Modern software teams face constant pressure to deliver faster without compromising quality. Traditional automation, reliant on heavy scripting, slows progress and sidelines non-technical members.
Low-code automation testing tools address this with record-and-playback, visual flows, keyword-driven models, and self-healing capabilities.
Overview
Here’s a quick look at the top 15 low code automation testing tools:
- BrowserStack Low Code Automation: Codeless testing with visual flows and real device/browser coverage.
- Selenium IDE: Simple record-and-playback extension for quick web tests.
- Robot Framework: Keyword-driven open-source framework for reusable tests.
- Gauge: Specification-first framework with Markdown-based test cases.
- Karate: API-first testing tool that also supports UI automation.
- Katalon Studio: All-in-one platform combining low code and scripting.
- BugBug: Cloud-based web test recorder with a visual editor.
- TestCafe: JavaScript/TypeScript framework for end-to-end web testing.
- Appium: Open-source mobile testing tool for iOS and Android apps.
- CloudQA: Scriptless cloud platform for regression and monitoring tests.
- SoapUI: Specialised drag-and-drop tool for REST and SOAP APIs.
- Kobiton: Real-device mobile testing cloud with automation support.
- Mendix: Low code application development platform with built-in testing.
- Appian: Enterprise low code platform with process and test automation.
- Creatio: Low code CRM and process automation with test capabilities.
This article gives you a complete overview of the top 15 low code automation testing tools.
Importance of Low Code Automation Testing Tools
Low-code automation testing tools are reshaping how teams approach quality. They cut down the complexity of traditional scripting, making testing faster, more reliable, and accessible to everyone.
- Faster test creation: Visual editors and record-and-playback reduce the time needed to build automation.
- Stable test execution: Features like self-healing locators keep tests reliable even when applications change.
- Scalable testing: Parallel execution and cloud-based device access allow teams to test more in less time.
- Easy integration: Most tools connect directly with CI/CD pipelines and version control systems.
- Broader coverage: Teams can test across web, mobile, APIs and multiple environments using a single platform.
Top 15 Low Code Automation Testing Tools
The market for low-code automation testing tools has grown rapidly, providing teams with a wide array of choices. While this variety is beneficial, it can also make selecting the right tool challenging.
To assist in this process, here is a list of the top 15 low-code automation testing tools.
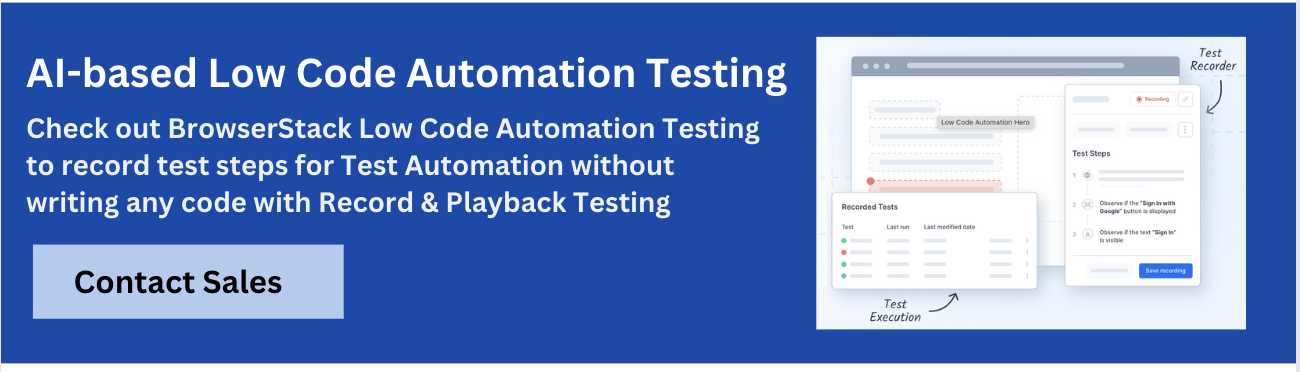
1. BrowserStack Low Code Automation
BrowserStack Low-Code Automation empowers teams to create, run, and maintain automated tests without writing code.
It combines an interactive test recorder, AI-powered self-healing, and real device cloud testing so teams can begin testing and start automation in minutes and scale across browsers and devices.
With AI-powered self-healing and low-code authoring agents, it speeds up test creation by up to 10x and reduces build failures by up to 40%, delivering faster, more stable automation for both technical and non-technical users.
Key Features of BrowserStack Low-Code Automation:
- Test Recorder: Easily capture user actions like clicks and form inputs and transform them into automated tests. This recorder supports complex functional validations including visual and text validations.
- Readable Test Steps: Actions recorded are converted into simple, human-readable English instructions, making it easy for anyone to understand and modify tests.
