- Supports large datasets for testing.
- AI-driven test creation and maintenance.
- Cloud-based with parallel execution.
- Detailed analytics and reporting.
Pros:
- Reduces maintenance effort using AI.
- Strong test coverage for complex workflows.
Cons:
- Higher cost compared to traditional tools.
- Learning curve for advanced features.
What is Data Driven Automation Testing?
Data driven automation testing is the practice of applying data-driven testing within an automated test execution environment.
Instead of manually executing tests for different data sets, automation is used so that tests run automatically (often as part of CI/CD pipelines) with external test data.
Automation makes test cycles faster, repeatable, and scalable by eliminating manual effort. In data-driven testing, the framework manages iterations, input/output substitution, logging, and reporting. This is enabled through driver scripts, parameterized tests, data providers, or built-in support for external data sources.
Key Use Cases of Data-Driven Automation Testing
Some common scenarios where data-driven automated testing is especially helpful:
- Testing user login functionality with many user credentials (valid, invalid, boundary etc.).
- Form validation across combinations of inputs (e.g. required fields, field lengths, special characters).
- Testing search or filter functions with many input variants.
- Testing workflows that depend on configuration or external settings (e.g. different user roles, locales, currencies).
- API testing with various input payloads, response validations.
- Regression testing after changes or updates.
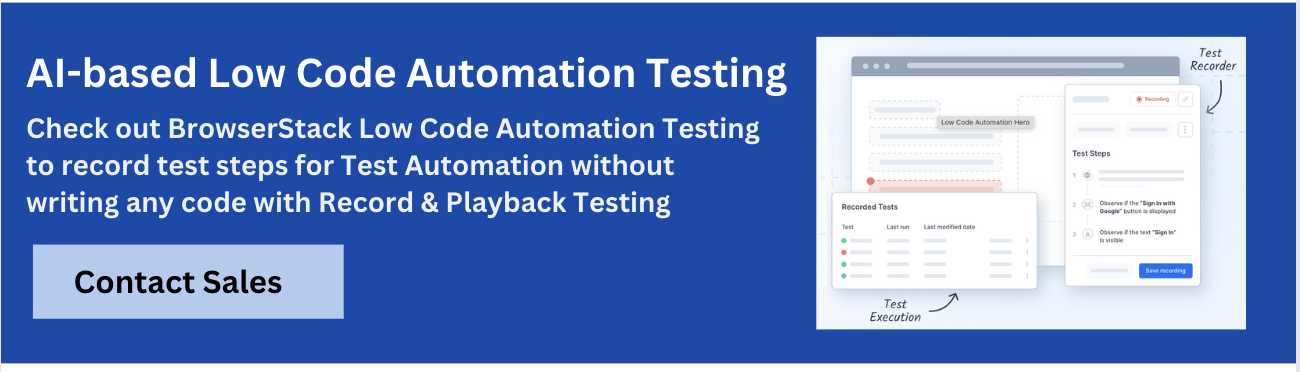
Data-Driven Testing with BrowserStack Low-Code Automation
BrowserStack Low-Code Automation makes data-driven test creation effortless. It enables teams to automate a single test scenario with a wide range of input data, for stronger coverage and reduced effort.
Instead of manually duplicating test cases, testers import datasets (such as CSV files) and the platform automatically iterates through each data set, mapping variables to test actions without any coding required.
Why Use BrowserStack Low-Code Automation for Data-Driven Testing?
BrowserStack Low-Code Automation lets testers execute the same test across real devices and browsers in the cloud. It ensures full coverage of user scenarios without complex scripts.
Teams import and manage test data files, quickly map dataset columns to test variables, and watch as the tool automatically executes each variation and logs detailed outcomes for every run.
With AI-powered self-healing and low-code authoring agents, it speeds up test creation by up to 10x and reduces build failures by up to 40%, delivering faster, more stable automation for both technical and non-technical users.
