When I first started with mobile automation, I assumed the cloud would solve most problems. Instead, I found that local test runs were where teams moved fastest. Debugging was easier, failures were more predictable, and feedback arrived sooner.
There is a reason why over 70% of teams run tests locally before pushing to the cloud. Early builds are unstable, network conditions vary, and logs matter. Cloud grids help with scale, but they are not ideal for rapid iteration or deep debugging.
That is where local mobile automation proves its value. It gives teams full control, faster feedback, and a safer place to catch issues before tests ever reach the cloud.
Overview
How to Set Up Mobile App Automation on a Local Server?
To set up mobile app automation on a local server for Android and iOS testing, follow these steps:
Step 1: Prepare the local machine
Use a system with sufficient resources and a supported OS. macOS is required for iOS testing.
Step 2: Install platform development tools
Set up official Android and iOS tools required for device communication and debugging.
Step 3: Configure the automation framework
Install and configure a mobile automation framework for local execution.
Step 4: Set up devices or virtual environments
Connect real devices or configure emulators and simulators for stable detection.
Step 5: Enable required permissions
Allow debugging and trust settings so automation tools can control devices.
Step 6: Add the application build
Keep the correct app build available locally for testing.
Step 7: Validate the setup
Run a basic test to confirm the environment is working correctly.
In this guide, I explain what mobile automation on a local server really means, why teams rely on it, what you need to get started, and how to set it up for both Android and iOS.
What is Mobile App Automation on a Local Server?
Mobile app automation on a local server means running test scripts on a team’s internal system instead of a cloud device. The tester connects a real device or a simulator to the local environment and runs automated tests directly on it. In simple terms, the app is tested within the team’s own setup, where they have full control over the device, the network and the configurations.
Here is what this setup usually includes:
- A local machine or server where the automation tools are installed
- Real Android or iOS devices connected through USB
- Or simulators and emulators configured for testing
- A test framework such as Appium, Espresso or XCUITest
- Local drivers and dependencies that allow the tests to run smoothly
This approach helps you check new features, debug issues and validate builds in a controlled environment before sending anything to the cloud.
Why Set Up Local Mobile Automation Environments?
Setting up mobile automation on a local server gives teams stronger control over how their apps behave during early development. Since the environment runs close to the codebase, it becomes much easier to reproduce issues, validate quick fixes and test unstable builds without relying on shared cloud devices.
It also removes delays because teams are not waiting for device queues or dealing with network delays that sometimes affect cloud based test runs.
Benefits of Testing Apps Locally Before Cloud Deployment
Testing locally gives several advantages before moving to cloud scale:
- Faster feedback: Since everything runs on a local machine or server, tests respond immediately and failures can be reviewed without delay.
- Better debugging: Local execution makes it easier to check logs, device output and network activity without switching between environments.
- More control over the environment: Teams can adjust device settings, test internal builds, simulate slow networks or apply custom configurations that may not be available on shared cloud devices.
- Reduced noise during early development: New or unstable features often trigger false failures on cloud platforms. Running them locally first ensures they are stable before using cloud resources.
- Safe testing of sensitive features: Some builds, internal APIs or confidential data are not ready for the cloud in early stages. Local testing keeps everything within the organisation.
Also Read: Overcoming Challenges of Local Testing
Key Requirements for Mobile App Automation on a Local Server
A stable mobile app automation on a local server setup depends on a few essential components. When these fundamentals are in place, teams can run tests locally with consistency, reliability, and minimal maintenance overhead.
- Capable local machine: The system should have sufficient CPU, memory, and storage to run automation scripts alongside emulators or simulators without performance bottlenecks.
- Android and iOS development tools: Official platform tools such as Android SDKs and Xcode are required to enable communication between the automation framework and mobile devices.
- Real devices or stable emulators and simulators: Physical devices provide the most accurate results, while well-configured emulators and simulators are useful for fast feedback and early-stage testing.
- Mobile automation framework: Frameworks like Appium, Espresso, or XCUITest are needed to create, manage, and execute automated test scripts effectively.
- Correct device permissions and drivers: Devices must be configured for debugging and automation access; missing permissions or drivers will prevent tests from running.
- Stable network connection: A reliable network ensures uninterrupted communication between the local machine, devices, and supporting services during test execution.
- Access to the correct app build: The relevant APK or IPA file must be available locally to ensure tests run against the intended version of the application.