- Visual Validation: Enables testers to add checkpoints during recording that verify the correct display of UI components or screens, ensuring that visual elements render as expected.
- AI-Powered Self-Healing: Uses AI to detect when UI elements change and automatically updates the test to prevent failures. This minimizes the need for manual test maintenance.
- Low-Code Authoring Agent: Uses AI to turn natural language prompts into executable test steps, automating tasks from simple instructions.
- Cross-Browser & Mobile Testing: Runs tests on real desktop browsers and mobile devices in the BrowserStack cloud, covering a wide range of operating systems and devices.
- Data-Driven Testing: Allows the same test to be executed with different input values, enabling broader coverage of scenarios without creating separate tests.
- Reusable Modules:Lets teams save common sequences of steps as reusable modules that can be inserted into multiple test cases, reducing duplication and simplifying maintenance.
- API Step Integration: Adds flexibility by letting testers call APIs from within the test for tasks such as generating data, setting up test conditions, or cleaning up databases.
- Test Scheduling and CI/CD Integration: Enables automated tests to run on a set schedule or trigger directly from build pipelines via REST APIs or popular CI tools, ensuring continuous validation without manual intervention.
- Test Editing Without Re-Recording: Allows testers to open an existing test and modify, insert, or delete steps without having to re-record the whole test, saving time during maintenance.
- Private Environment Testing & Email Notifications: Teams can test websites behind firewalls or on internal and staging environments with zero setup. BrowserStack Low-Code Automation also sends detailed email reports with build pass/fail status and logs, giving stakeholders timely insights while validating applications securely.
Pricing:
- Free Plan: Offers unlimited test creation along with AI-generated test data, intelligent wait handling, API steps, secure private environment testing, video debugging, and 24×7 support.
- Paid Plan: Unlocks AI agents, advanced self-healing, parallel execution, and enterprise-grade features, with custom pricing based on organizational needs.
Try BrowserStack Low Code Automation
2. Selenium IDE
Selenium IDE is a lightweight browser extension that records and replays user actions in a web browser. It’s great for quickly building simple web UI tests without any coding. It helps teams get started with automation fast and is ideal for beginners.
Key Features
- One-click record-and-playback for browser actions.
- Ability to export tests to multiple programming languages.
- Supports conditional logic and control flow in tests.
- Built-in breakpoints and debugging tools.
Pros
- Beginner-friendly and is completely free.
- Quick for building smoke and regression tests.
- Works seamlessly within the browser.
Cons
- Lacks scalability for enterprise-level testing.
- No mobile or cross-platform support.
- Complex workflows often require moving to Selenium WebDriver.
Must Read: Architecture of Selenium WebDriver
3. Robot Framework
Robot Framework is an open-source tool that uses keywords to describe test cases. Its simplicity makes tests easy to read and reuse. With libraries for web, API and database testing, it’s highly flexible for many projects.
Key Features
- Keyword-driven syntax that reads like plain English.
- Flexible integration with libraries like Selenium, Appium and Database.
- Parallel execution supported via Pabot.
- Strong support for data-driven testing.
Pros
- Easy for onboarding non-technical testers.
- Extensive libraries and community plugins.
- Works well across small projects and large enterprise suites.
Cons
- Large test suites can execute slowly.
- Setup may feel complex for new users.
- Debugging at the keyword level can be tricky.
4. Gauge
Gauge is a specification-first tool where tests are written in Markdown. This makes them easy to understand for both technical and non-technical users. With plugins and integrations, it promotes maintainable and scalable testing.
Key Features
- Markdown-based test specifications for readability.
- Language-agnostic with support for Java, C#, Python, etc.
- Extensible with CI/CD and reporting plugins.
- Step-level execution results with screenshots.
Pros
- Human-readable test cases improve collaboration.
- Encourages modular, maintainable test design.
- Supports multiple languages.
Cons
- Smaller user base than Selenium or Robot Framework.
- Some plugins lack maturity when compared to bigger tools.
- Requires a mindset shift to “spec-first” style testing.
Also Read: 12 Open source Low Code Testing Tools
5. Karate
Karate is a testing tool designed for APIs but extends to UI and performance testing. It uses a BDD-style syntax so tests look like natural language. Teams love it for quick, readable tests that need minimal coding.
Key Features
- First-class API testing with JSON and XML handling.
- Built-in support for BDD syntax (Given-When-Then).
- Parallel execution for faster test cycles.
- Supports API mocking and performance tests.
Pros
- Excellent for API automation with very minimal setup.
- BDD syntax improves readability.
- Performance testing is included in the same tool.
Cons
- UI testing features are less polished.