Key Features of BrowserStack Low-Code Automation:
- Test Recorder: Easily capture user actions like clicks and form inputs and transform them into automated tests. This recorder supports complex functional validations including visual and text validations.
- Readable Test Steps: Actions recorded are converted into simple, human-readable English instructions, making it easy for anyone to understand and modify tests.
- Visual Validation: Enables testers to add checkpoints during recording that verify the correct display of UI components or screens, ensuring that visual elements render as expected.
- AI-Powered Self-Healing: Uses AI to detect when UI elements change and automatically updates the test to prevent failures. This minimizes the need for manual test maintenance.
- Low-Code Authoring Agent: Uses AI to turn natural language prompts into executable test steps, automating tasks from simple instructions.
- Cross-Browser & Mobile Testing: Runs tests on real desktop browsers and mobile devices in the BrowserStack cloud, covering a wide range of operating systems and devices.
- Data-Driven Testing: Allows the same test to be executed with different input values, enabling broader coverage of scenarios without creating separate tests.
- Reusable Modules:Lets teams save common sequences of steps as reusable modules that can be inserted into multiple test cases, reducing duplication and simplifying maintenance.
- API Step Integration: Adds flexibility by letting testers call APIs from within the test for tasks such as generating data, setting up test conditions, or cleaning up databases.
Try BrowserStack Low Code Automation
How to Perform Data Driven Testing with BrowserStack Low Code Automation
Instead of writing separate test cases for each variation, testers can create test datasets and execute them efficiently. Data-driven testing with BrowserStack ensures applications are tested against real-world scenarios.
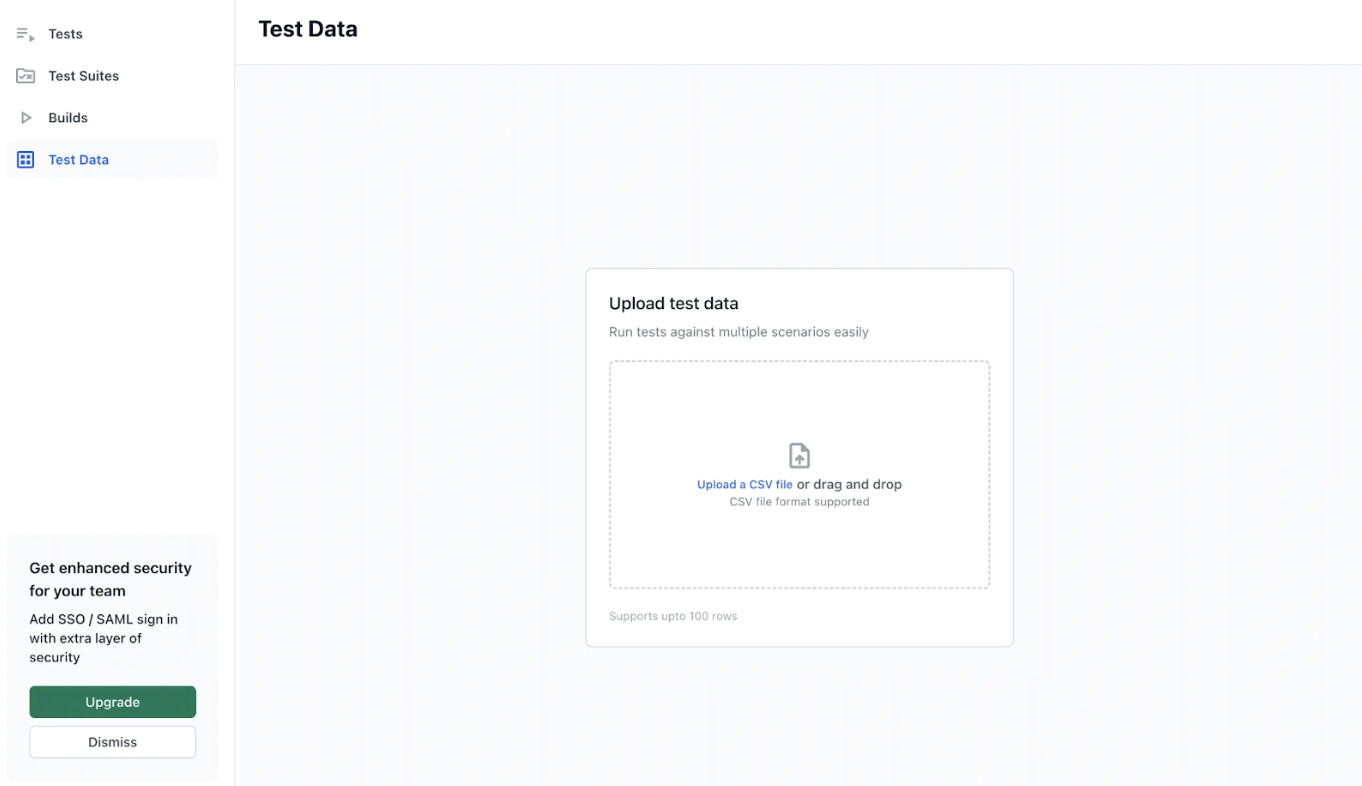
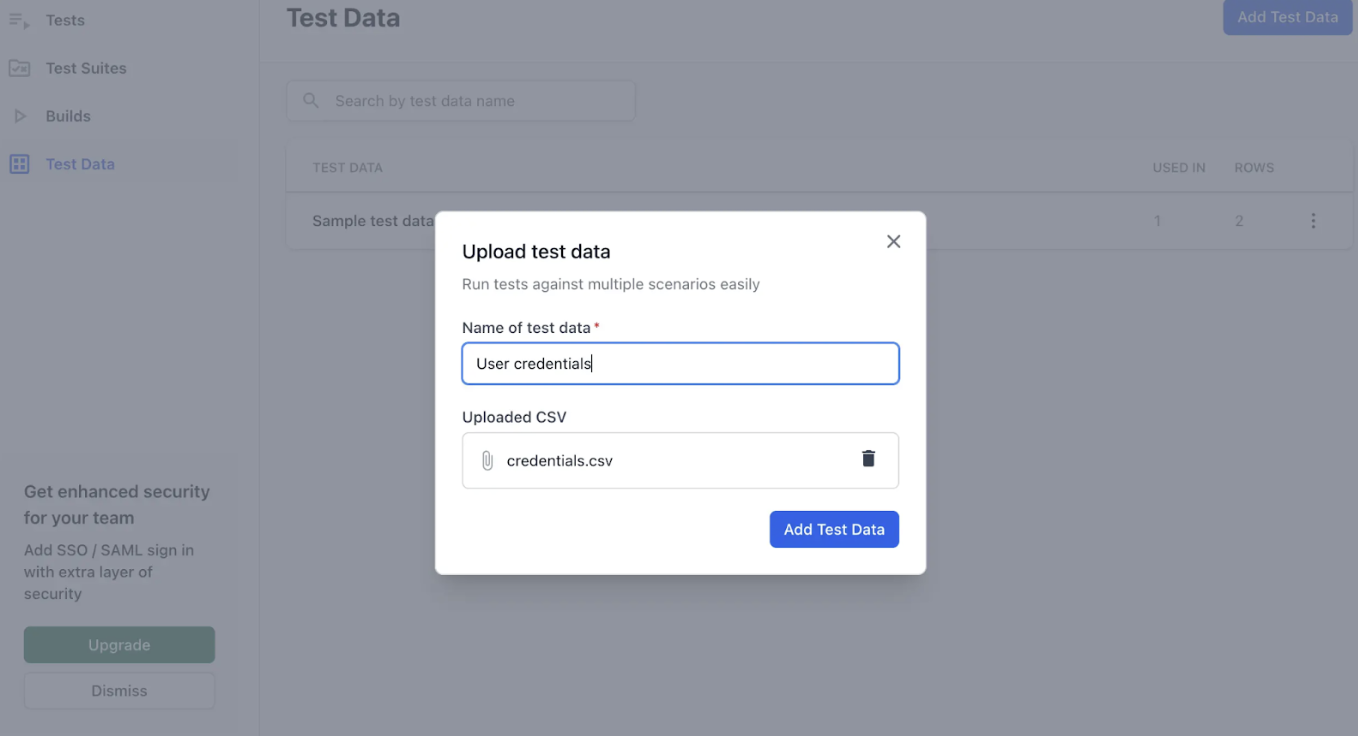
Step 1: Create a Test Dataset. Upload a CSV file via Test Dataset in the desktop app or web.