Choosing the Right Framework for Mobile App Automation
Choosing the right automation framework determines how stable, efficient, and scalable your mobile app automation on a local server will be.
The ideal framework should align with the platforms under test, the team’s technical expertise, and the type of automation required, while also supporting future expansion to real-device testing platforms like BrowserStack App Automate.
The table below compares the most widely used mobile automation frameworks and highlights where each one fits best in a local testing setup.
| Framework | Platform Support | Best Fit | Key Strengths | Considerations |
| Appium | Android & iOS | Cross-platform mobile automation | Single framework for both platforms, supports multiple programming languages, Selenium-like architecture | Slower than native frameworks, higher setup and maintenance effort |
| Espresso | Android | Android-native app testing | Fast execution, high stability, runs inside the app process, strong developer support | Limited to Android apps |
| XCUITest | iOS | iOS-native app testing | Official Apple framework, excellent stability, seamless Xcode integration | Requires macOS and Xcode, iOS-only |
| Detox | Android & iOS | React Native applications | Synchronized test execution, reduced flakiness, easier debugging | Best suited only for React Native apps |
| Flutter integration tests | Android & iOS | Flutter applications | Deep integration with Flutter apps, suitable for integration-level testing | Less flexible for complex end-to-end UI scenarios |
| Calabash / legacy tools | Android & iOS | Legacy automation setups | Still present in older projects | No active support, not recommended for modern automation |
How to Set Up Mobile App Automation on a Local Server (Step-by-Step Guide)
Setting up mobile automation on a local server follows a straightforward sequence. These are the steps most teams use during early development.
Step 1: Install the required tools
Install Android Studio for Android and Xcode for iOS. These tools provide everything the machine needs to communicate with devices and run automation scripts.
Step 2: Set up device access
For Android, USB debugging must be enabled on the device. For iOS, the device must be trusted on the Mac and the required debugging permissions allowed. Without proper access, tests will not start.
Step 3: Prepare your build files
Download the correct APK or IPA from the development team.
This ensures the local run matches the exact version of the app under testing.
Step 4: Install your automation framework
Install the chosen framework, such as Appium, Espresso or XCUITest.
This works as the engine that runs the automation scripts.
Step 5: Start the device or emulator
Launch a physical device, emulator or simulator.
The device should be stable and responsive before starting the tests.
Step 6: Write a simple test to confirm the setup
Create a basic script that opens the app and performs one small action such as a tap or text entry. This confirms that the local environment is functioning correctly.
Step 7: Run the tests locally
Execute the scripts through the chosen framework.
If everything is set up correctly, the app should launch and follow the steps you automated.
Step 8: Review logs and fix issues
Check the logs, screenshots or console output.
Local tests help to catch permission issues, driver problems or incorrect locators early.
Step 9: Repeat and expand
Once the setup is stable, more tests, devices and scenarios can be added. This is where the local environment becomes strong for quick debugging and faster iteration.
Configuring Test Environments for Android and iOS
Once the basic setup is ready, the next step is configuring the actual test environments for both Android and iOS. This ensures the devices, tools and frameworks work together without errors.
Android Test Environment Configuration
This step focuses on preparing Android devices and emulators so they can be detected, controlled, and used consistently during local automation runs.
- Install Android Studio to access SDK Manager, ADB, and platform tools
- Install required device drivers so physical devices are detected correctly
- Enable Developer Options and USB debugging on test devices
- Configure emulators with the required Android version and adequate resources
- Verify device or emulator availability using standard device detection tools
iOS Test Environment Configuration
This step ensures that iOS simulators and physical devices are correctly configured to support automation within Apple’s development ecosystem.
- Install a compatible version of Xcode on macOS
- Trust connected iOS devices to allow automation and debugging access
- Install required signing permissions or provisioning profiles if needed
- Configure simulators with the target device models and iOS versions
- Verify device or simulator visibility through Xcode or system tools
Running Mobile App Automation Tests Locally
Running mobile app automation tests on a local server becomes straightforward once the setup is complete. The goal is to ensure that scripts run smoothly on a real device, emulator or simulator without relying on cloud resources.
Here is how it usually works:
- Start your device or emulator: Make sure the device is connected, unlocked and ready. For emulators and simulators, confirm that they are running and stable.
- Launch your automation framework: Open Appium, Espresso, XCUITest or whichever tool is being used. This framework sends commands to the device during the test.