- Limited support for mobile testing.
- Community and ecosystem are much smaller than Selenium.
6. Katalon Studio
Katalon Studio offers an all-in-one solution for web, mobile, API and desktop testing. Its record-and-playback interface is supported by scripting options for advanced users. With self-healing tests and rich reporting, it’s built for both speed and scale.
Key Features
- Supports cross-platform (web, mobile, API, desktop) automation.
- Record-and-playback with scripting in Groovy/Java.
- Self-healing locators for reduced test maintenance.
- Built-in test scheduling and CI/CD integration.
Pros
- Combines low code simplicity with scripting flexibility.
- Rich integrations with DevOps and test management tools.
- User-friendly interface lowers the learning curve.
Cons
- Limited programming language options.
- Performance issues in very large projects.
- Enterprise features are locked behind paid licenses.
7. BugBug
BugBug is a lightweight codeless testing tool focused on web apps. It lets users record, edit and run tests in the browser without complex setup. Its affordable and simple and is well-suited for startups and small teams.
Key Features
- Browser extension for recording test cases.
- Editable test steps with rewind and resume options.
- Test scheduling with local or cloud execution.
- Smart selectors that adapt to UI changes.
Pros
- Extremely easy for non-technical users.
- Saves time with fast recording and editing.
- Cost-effective for small teams.
Cons
- Limited to Chromium browsers.
- Complex UI flows may require extra tweaking.
- Reporting and analytics are fairly basic.
8. TestCafe
TestCafe is a JavaScript-based tool for end-to-end web testing. It eliminates the need for WebDriver reducing setup effort and complexity. With built-in waits and parallel runs, it’s powerful yet easy to adopt for modern web apps.
Key Features
- End-to-end web testing without WebDriver.
- Automatic waits for elements to appear.
- Parallel test execution across browsers.
- Supports both JavaScript and TypeScript.
Pros
- Easy setup compared to Selenium.
- High stability for web-based testing.
- Active open-source support.
Cons
- Requires JavaScript/TypeScript knowledge.
- Limited to web testing, no mobile support.
- Weaker API and hybrid app testing capabilities.
Must Read: Comprehensive Guide to Low-Code Development
9. Appium
Appium is an open-source framework for automating mobile apps across iOS and Android. It works with native, hybrid and web apps using the WebDriver protocol. Supporting many programming languages, it’s flexible but requires careful setup.
Key Features
- Supports native, hybrid and mobile web testing.
- Compatible with multiple programming languages.
- Built on the Selenium WebDriver protocol.
- Large and active community.
Pros
- Extremely flexible across mobile platforms.
- Reuses WebDriver knowledge for mobile testing.
- Open-source and widely supported.
Cons
- Complex to set up and configure.
- Tests may be flaky on emulators/simulators.
- Maintenance-heavy for gestures and device-specific flows.
10. CloudQA
CloudQA is a scriptless testing platform that runs tests in the cloud. It allows teams to automate regression and smoke tests quickly without writing code. With monitoring and scheduling features, it ensures applications stay reliable after every release.
Key Features
- No-code test recorder with cloud execution.
- Continuous monitoring of applications.
- Supports regression and functional testing.
- Cross-browser execution with scheduling.
Pros
- Very easy to adopt for non-technical users.
- Reduces maintenance with scriptless approach.
- Customer support is highly rated.
Cons
- Limited flexibility for advanced customisations.
- UI lag and occasional reliability issues.
- Smaller ecosystem compared to major open-source tools.
11. SoapUI
SoapUI is a well-known tool for testing SOAP and REST APIs. It lets testers build API tests through a drag-and-drop interface. It’s a strong choice for backend validation as it supports mocking and data-driven testing.
Key Features
- Drag-and-drop API test creation.
- Data-driven testing for multiple inputs.
- Service mocking and simulation.
- Detailed debugging for API flows.
Pros
- Excellent for backend/API testing.
- Mature, stable and widely used.
- Advanced service mocking capabilities.
Cons
- Outdated interface design.
- Steeper learning curve for beginners.
- Not suitable for UI or device testing.
12. Kobiton
Kobiton is a mobile testing platform offering access to a large pool of real devices. It supports both scriptless and scripted automation for mobile apps. By testing on actual hardware, it helps teams catch issues emulators often miss.
Key Features
- Real-device cloud for mobile automation.
- Scriptless test creation alongside scripted options.
- AI-driven analysis of mobile test sessions.
- Parallel execution on multiple devices.
Pros
- Real devices provide accurate results.
- Great for diverse mobile OS versions.
- AI tools speed up test creation.
Cons
- Higher costs for scaling.
- Slower performance at busy times.
- Limited beyond mobile use cases.