- File Rules: Use a CSV with consistent columns, max 100 rows × 40 columns, values under 1000 characters, and at least one data row.
Step 2: Assign a unique dataset name.
- Verify uploaded data through the preview table.
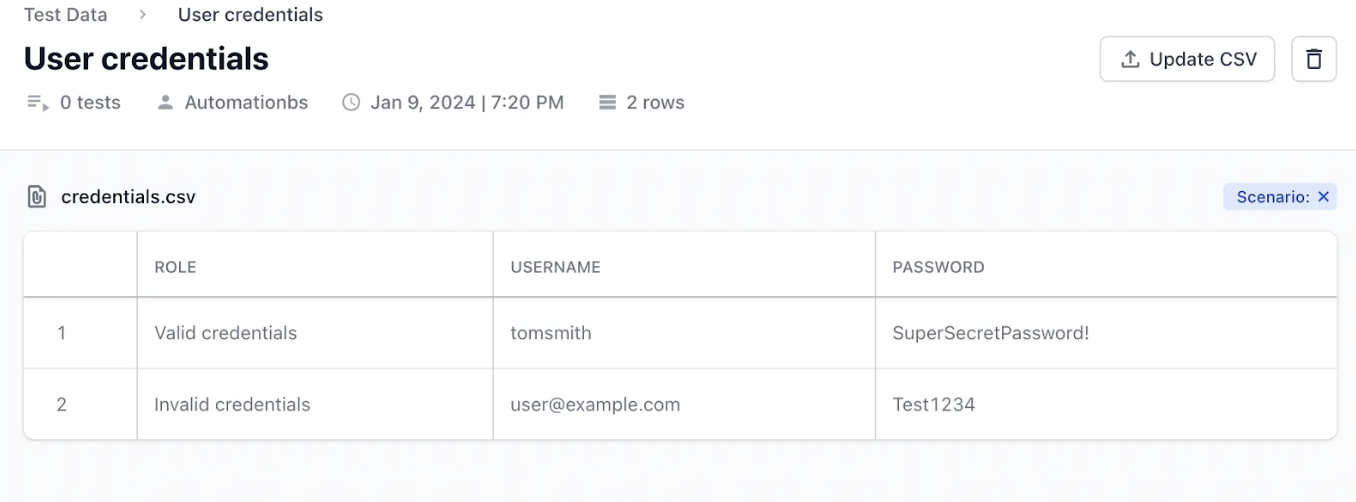
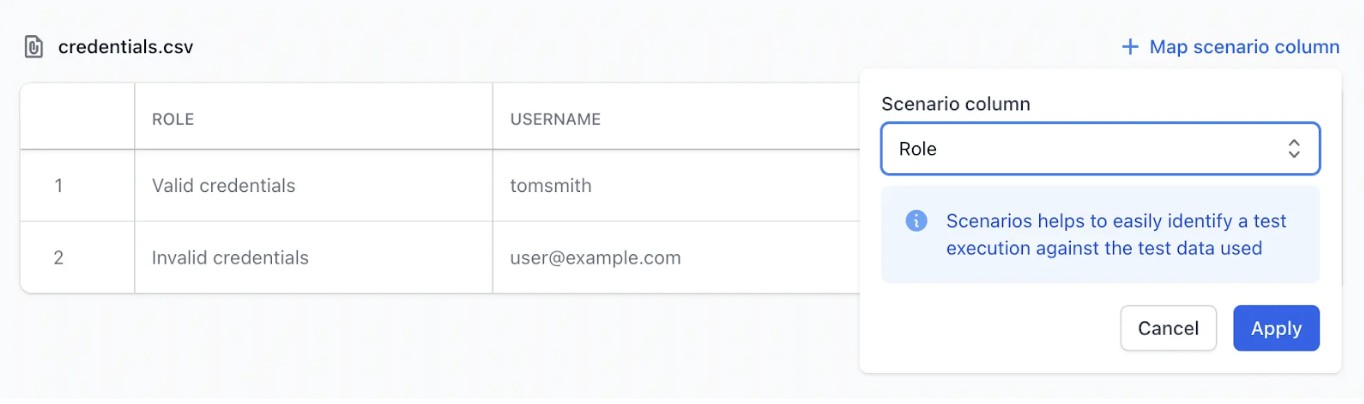
Step 3: Map a Scenario Column (Optional)
Choose a column (e.g., “Test Case ID” or “Scenario Name”) to label each dataset row. This label appears in build reports making it easier to trace failures to specific data rows.
Step 4: Import any dataset column into a test step as a variable. Link the dataset, then pick the required column.
Note: A test can only pull data from one dataset at a time. Dataset variables aren’t yet supported inside modules.
Test Execution with Data Sets
- Local Execution: Runs using only the first row (excluding headers) for quick replay and debugging.
- Cloud Execution: Runs the test against all rows in the dataset. Reports display each iteration separately, grouped for clarity. If a scenario column is mapped, its values appear as labels in the report.
Note: Each execution is counted toward test usage for billing.
Challenges of Data-Driven Testing
While Data Driven Testing has many benefits, there are also challenges to be aware of:
- Data quality: Poor, incorrect or incomplete test data leads to misleading test results.
- Maintenance overhead: As data sets grow, managing them, organising them and keeping them updated becomes harder.
- Test script complexity: Tests need to handle parameterization, input formats, setup/teardown and sometimes different data types which adds complexity.
- Performance / execution time: Running many data combinations increases test execution time, especially if each iteration is expensive (e.g. network calls, UI interactions).