- Point the framework to your app build: Select the required APK or IPA so that the test runs against the right version of the application.
- Run the test script: Execute the script from the terminal, IDE or test runner. The device should open the app and follow the automated steps.
- Watch the logs and device behaviour: Local execution makes it easy to observe what is happening in real time. Teams can check console logs, device output or screenshots to confirm the workflow.
- Fix issues instantly: If something breaks, the issue can be reproduced and resolved on the spot because the full environment is right in front of the team. This is one of the strongest advantages of testing locally.
Read More: How to set up your Appium Grid
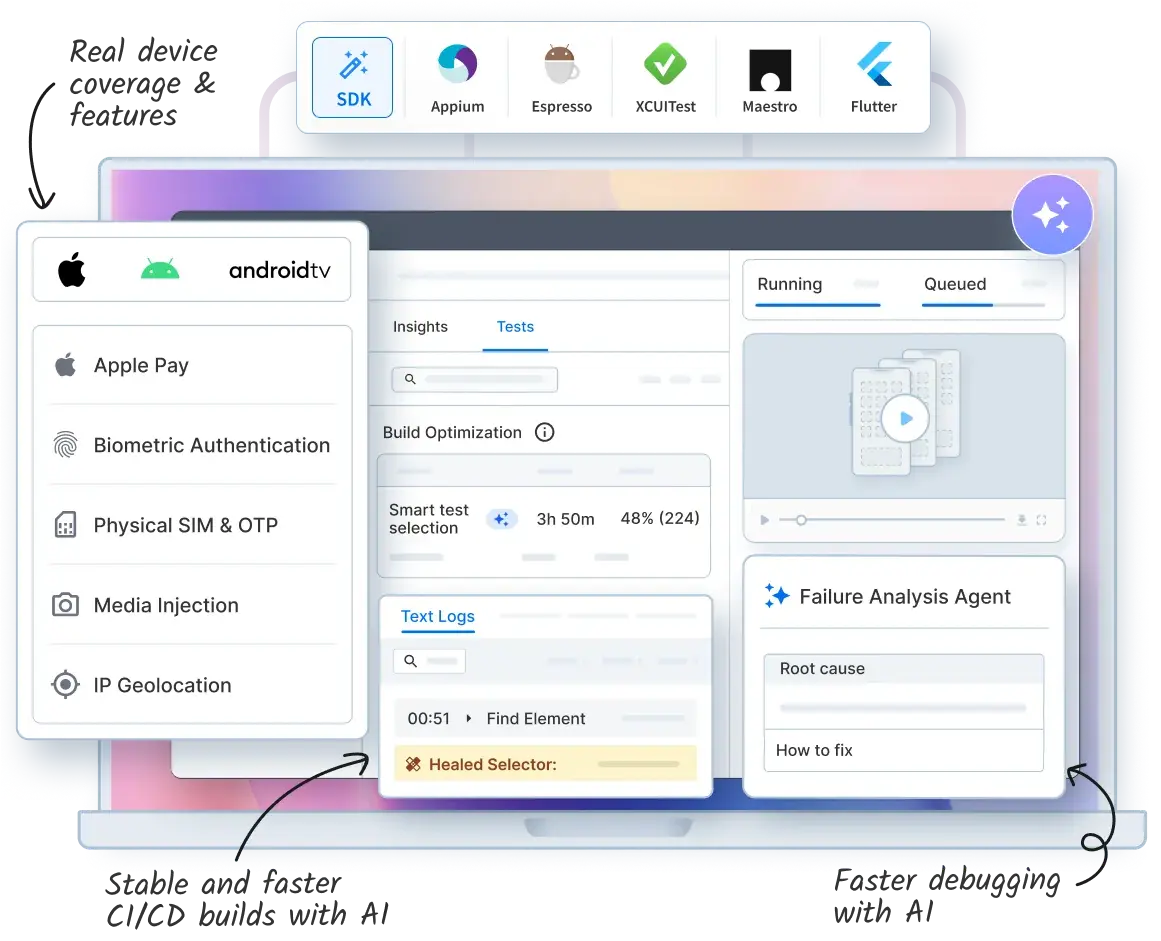
Using BrowserStack App Automate for Extended Local Testing
Local execution works well for early development and quick debugging, but it has clear limits. As test coverage grows, maintaining devices, handling OS fragmentation, and running tests in parallel become difficult with mobile app automation on a local server alone. This is where BrowserStack App Automate fits into the workflow.