Learn More: Top 12 AI Automation Testing Tools
13. Mendix
Mendix is a low code platform for building and deploying apps quickly. It comes with built-in testing features to validate models and workflows which makes it ideal for organisations wanting to combine development and testing in one ecosystem.
Key Features
- Model-driven app development and testing.
- Built-in validation of workflows and models.
- Cloud-native deployment support.
- Collaboration tools for dev and QA in one platform.
Pros
- Strong for teams already building apps in Mendix.
- Speeds up app creation and validation.
- Enterprise-ready with scalability.
Cons
- Testing features limited compared to dedicated tools.
- High licensing cost.
- Steep learning curve for new users.
14. Appian
Appian is an enterprise-level low code platform that combines process automation with testing support. It allows teams to create workflows and applications visually. It offers strong governance and compliance features, making it well-suited for large organisations
Key Features
- Visual workflow and app building.
- Automated regression testing for processes.
- Secure cloud-native deployment.
- Integrates with DevOps pipelines.
Pros
- Strong governance and compliance features.
- Combines process automation and testing in one place.
- Designed for enterprise scalability.
Cons
- Very costly for smaller organisations.
- Less flexible for UI or mobile testing.
- Customisations often need technical expertise.
15. Creatio
Creatio is a low code CRM and business process automation platform. Alongside managing workflows and customer data, it supports automated testing features. It’s best for teams who want testing tightly connected to business applications.
Key Features
- Integrated CRM and workflow automation.
- Automated process validation features.
- Cloud support with scalable deployment.
- Prebuilt business process templates.
Pros
- Great fit for CRM-driven organisations.
- Strong business workflow alignment.
- Simple to use within its ecosystem.
Cons
- Limited outside of CRM or workflow scenarios.
- Pricing can be high at scale.
- Smaller testing community.
How to Choose the Right Low Code Automation Testing Tool?
Choosing the right tool depends on the team’s goals, skills and project needs. Here are some factors to consider:
- Type of application: Decide if the focus is on web, mobile, APIs or enterprise workflows. Some tools specialise in one area, while others cover multiple.
- Ease of use: Teams with non-technical testers may need a codeless tool, while mixed teams may prefer platforms that also allow scripting.
- Integration: Ensure the tool fits well with CI/CD pipelines, version control systems and reporting dashboards.
- Scalability: Look for features like parallel execution, real device testing and cloud support to handle growing test needs.
- Cost vs. value: Open-source tools are free but may need more setup. Enterprise tools offer convenience and support but come at a higher price.
Why Choose BrowserStack Low Code Automation?
BrowserStack Low-Code Automation helps teams create and scale tests quickly without coding. It combines AI-driven stability with real-device coverage to deliver reliable, enterprise-grade automation.
Key advantages:
- Test Recorder: Capture user actions and turn them into automated tests with support for functional and visual validations.
- Readable Test Steps: Convert actions into simple, human-readable instructions for easy editing and collaboration.
- AI-Powered Self-Healing: Detect UI changes automatically and update tests to reduce failures and maintenance effort.
- Low-Code Authoring Agent: Generate test steps from natural language prompts, speeding up test creation by up to 10x.
- Cross-Browser & Mobile Testing: Run tests on thousands of real browsers and devices in the BrowserStack cloud.
Combined with seamless CI/CD integrations, it enables continuous testing without slowing down delivery. For teams looking for both ease of use and enterprise-grade scalability, BrowserStack is a strong choice.
Best Practices of Using Low Code Automation Testing Tools
Some of the best practices are:
- Start small: Begin with smoke or regression tests, then expand coverage as confidence grows.
- Modularise tests: Create reusable test components to reduce duplication and improve maintainability.
- Run tests on real devices: Avoid relying only on emulators or simulators; real devices reveal real-world issues.
- Combine manual and automated testing: Automation is powerful, but exploratory and usability testing still need human insight.
- Integrate into CI/CD: Continuous integration ensures tests run automatically with every build or release.
- Maintain regularly: Review and update tests often to prevent flakiness and keep results reliable.
Conclusion
Low code automation testing tools are reshaping the way teams ensure software quality. They make it possible for technical and non-technical members to contribute, reduce the time spent writing scripts and expand coverage across devices and platforms.
From lightweight tools like Selenium IDE and BugBug to enterprise-grade platforms such as Appian and Creatio, each tool brings unique strengths. For teams seeking a solution that combines simplicity, real-device accuracy and strong CI/CD integration, BrowserStack Low Code Automation is a standout option.
Ultimately, the best tool is the one that fits the team’s workflow, project scope and long-term growth goals. By making a thoughtful choice, teams can deliver faster, reduce defects and build software that users can truly trust.