- Tool limitations: Some tools or frameworks may not support all desired data sources or may have limitations in how they map data to test steps.
- Dependency on skills: Requires testers or automation engineers who understand how to separate test logic from data, how to design good data schemas, etc.
Best Practices for Implementing Data-Driven Testing
To get the most from Data Driven Testing, teams should follow good practices:
- Design test data carefully, including edge / negative / boundary cases, not just “happy path”.
- Keep data sources clean and well organised (naming conventions, consistent formats).
- Limit duplication of tests or data: reuse where possible, avoid repeating similar scenarios.
- Use version control for both test scripts and test data.
- Build good reporting to see not just pass/fail but which data sets failed, enabling quick debugging.
- Integrate into CI/CD so tests run on every build or change.
- Consider test data size vs execution cost: for large datasets, perhaps sample or prioritize critical combinations.
- Use abstraction and parameterization in test logic so changes in UI or behaviour require minimal changes.
- Validate test data itself (e.g. check that expected outputs are correct).
Conclusion
Data-driven testing is a powerful and practical testing methodology for improving software quality. By separating test logic from test data, teams gain greater reusability, scalability and maintainability.
While it brings challenges especially around data management, performance and required skills, using the right tools, frameworks and practices can help mitigate them. Low code automation platforms like BrowserStack make it easier for teams to adopt Data Driven Testing without needing to build everything from scratch.
With thoughtfully designed data, robust tools and integration into existing workflows, data-driven testing can become a core part of reliable, efficient test automation.