BrowserStack App Automate extends local automation by letting teams run their existing automated tests on a large cloud of real Android and iOS devices, without replacing local setups. Teams can continue using local servers for fast iteration while relying on App Automate for scale, coverage, and reliability.
Why do teams move beyond local-only testing?
That’s because local environments often struggle with:
- Limited access to real devices and OS versions
- Slow execution due to lack of parallelism
- Flaky tests caused by unstable emulators
- High maintenance effort as test suites grow
App Automate addresses these gaps without disrupting established workflows.
How does BrowserStack App Automate complement local automation?
BrowserStack App Automate provides the following capabilities to support scalable mobile automation testing:
- Real device cloud at scale: Instant access to 30,000+ real iOS and Android devices, covering both legacy models and the latest releases.
- Seamless integration with existing tests: Works with popular frameworks like Appium, Espresso, XCUITest, Flutter, and Detox, allowing teams to reuse local test suites without rewrites.
- AI-powered stability and speed: Agentic AI features such as Self-Healing Agent detects and heals broken locators, Test Failure Analysis agent analyzes failures, and the Test Selection Agent optimizes the tests to reduce flakiness and feedback time.
- Parallel execution for faster releases: Run large test suites simultaneously across multiple devices and OS versions, cutting execution time from hours to minutes.
- Deep debugging visibility: Each test run includes videos, logs, network data, and device insights, making it easy to diagnose failures quickly.
A balanced automation strategy is crucial.
The most effective approach combines both:
- Local testing for fast development feedback and debugging
- BrowserStack App Automate for scalable, production-ready validation on real devices
This layered strategy keeps local automation lightweight while ensuring applications are tested reliably across the real-world device setting before release.
Try BrowserStack App Automate Now
Common Challenges in Mobile App Automation on a Local Server
Even with a strong setup, teams often face a few common issues while running mobile automation on a local server. These challenges usually affect speed, stability or consistency.
- Device connection issues: Local devices may disconnect, fail to appear in the device list or stop responding during long test runs. This disrupts the workflow and forces frequent restarts.
- Slow or unstable emulators and simulators: Emulators can lag or freeze, especially on low powered machines. This results in flaky test outcomes and long execution time.
- Permission and signing errors: Android and iOS require specific permissions, certificates and trust settings. If any of these are missing, tests will not start.
- Differences between developer devices: Team members often work on different machines, OS versions or device configurations. This leads to inconsistent results across local setups.
- Limited device coverage: Local environments cannot match the variety of devices, OS versions and screen sizes available in the cloud. This increases the chance of missing device specific issues.
- Environment drift over time: Drivers, SDKs and dependencies become outdated. When updates are not applied consistently, tests may stop working or behave unpredictably.
Read More: Android vs iOS Mobile App Testing
Best Practices for Reliable Mobile App Automation on a Local Server
To keep your local setup stable in everyday work, these are the practices that helped me the most:
- Keep your local environment clean and updated: Ensuring Android Studio, Xcode, SDK tools, device drivers and emulators are up to date helps avoid random failures and setup conflicts.
- Use a stable set of real devices and simulators: Quick checks can run on emulators, but critical paths should always be validated on physical devices for accurate results and fewer surprises.
- Start small and expand your test coverage gradually: Beginning with a few simple flows and confirming stability before adding more helps maintain predictability.
- Maintain consistent device permissions and settings: Enabling debugging, trusting iOS devices and keeping test devices free from unnecessary apps or pop ups reduces flaky behaviour.
- Review logs and results after every run: Local runs provide detailed logs and screenshots. Reviewing them immediately helps catch broken locators, network issues and permission errors early.
- Sync your local tests with cloud runs regularly: Local testing is ideal for fast debugging, but final behaviour should be confirmed on cloud devices such as BrowserStack App Automate to ensure coverage across many device types.
Conclusion
Setting up mobile app automation on a local server may seem complex at first, but once the core setup is ready, it becomes one of the most reliable ways for teams to test early builds, debug quickly and maintain smooth development. A local setup provides full control over the environment, supports fast feedback and helps catch issues long before they reach shared cloud devices.
With the right tools, frameworks and workflow, local automation becomes a strong part of any mobile testing strategy. And when combined with BrowserStack App Automate, teams gain the benefits of both fast local debugging and large scale testing on real devices in the cloud. Together, they help teams deliver stable, consistent and high quality mobile applications with confidence.